Solar panel recycling has become one of the newest environmental challenges, and here’s why:
Solar has proven its value as an efficient and cheap renewable energy source over the last two decades.
Because of its many advantages, the world’s demand for solar panels has increased rapidly. The best panel manufacturers have responded by offering technological improvements and cost reductions. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar became the “cheapest electricity in history” in 2020.
However, this incredible technology is not all sunshine and butterflies.
Solar panels have an average lifetime of 30 years. Given that the use of solar only really picked up in the early 2000s, solar panel waste hasn’t become a huge problem yet – but pretty soon, it will.
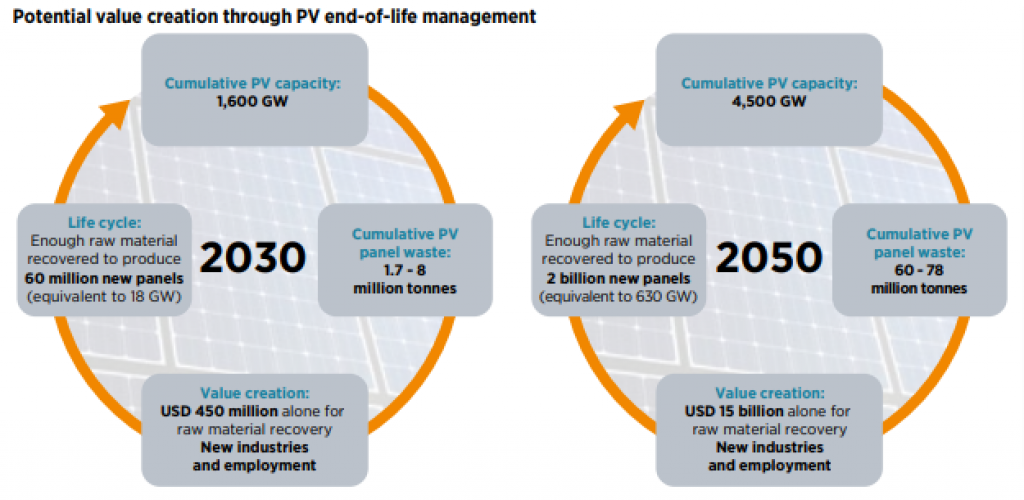
IRENA (International Renewable Energy Agency) predicts that total PV (Photovoltaic) panel waste will be between 1,7 to 8 million tonnes by 2030.
We currently don’t have a real plan to deal with this amount of waste. The good news is that the recycling industry is working on this problem, and progress is being made.
In this article, we’ll discuss solar panel recycling in detail. By the end of it, you’ll know how to recycle your solar panels safely.
Table of Contents
Can Solar Panels Be Recycled?
Yes, it is possible to recycle solar panels.
However, the process is not as simple as throwing them into the correct recycling bin. You need to take specific measures to recycle solar panels safely and effectively.
Firstly, you shouldn’t dispose of them prematurely; solar panels usually last 25 to 30 years. After this period, their ability to generate energy may decrease by around 20%. Only then should you decommission them.
Secondly, despite the modules’ recyclability, separating materials is complex and requires advanced machinery. Therefore, you should ensure you’re dealing with a reputable recycling center capable of efficiently recycling solar panels. (we present a list of companies that offer this service in the U.S. later in this article).
Let’s first look at the components of solar panels so that you can better understand how to recycle them.
What Are The Components Of Solar Panels?
Several photovoltaic (PV) cells compose solar panels (also called modules). These cells work using the photovoltaic effect of the semiconductor material to convert solar radiation directly into electrical energy.
There are two main types of solar panels:
- Crystalline Silicon: Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline
- Thin-film (amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, copper indium gallium selenide – CIGS)
Because of their higher energy conversion efficiency, Crystalline-silicon currently represents about 95% of panels used in solar systems.
Here’s an illustration of the essential components of crystalline-silicon solar panels:
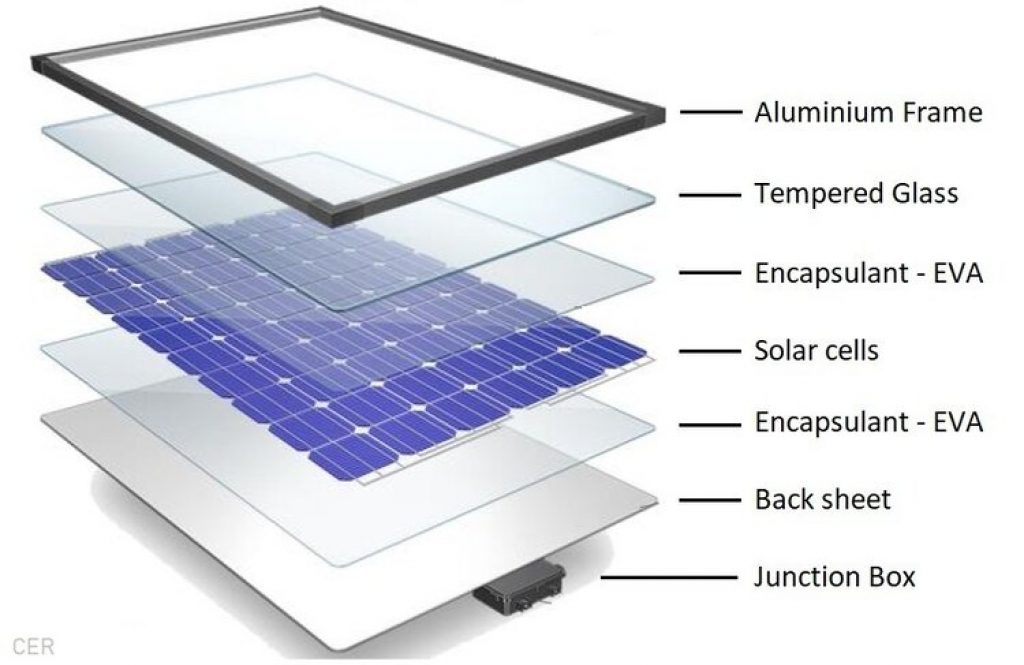
Source: cleanenergyreviews.info
The main components of solar panels are:
- Metal Frame (usually aluminum)
- Tempered glass
- Semiconductor (doped silicon)
- Plastic (encapsulant: EVA film and Back sheet: PP, PET, and PVF)
- Junction box (needed to attach wires)
Technically speaking, you could recycle all materials used in solar panels. You just need to use the appropriate recycling method.
Most of the weight of solar panels (around 70%) is glass, and recycling glass is already a well-established practice in the recycling industry.
In addition, the extraction of aluminum frames and copper wires (used to make new solar panels) is an easy recycling step.
The recycling process gets a bit complicated to recover the silicon, silver, copper, and other heavy metals present in solar panels. That’s because the polymer layers that encapsulate the cells (to protect them from external harm) make disassembling the panel quite tricky. Therefore, applying thermal processes loosens the adhesive that keeps the layers together.
Furthermore, grinding machines and chemical processes ensure the recovery of as much material as possible.
Why Should Solar Panels Be Recycled?

Source: nrel.gov
Solar energy is an environmentally friendly and inexpensive technology. That makes it a fantastic renewable energy source that is advantageous for the consumer and the environment.
However, if not recycled once they reach the end of their lives, they most likely end up in landfills.
There are many reasons for recycling solar panels. Here we present the main ones:
Solar Panel Recycling Is Good For The Environment
Most broken, or unusable solar panels find their way to landfills. Why? Because the solar panel recycling process has not yet garnered widespread appeal (except in the E.U.).
That’s highly harmful to the environment, given that solar panels – especially thin-film – contain heavy metals like cadmium, lead, arsenic, gallium, indium, tellurium, tin, antimony, and selenium. Some of these metals are highly poisonous and could be lethal at certain levels.
Although these elements are present in solar panels in minimal amounts, they can contaminate soil and water if not properly recycled. As a result, the federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) considers solar panel waste hazardous.
Solar Panel Recycling Recovers Rare And Expensive Materials
According to this paper, recycling solar panels is crucial to ensure that we recover valuable resources.
For example, we can recycle aluminum frames to reuse future solar panels. A recent study published in Nature shows that, according to the current demand for solar technologies, more than 40% of the world’s aluminum production will be required to mount and install solar panel arrays by 2050.
Although aluminum is the most abundant metal on earth’s crust, it’s usually found in minerals. And the Hall–Héroult process used for commercial aluminum production is a major concern. This process contributes to greenhouse gas emissions through the emission of CO2 in the electrolytic reaction and the consumption of large amounts of electricity.
In addition, scarcity issues are related to some elements in thin-film solar cells like gallium, indium, and selenium. Therefore, recycling solar panels keeps them from being depleted from the environment over time.
Efforts To Recycle Solar Panels Could Be Beneficial To The Economy
Recent studies show that solar panel recycling advancements could lead to increased supply chain stability and resource security for producing new solar panels and decreased manufacturing costs.
In addition to supporting a circular economy, improvements in waste management and development of efficient recycling processes could enhance a company’s green reputation, provide new revenue streams, and create new jobs and business opportunities.
Unfortunately, the current lack of incentives and regulations regarding solar panel recycling in the U.S. (as opposed to the well-established recycling model in place in the E.U.) demotivates the recycling industry to make great efforts to recycle such materials.
In fact, as of now, solar panels carry a high cost to recycle correctly, and the proceeds from this operation aren’t yet enough to cover the costs, let alone make it a profitable market.
That’s why many studies show the immense need for implementing government policies and incentives to stimulate the market of solar panel recycling.
In 2021, SETO (Solar Energy Technologies Office) from the U.S. Department of Energy (DEO), whose mission is to accelerate the advancement and deployment of solar technology, released a report describing the office’s activities and specific goals for 2025. Here is the link if you are curious.
How Can You Safely Recycle Solar Panels?
Safely disassembling solar panels for recycling is a tricky task.
To ensure a safe and efficient recycling process for your solar panels, you should turn to a company that specializes in recycling such materials.
Separating and recycling solar panels is a complex process that requires specific machinery.
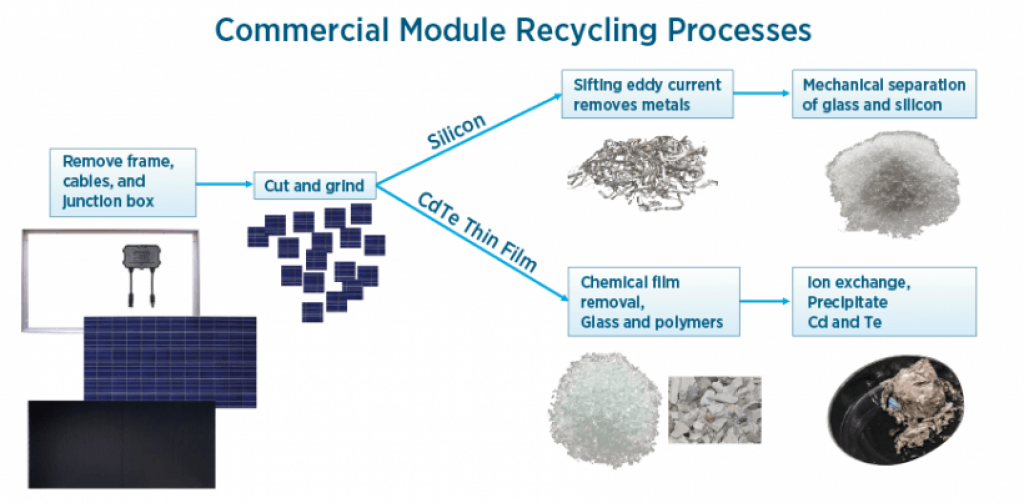
Source: energy.gov
Breaking Down Solar Panels Into Their Components
Once panels reach the recycling facility, they are stripped down into their components. The aluminum frame and copper wires are easily separated and recycled or repurposed.
Then, the remaining glass, silicon, wiring, and various metals are ground into a “glass cullet” mixture, which receives further treatment to separate the materials. Almost 95% of the glass recovered from solar panels can be reused. This process requires specific machinery.
Some companies use more sophisticated methods to physically separate the main parts of the solar panels, such as the silicon itself and the intra-cell wiring. This takes more time and labor, so the costs associated are higher.
Thin-film panel recycling is slightly different: First, the panels go through a shredder. Afterward, a hammermill breaks the pieces even more until the lamination that keeps the materials together cracks (when pieces are around 5 mm ). This process releases materials for further treatment.
Thermal And Chemical Treatment
As previously mentioned, after mechanical separation, further treatment helps extraction and recovery of more materials.
One of these treatments is thermal: heating the remaining materials to 500ºC (932ºF) eases the binding of the solar cell elements. The extreme heat also degrades the encapsulant polymer, leaving silicon and other materials to be collected and further refined.
Chemical processes are also used to recycle solar panels. For example, silicon wafers are treated with acid to collect metals using eddy current separation.
Contrary to silicon-based panels, a heterogeneous mixture is obtained through the shredding of thin-film panels. The mixture goes through a rotating screw to separate the solids from the liquid. The rotating tube keeps the solids inside while the liquid drips into a separate container.
This liquid then undergoes chemical processes such as precipitation and hydrolysis to ensure purity.
The solids go through a vibrating surface, separating materials according to their mass. Finally, the solid materials are rinsed. Most of what is left is glass, but other materials like metal remain, (in small amounts).
Here’s a video showing the solar panel recycling process:
If you enjoyed watching this video, here’s another one for you.
How Much Does It Cost to Recycle Solar Panels?

Source: cyberrecycling.com.au
Currently, it costs an average of $20 to recycle a standard 18 square foot solar power module. Companies usually charge this amount to offset their processing costs (to recycle a single solar panel).
This high price is due to the extensive chemical and thermal processes involved in recycling distinct materials. In addition, labor and specific transport conditions for materials considered hazardous add to the cost.
The high cost of recycling makes it almost ten times more expensive than simply disposing of panels in landfills. In the U.S., this practice is still legal in many states.
Currently, only Washington, New York, and California are creating incentives and regulating solar panel recycling. In 2017, Washington passed the first bill to promote solar panel recycling. This law requires manufacturers to finance the takeback and recycling system at no cost to the owner of the solar module. Other states are considering doing the same.
How Much Are Recycled Solar Panels Worth?
A review published in 2019 showed a potential revenue of approximately $11 based on material extraction from a 60-cell solar module. This study also showed that reused modules could be worth $22.
Despite tax policies and the relatively low prices of new solar panels making them a poor investment, there is a market for used panels.
Companies refurbish old solar panels, test their electricity output, and check if they’re still working correctly. They then sell these used panels for a fraction of the price of a new one. So while a typical cheap 250W panel will cost you around $175, a recycled panel can cost you $30.
When not refurbished and resold, solar panel recycling companies extract and sell the raw materials obtained from solar panels; this revenue is relatively low.
We Recycle Solar spends a total of $25 per panel in processing costs, and they yield around $4 from silicon, aluminum, copper, glass, and other materials.
Despite these current numbers, the “End-of-life management” report from IRENA (International Renewable Energy Agency) estimates that by 2050, raw materials recovered from solar panels will be worth a total of USD 15 billion (see image below).
Where To Recycle Solar Panels In The United States?
Currently, U.S. federal regulations don’t require manufacturers to handle their product recycling (yet, hopefully). In turn, several private companies offer this type of service. Here are a few of them:
We Recycle Solar
Located in Phoenix, Arizona, We Recycle Solar specializes in processing photovoltaic devices. They offer decommissioning planning (including the actual tear downs), recovery of raw materials, and returns management solutions (repair, refurbishment, recycling, repacking).
Their recovery operations span over 4 countries, providing the global capability to process up to 100,000 pounds of equipment every day in each facility.
First Solar
With headquarters in Tempe, Arizona, and offices in Texas and California – and even in other countries such as Mexico, Germany, Brazil, Japan, Belgium, and India – First Solar invests heavily in the research and development of solar technologies. Among their many services, they ensure the collection and recycling of their products once they are no longer usable.
Recycle PV
Founded in Nevada, Recycle PV Solar has invested in equipment to build their state-of-the-art processing plant that accepts panels from across the country. They offer proper management of PV modules waste. They assess damaged and end-of-life panels, determine the costs to recycle unusable panels, and help repurpose solar panels with usable life.
Interco
Interco is a global recycling company headquartered in Madison, Illinois. This company claims to be a leader in solar panel scrap recycling in the United States, recycling panels from all across North America. Interco processes more than 1,000 tons of scrap solar panel modules each month.
Each company has its recycling processes for silicon-based and thin-film panels that differ slightly. However, they are all pretty similar to the recycling processes previously mentioned in this article.
Final Thoughts
The International Energy Agency (IEA) published a “Net Zero by 2050” roadmap, which states that solar will become the most significant energy source by 2050, accounting for 20% of energy supplies.
Therefore, we must prepare to deal with the immense amount of solar panels waste that is to come.
For an industry known for its sustainability, there must be a focus on recycling end-of-life and damaged solar panels so they don’t end up in landfills, which is prejudicial to the environment and human health.
Studies show that research on solar panel recycling is currently facing many problems. The creation of government incentives and regulations is crucial to solving solar waste issues.
With the information provided in this article, we hope you can make an informed decision when the time to decommission your solar panels arrives.

