DC to AC conversion — what is it, and why does it matter?
Since the war of the currents unofficially ended in the 19th century, Alternating Current (AC) became the definitive winner as major contracts were given to AC developers.
However, the war’s end did not mark the end of Direct Current (DC) since this current still exists in different electronics such as batteries, photovoltaic (PV) systems, and more.
Homes using battery banks or PV systems require inverters that convert DC into AC. The DC to AC conversion is one of the most critical subjects in PV residential, commercial, and even industrial systems.
In this article, you’ll learn about the relationship between DC and AC, how they differ, and why they are necessary.
Additionally, you’ll learn about the best inverters out there.
Table of Contents
DC vs. AC: what are the differences?
There are two forms of electricity — alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). One is not better than the other, as both are necessary.
Here we’ll explain each of them and how they differ.
How does DC work?
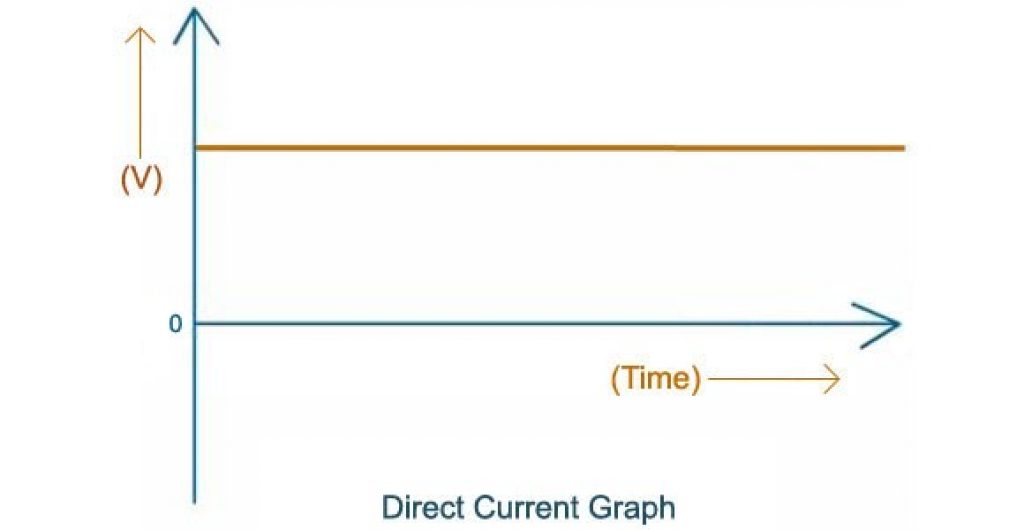
DC is a linear type of electrical current — it moves in a straight line/flows in one direction.
This current moves from the positive pole to the negative pole, while electrons produce electricity while moving from negative to positive.
For DC, the positive and negative poles always remain the same.
DC powers appliances with delicate electronic circuits that require a simple and steady current flowing in one direction.
Nowadays, this type of current powers cell phones, computers, and most other electronics.
How does AC work?
AC is a current that constantly changes its flow between positive and negative terminals.
This means that electrons also change their flow, following the negative to positive end as the polarity changes.
The speed at which AC changes polarity and completes several cycles in one second is called frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz).
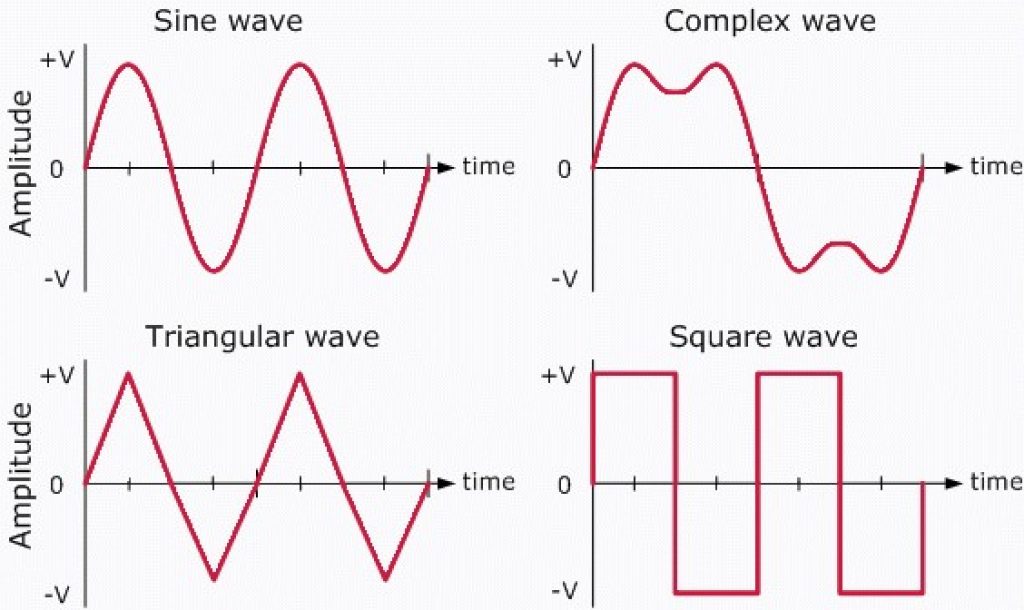
Source: The Basic Quantities of AC Waveform – EEWeb
AC can come in different forms, as seen in the figure above. There are triangular, square, sine, and complex waves.
Standard AC, found in U.S. homes, is a 120V amplitude pure sine wave with a 60Hz frequency.
Differences between DC vs. AC
DC and AC are pretty different. While the positive and negative terminals remain the same for DC, the same cannot be said for AC since the polarity constantly changes from positive to negative.
DC energy is unidirectional and does not vary in time, while AC is bidirectional, with the direction and magnitude of the wave changing over time.
Most DC appliances work at low voltages of 5V, 12V, or up to 24V, while AC devices usually operate at higher voltages of 120-240V.
How does DC to AC conversion work?
Understanding how DC to AC conversion works is essential to comprehend your PV system’s operation.
PV modules generate DC energy, and solar batteries also store energy in DC. To use this energy, you need to convert DC into AC, which is the required current by your appliances.
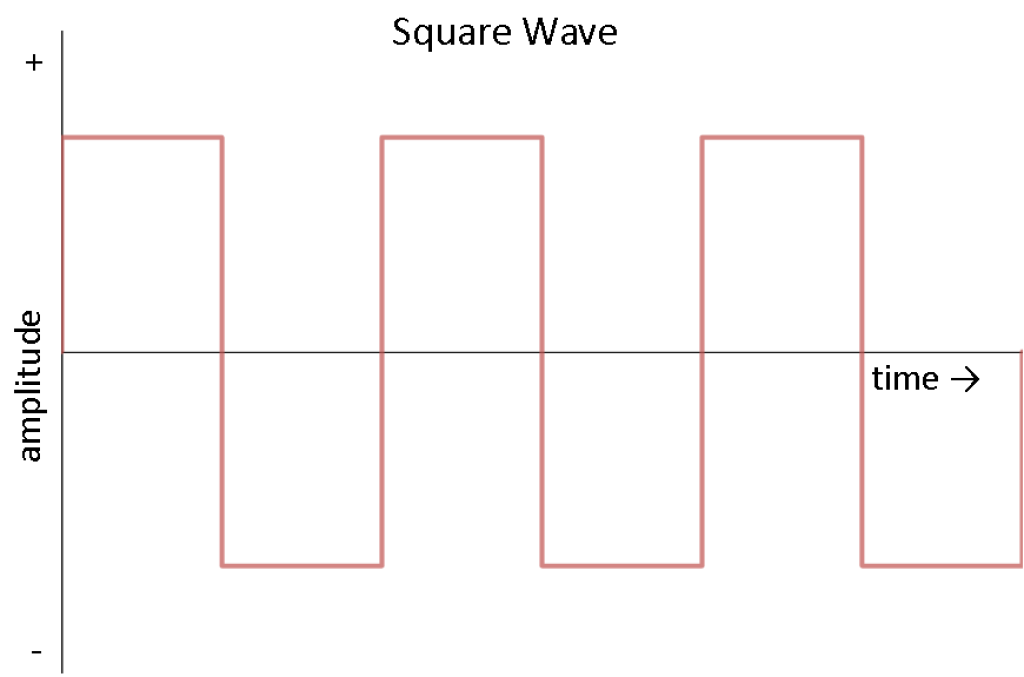
In the past, inverters converted DC into AC by rapidly switching the polarity for the output from positive to negative back and forth, creating a square wave.
First, inverters increase the DC voltage using a DC-to-DC converter. Then create the square wave. The output wave has an increased voltage with a reduced current, maintaining a power output similar to the input.
Source: Alternating Current (AC) vs. Direct Current (DC)
AC square waves are very abrupt and can damage some delicate electronics in your home.
To solve this, manufacturers invented rectification devices that modify the wave, creating what is known as a modified sine wave (MSW).
The MSW is more subtle with regular appliances and can power them without causing any damage.
While MSW is better than a square wave, it’s still not a pure sine wave, which is required to power certain delicate electronics.
Further developments in the industry allowed for the creation of rectification circuits, giving way to the creation of pure sine waves.
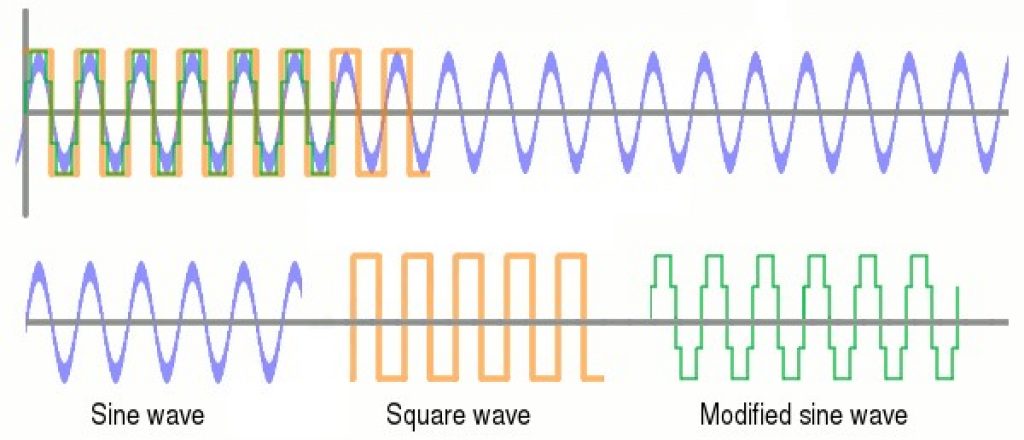
Source: Inverters – ExplainThatStuff
With DC to AC pure sine wave inverters, solar technology could finally convert DC-generated and stored energy into usable AC energy to power your appliances.
By creating a pure sine wave with a 110-120V amplitude, solar inverters can provide you with the same AC energy you get from your electrical utilities but in the form of 100% renewable energy.
Why is DC to AC conversion necessary?
DC to AC conversion is fundamental because your appliances require a 120V sine wave. Most devices are designed like this since AC has been the norm for several decades.
In the 19th century, DC tried to take over, but AC provided more advantages and ended up winning. This is because transporting and converting AC energy costs less than DC, which is why it became the global standard.
Nowadays, some appliances use both DC and AC. Generally, though, appliances require AC power. This is why you must have the correct DC-to-AC converter at home. It’ll allow you to power all your appliances with the correct voltage and AC wave.
What inverters convert DC to AC the best?
Finding the best DC to AC inverters takes time and effort. To help you choose, we reviewed the top 5 options for you.
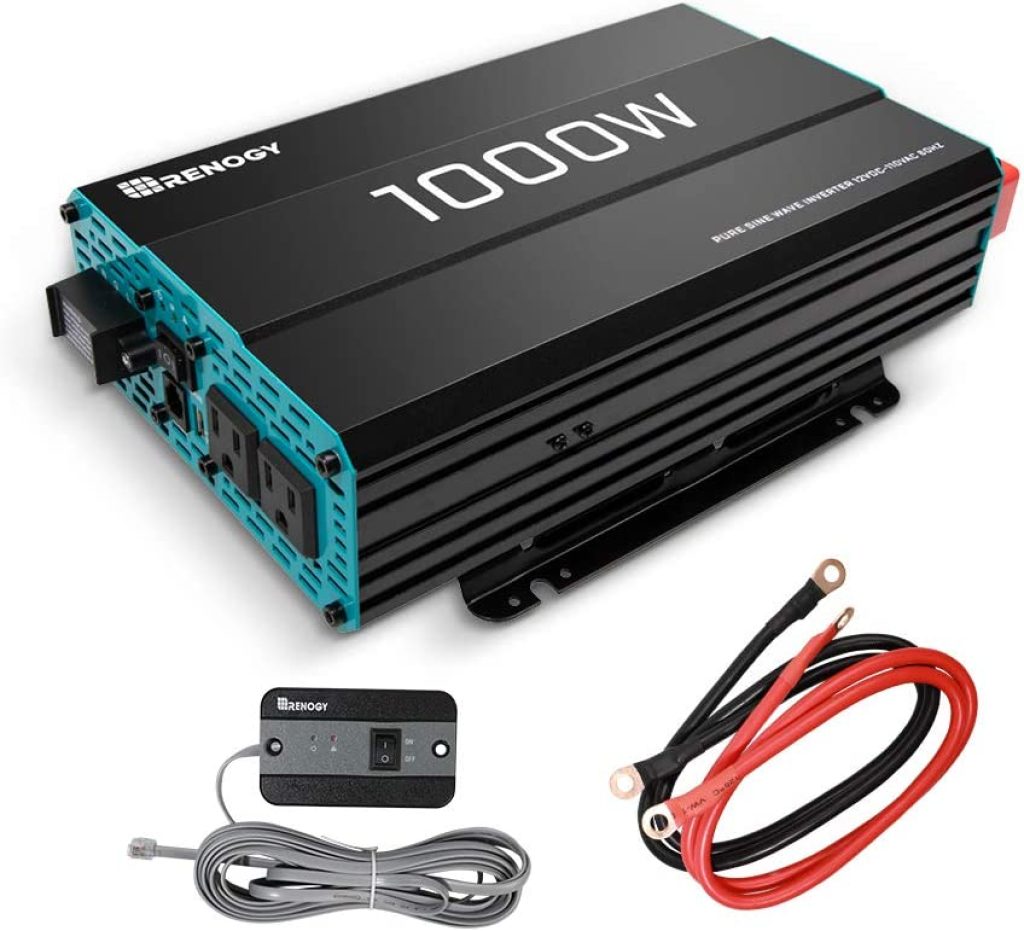
1. Renogy 1,000W 12V battery-powered inverter
- Optimized for 12V DC systems.
- Protection against LVD, HDV, AC overload, and over-temperature.
- GFCI protection.
- Can deliver a power peak of 2,000W.
- Includes 2 x AC pure sine wave outlets (115V).
- Additional Renogy remote control included.
- 1-year warranty.
The Renogy 1,000W pure sine wave inverter is light, robust, and compatible with 12V batteries.
This model is 90% efficient, delivering a 115V pure sine wave at 60Hz. Additionally, it provides a constant power output of 1,000W and a surge output of 2,000W.
The inverter includes 2 x AC sockets and 1 x USB port, while the equipment features protection against:
- Low Voltage Disconnection (LVD).
- High Voltage Disconnection (HVD).
- AC overload.
- Over-temperature.
What’s more, it includes ground-fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protection.
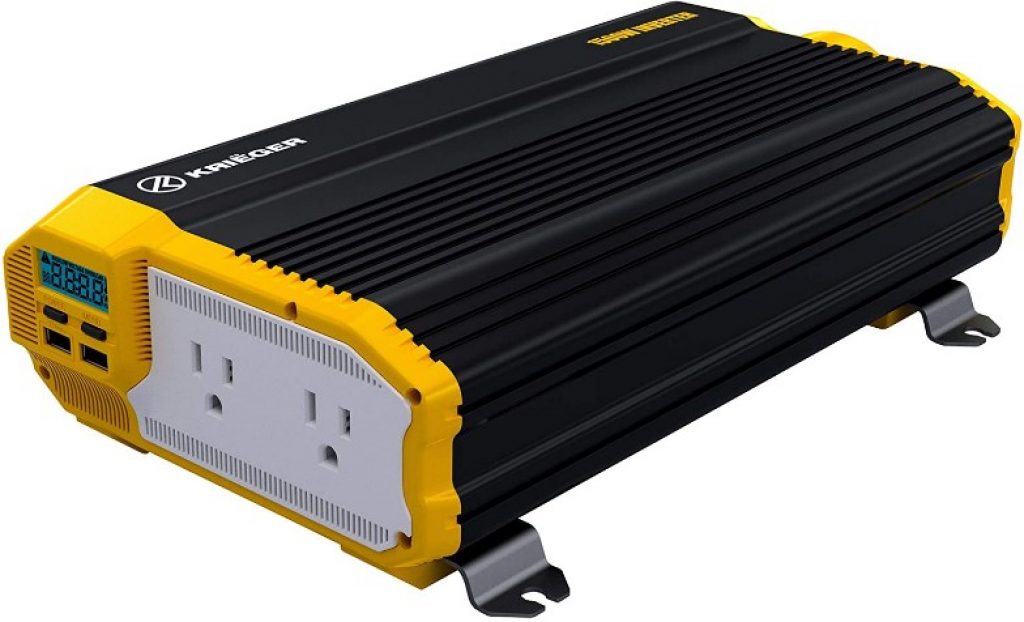
2. Krieger 1,500W power inverter
- Can operate at 10.5-15.5 VDC.
- Includes 2 x AC modified sine wave outlets (115V/13A).
- Remote control included.
- Ultra silent inverter.
- Handles a maximum peak power output of 3,000W.
- 3-year warranty.
The Krieger KR1500 is a very light and compact DC-to-AC inverter. This model outputs a modified sine wave, delivered through 2 x AC outlets that operate at a maximum constant power of 1,500W with an additional 10W for the USB ports.
This device handles output currents of 13A, operating with 90% efficiency. The inverter is very silent because of its thermal fan.
Additionally, it comes with protection against the following:
- Power overload.
- DC short-circuit.
- Low voltage.
- High voltage.
- Voltage overload.
- Over temperature.
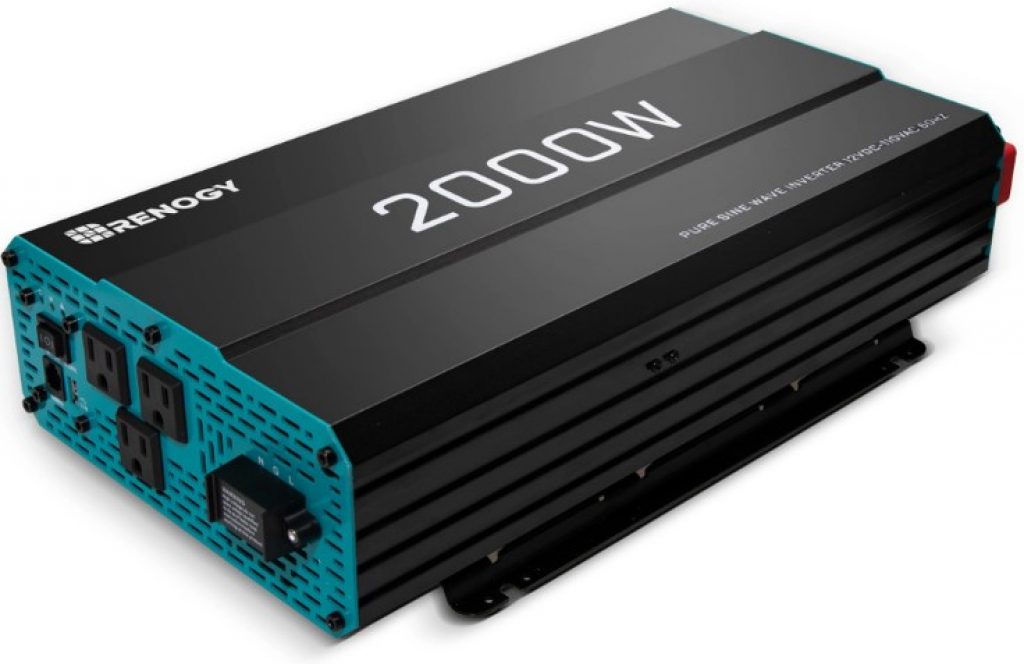
3. Renogy 2,000W 12V battery power inverter
- Suitable for 12VDC systems.
- Protection against LVD, HDV, AC overload, and over-temperature.
- GFCI protection.
- It can deliver a peak power output of 4,000W.
- Includes 3 x AC pure sine wave outlets (115V).
- Additional remote control included.
- 1-year warranty.
Manufactured by one of the best brands, the 2,000W Renogy power inverter is suitable for high-capacity batteries. It can power various devices, delivering a constant power output of 2,000W or a surge output of 4,000W.
This model is incredibly secure. It includes the following protection systems:
- LVD.
- HVD.
- AC overload.
- Over-temperature.
- GFCI protection.
Finally, it comes with 1 x USB port and 3 x AC sockets with a 115V pure sine wave.
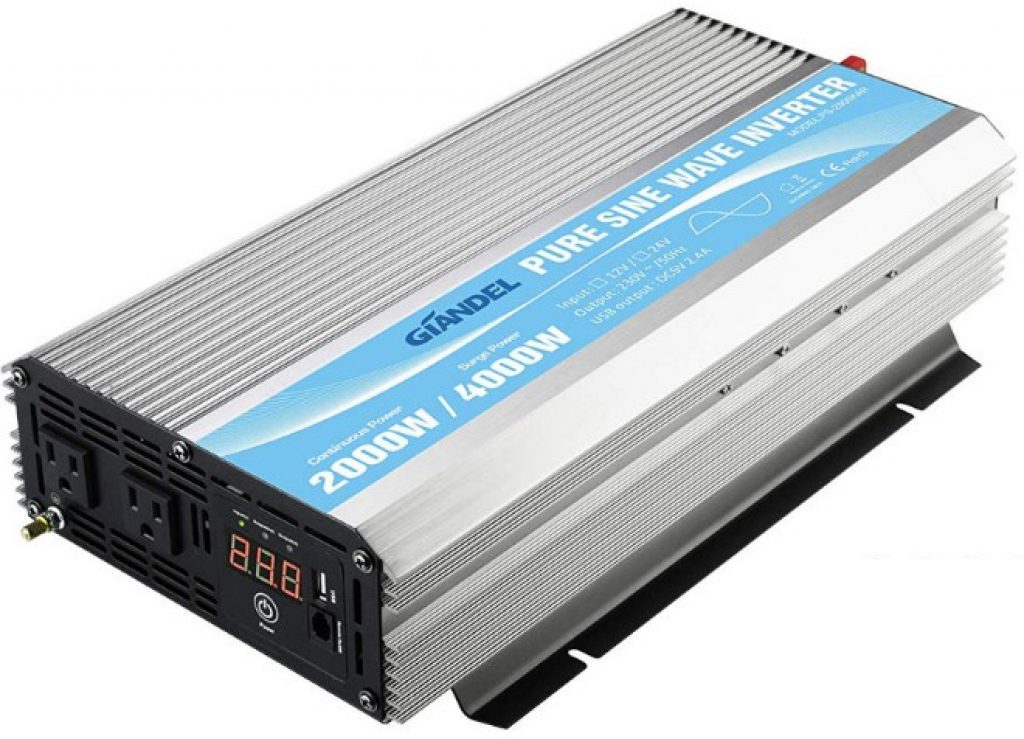
4. Giandel 2000W pure sine wave power inverter
- Optimized for 24VDC systems.
- Can deliver peak surges of 4,000W.
- Includes 2 x AC pure sine wave outlets (110 – 120V).
- Includes protection against AC overload, over-temperature, LVD, and HVD.
- GFCI protection.
- 18-month warranty.
The 2,000W Giandel DC to AC pure sine wave inverter is a lightweight device with silent functioning that’s ideal when paired with battery banks and small PV systems.
Its specs can deliver a power output of 2,000W and a peak power surge of 4,000W.
This model has a very low Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) of under 3% and an overall efficiency of 90%.
Finally, it includes protection against AC overload and over-temperature and has LVD and HVD.
5. Growatt 3000W (SPF 3000TL LVM-24P)
- Parallel capacity.
- Integrated MPPT charge controller.
- You can prioritize a grid or solar input.
- Monitoring through Wi-Fi/GPRS.
- Delivers a peak power surge of 6,000W.
- Can operate with a maximum PV array of 2,000W.
- MPPT operating voltage of 30-115VDC.
- 5-year warranty.
This offering from Growatt boasts a 120VAC pure sine wave inverter with 93% efficiency. It can deliver a constant power output of 3,000W and a peak power of 6,000W.
Not only does this model operate as a power inverter, but it also works as a charge controller for self-consumption applications. This makes it ideal for both grid-tied and off-grid homes.
Depending on your needs, you can configure this inverter to prioritize grid power or solar input. What’s more, you can monitor it using Wi-Fi or a GPRS network.
Finally, this model comes with parallel capacity — you can install it alongside several other Growatt 3,000W power inverters to increase the overall power output or provide two or three phases at your home.
FAQs
Why do we need to convert DC to AC for home appliances when DC is available from sources like batteries?
We need to convert DC to AC because most home appliances are designed to run on AC power.
AC power is the global standard for power distribution due to its ability to be easily transformed to different voltages and its capability to travel over long distances with minimal loss.
What can happen if a device designed for AC is powered with DC?
If a device designed for AC is powered with DC, it can lead to various problems like malfunction, reduced efficiency, overheating, or even damage to the device, as the device’s components are not designed to handle a constant flow of current in one direction.
Why is a pure sine wave inverter considered better than a modified sine wave inverter?
A pure sine wave inverter is considered better because it replicates the smooth, natural wave form of AC power from the grid, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of appliances.
It is more suitable for sensitive electronic devices, reducing the risk of malfunctions and damage due to harmonic distortion that can occur with modified sine wave inverters.
Are there any applications where DC is preferred over AC? Why?
Yes, DC is preferred in applications like electronic gadgets, battery charging, and solar panel systems because DC provides a constant voltage level, ensuring the smooth and stable operation of sensitive electronic components and is efficient for low-voltage, high-current applications.
What are the implications of using a low-quality inverter for DC to AC conversion?
Using a low-quality inverter can lead to inefficient conversion, resulting in energy loss and decreased performance of appliances. It might produce a lot of harmonic distortion, affecting the operation of sensitive electronic devices and potentially damaging them.
Additionally, low-quality inverters may lack sufficient protection features, risking damage due to overloads, short circuits, or overheating.
Can a household run exclusively on DC power with all the modern appliances?
Running a household exclusively on DC power is theoretically possible, but it would require significant modifications and accommodations due to the prevalence of AC-powered appliances and the existing AC power distribution infrastructure.
All the appliances would need to be DC-compatible, and a robust system would be needed to manage voltage requirements for different devices, making it impractical and cost-inefficient in most cases.
Final thoughts
DC to AC conversion is vital for PV systems and homes with energy storage banks. The right solar power inverter will allow you to power your appliances with the right, pure sine wave inverter.
These should have a 120V amplitude and 50-60 Hz, which is required for most home appliances.
When picking a solar inverter for your home, you should consider the different features, specifications, and nominal capacity, compared to your home’s cost and power needs.
We recommend you purchase the Renogy 1,000W or the 1,5000W Krieger inverter for small-medium systems and the 2,000-3,000W options for larger systems.
Which of our inverters would you pick? Let us know on Twitter or in the comments section below.