Believe it or not, there are quite a few types of solar energy. Yes, you read that right!
Generally, when you think about solar energy, the mind is usually drawn toward the thought of photovoltaic panels. However, there is more to solar energy than just photovoltaics.
This article aims to cover all these types and spread the wonders of solar energy as a green investment in your future.
You may just be surprised by how you could implement solar energy into your life.
Table of Contents
What Is Solar Energy?
In simple terms, solar energy is the light and heat that come from the sun.
Interestingly, only about one one-billionth of the sun’s total energy output reaches our earth. Of the solar energy that does reach our planet, 66% is reflected out to space by the earth itself.
The Duality Of Sunlight
When scientists discuss solar energy, they consider the duality of sunlight, as introduced in 1909 by Albert Einstein.
Sunlight is simultaneously a wave and a particle: the photon. Each photon carries an amount of energy that we calculate with the formula below:
E=h.v — “h” represents the Plank constant, while “v” represents the photon frequency.
Photon energy is frequency dependent. Indeed, pure sunlight is white, but if this light goes through a prism, you’ll see more colors, similar to a rainbow. Each color corresponds to a specific photon frequency or wavelength.
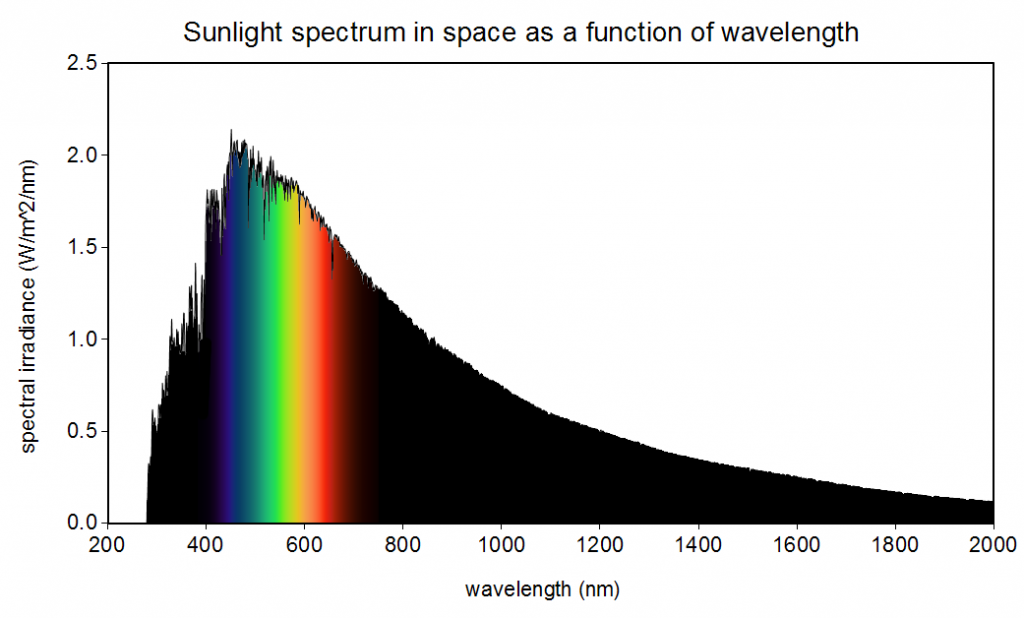
The sunlight wavelength varies from 300nm (ultraviolet) to 2.5um (infrared), but the visible light wavelength is between 400nm (blue) to 700nm (red).
As you can see in the chart below, solar energy is the highest at around 500nm (green/yellow color). Therefore, scientists are developing systems that harvest solar energy in the visible spectrum up to infrared.
Knowing this will come in handy later when we discuss the types of solar energy.
Types of Solar Energy
The 4 types of solar energy we will describe in the following sections take advantage of sunlight’s amazing properties, helping to produce either electricity or heat for human use.
Photovoltaic Systems
One of the most common examples of solar energy — and the best way to utilize the sun’s energy — is photovoltaic systems comprised of solar panels. These systems transform solar energy into electricity.
The winning ingredient inside a solar cell is silicon. This material has specific electronic properties that allow the element to convert sunlight into electricity.
When sunlight interacts with the silicon, it forces the electrons inside it to move — this movement then initiates a flow of electricity. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect (‘photon-light, ‘voltaic’ – electricity), discovered by Raymond Becquerel.

A fully functional photovoltaic home setup would include the following:
- Solar panels: these are often connected in an array to provide higher overall power outputs/DC voltages.
- Solar batteries: the electricity generated by your solar panels is stored here.
- Charge controller: These devices regulate the charge of the battery and prevent overcharging, which could compromise your storage battery’s health.
- Inverter: solar panels produce DC (direct current), and most appliances utilize AC (alternating current). An inverter is used to convert DC to AC which we can then use in our homes or campervans.
Related Reading: How do solar panels work?
Solar Water Heating Systems
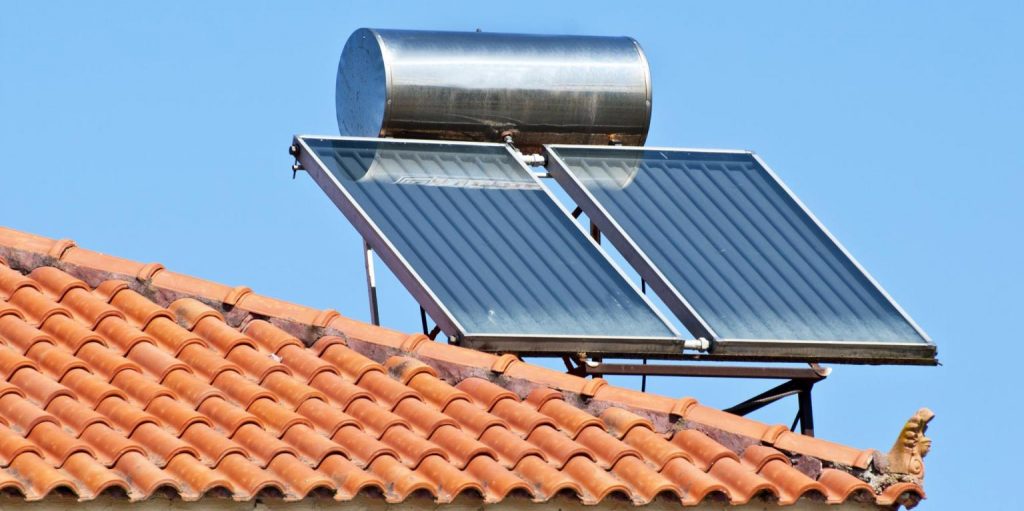

Another type of solar energy is solar thermal. This type of energy involves heating water using the sun’s heat.
Solar thermal energy is perhaps the easiest way to harvest solar energy — it doesn’t require complex set-up and manufacturing processes as only a dark surface (black or deep blue) will soak up the most heat from the sun. Therefore, solar water heating systems are extremely popular.
Many countries, such as Israel, are responsible for a large portion of water heating, with 85% of the domestic hot water supply.The concept of solar water heating comes directly from nature herself — have you ever noticed how shallow pools of water are much warmer than deeper ones? This is because most of the sunlight energy is absorbed by the water in the first meters — the thinner the water layer, the hotter it will get.
Humans created solar water heating systems which mimic the genius of nature. Two parts comprise this system — the solar collector and the storage tank.
Flate-Plate Collector
The most common collector is called a flat-plate collector; it’s mounted onto your home’s roof and is angled to face the sun.
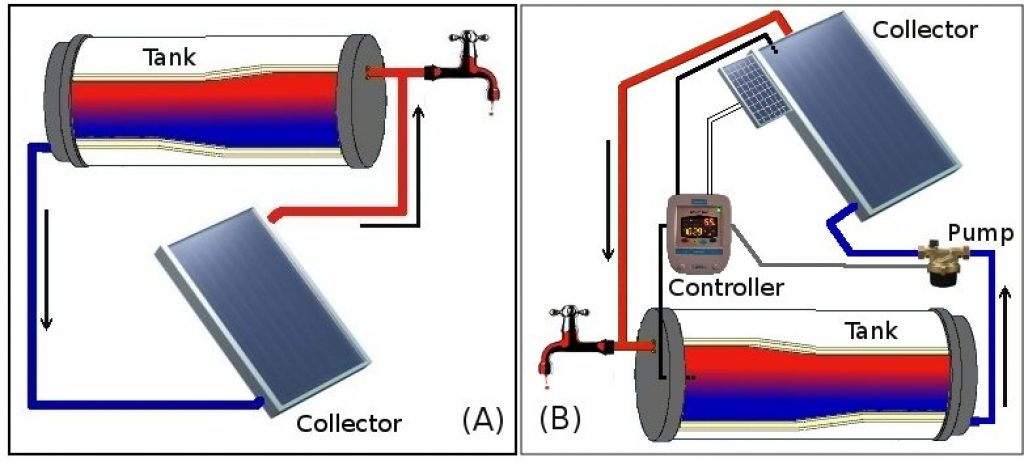
There are many small tubes that run through the plate and carry the fluid.
As the collector begins to heat up it warms the fluid passing through its tubes. This warm water then gets stored in the storage tank, ready to be used.
Solar Power Plants
The third way you can utilize solar energy is through producing electricity generated by solar thermal power plants.
As you may know, most power plants today use unsustainable forms of energy, such as fossil fuels, to boil water. This boiling water creates high-pressure steam that rotates large turbines, which activates the generator that then produces electricity.
This conventional way of generating electricity is toxic to our health and is largely responsible for global warming.
The Future Looks Bright
However, there is light at the end of the tunnel. There are new forms of power plants being introduced that rely solely on solar power.
These power plants use the sun as a heat source and can do so in 3 different ways:
Parabolic-Trough System
This system captures the sun’s energy via long rectangular, curved mirrors angled toward the sun, enabling sunlight to focus its super rays onto a pipe that contains oil.
This oil is then heated and then used to boil water in a conventional steam generator to produce electricity.
Dish/Engine System
These systems use a large, mirrored dish that resembles your household satellite dish (except 1000 times bigger). This dish concentrates the sun’s heat onto a receiver. The receiver then absorbs the heat and transfers it to the fluid within an engine.
Heat causes this fluid to expand, pushing against a piston or turbine and producing mechanical power. Finally, mechanical power runs a generator or alternator to generate electricity.
Power Tower System
Power tower systems use large fields of mirrors that concentrate the sun’s sunlight onto the top of the tower. On top of the tower, there is a receiver containing molten salt.
The salt’s heat can generate electricity through a conventional steam generator (minus all the pollution). Molten salt effectively retains heat efficiently and can be stored for days until it needs to be converted into electricity. This means electricity can still be produced on cloudy days or even at night.
Passive Solar Heating
Another type of solar energy takes the form of passive solar heating. Though you’d be mistaken for thinking this is a new concept. In fact, ancient civilizations such as the Anasazi Indians used passive solar heating in their household designs.
The impact the sun’s energy has on our planet is relatively easy to understand. If it’s a hot sunny day where you live, take a break from your computer, go outside and stand in the sun for a moment.
The proper design allows many buildings to “feed off” the sun’s energy.
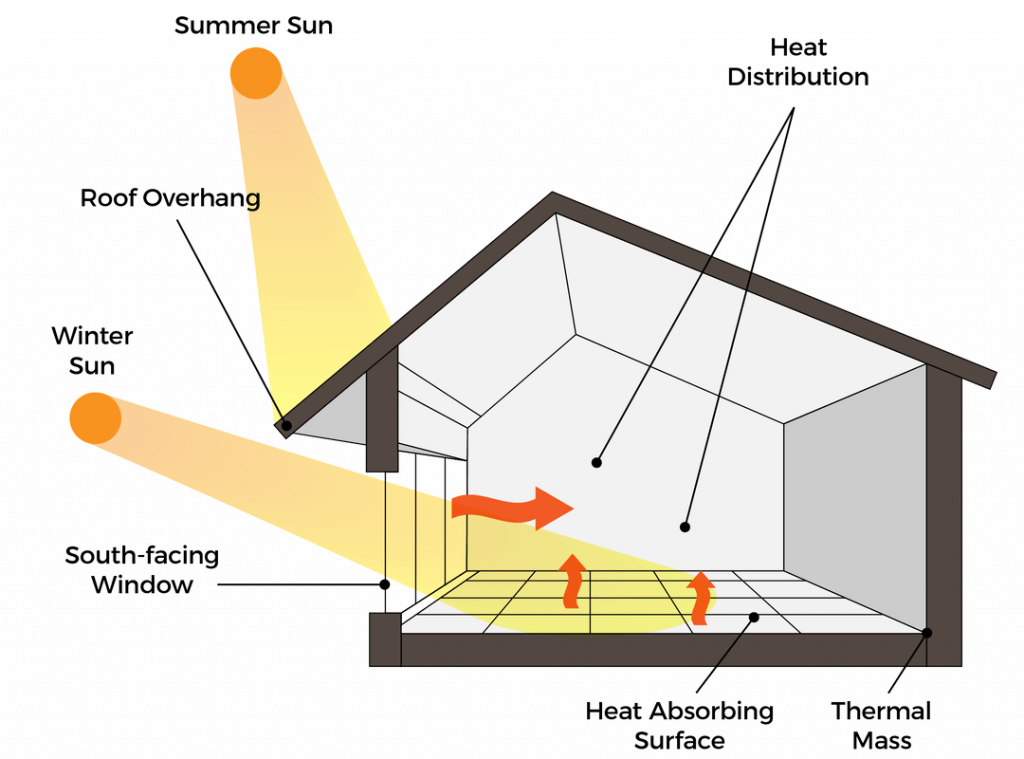
Buildings, for example, can install materials such as sunlit floors and walls that will actively absorb and store the sun’s heat.
These materials heat up during the day and, at a slow pace, release the heat during colder nights.
Other home designs include features such as a sunspace. These “spaces” resemble greenhouses, which concentrate a lot of heat. With the correct ventilation, you can warm up an entire space.
Interestingly, you’d imagine these designs overheating entire buildings on sweltering days, right? Wrong! In fact, there are ways to ensure these features do not overheat households.
Related Reading: Solar Tube Skylight: All you need to know
How Is Solar Energy Classified?
Solar energy is classified as a renewable energy source. A renewable energy source is any source of energy that can replenish itself naturally on a human timescale.
Energy sources like coal are considered non-renewable due to the fact they take over a hundred thousand years to reform. This makes them unable to replenish at the rate at which humans use them today.
Solar energy is therefore classified as a renewable energy source that will never run out or be in short supply (at least in a human’s lifetime).
Then there’s silicon — we use this to manufacture solar panels.
Silicon, by itself, is not renewable. However, it’s highly abundant and easily accessible (sand) on earth. Furthermore, we can recover silicon by recycling solar panels. All we need to do is continue developing different types of solar energy to capture it!
What Are 4 Advantages Of Solar Energy?
1. Pollution Free
Solar energy is pollution-free and causes no greenhouse gases to be emitted after installation.
A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory shows that pollution created by solar panel production is generally recouped in clean energy within 4 to 5 years of a solar panel’s life span (+- 30 years).
2. Return On Investment
Solar panel installation does have a somewhat higher initial investment (reducing every year, with technological advancements). However, unlike utility bills, you’ll receive a return on your once-off investment within 6 to 8 years, depending on the electricity cost and solar equipment subsidies.
Additionally, you can sell or offset your excess solar energy in many states, further reducing your energy bill.
3. Diverse Applications
As previously mentioned, there are many types of solar energy, and they can all be used for multiple purposes.
4. Low Maintenance Costs
Photovoltaic systems require very little maintenance. Because there are no moving parts, there is no wear and tear.
All you’ll need to do is ensure that you clean your panels properly from time to time.
For this reason, other solar panels can last up to 25 – 30 years.
Final Thoughts
Solar energy is fantastic! Our sun shines every day on our planet.
We can now harvest solar energy with reliable, simple, and cheap systems thanks to decades of scientific research.
As our article demonstrates, solar energy has many different uses, from electricity production to heat generation.
In 2022, it’s even the cheapest way to produce heat and electricity. There is no doubt that in the coming year, solar energy, coupled with storage systems and smart electricity grids, will take an even more prominent place among all energy production systems.

