Tesla was founded on the 1st of July in 2003 by a group of engineers based in San Carlos, California.
They launched their first electric car 5 years later in 2008 – the Roadster.
Since then, they have gone on to design the world’s first-ever premium all-electric sedan, the Model S, along with many more mind-boggling electric cars that all use the same cutting-edge battery technology Tesla has become so famous for.
Unique visual design aside, you may be asking yourself…
How exactly do Tesla cars work?
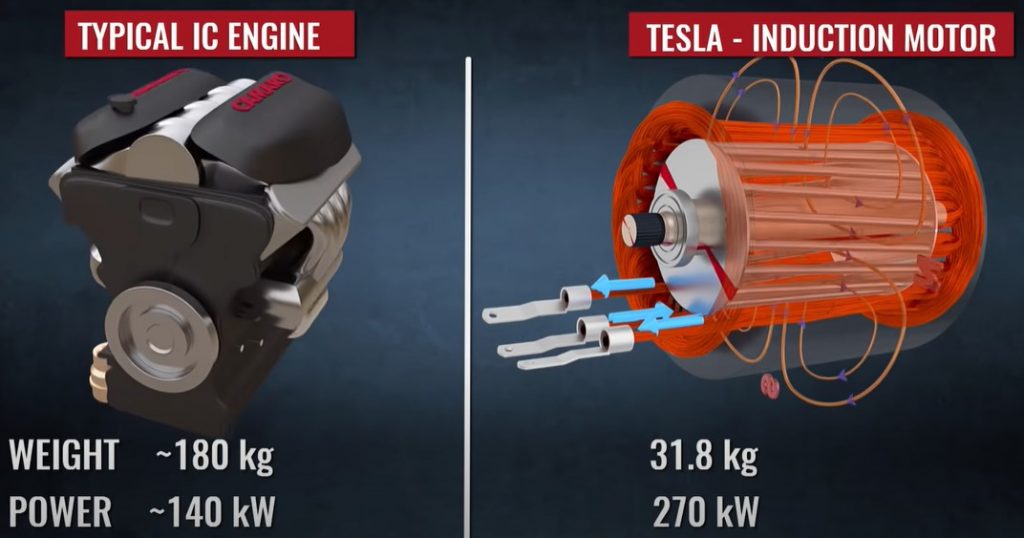
Tesla vehicles, also referred to as Electric Vehicles (EVs), employ an electric motor in lieu of an internal combustion engine. These automobiles are powered by a substantial traction battery pack that supplies energy to the electric motor. By relying on electricity, Tesla cars circumvent the production of exhaust emissions and eliminate the traditional liquid fuel components, including fuel lines, fuel pumps, and fuel tanks.
In this article, we aim to dissect a Tesla car and explain how each component works in detail.
Table of Contents
How Do Tesla Cars Work?
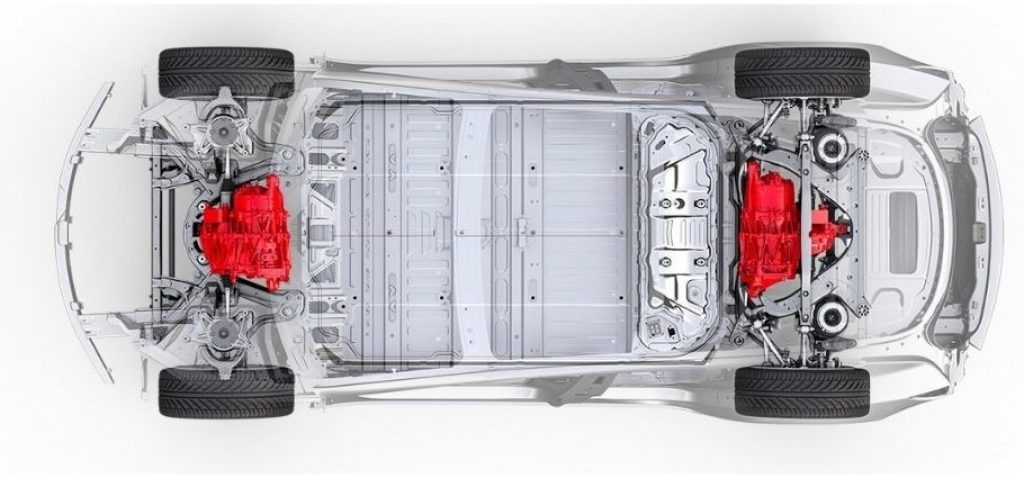

Induction Motor
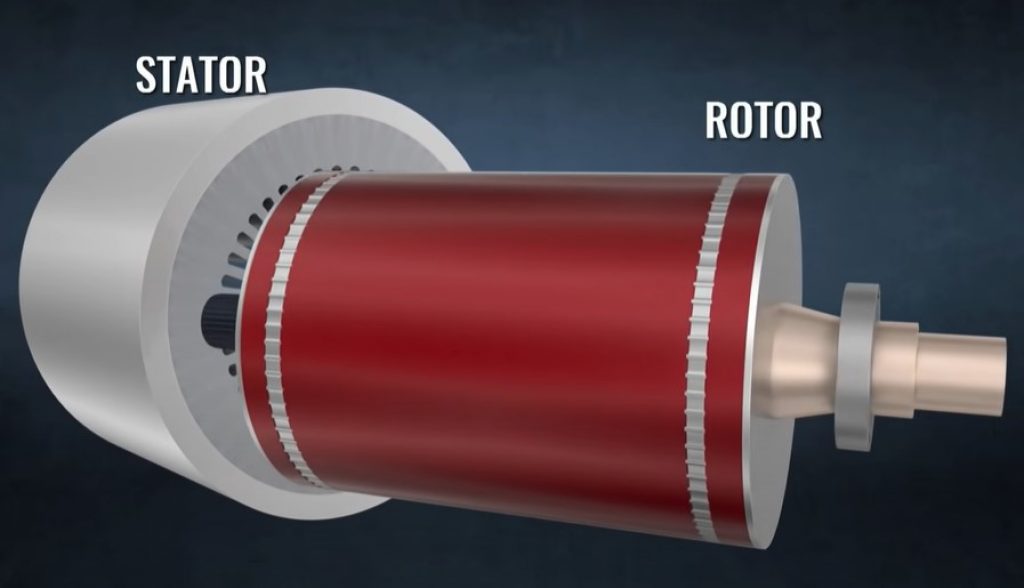
The first induction motor was invented by Nikola Tesla around 100 years ago. It has two main parts, the stator and the rotor.
The rotor is simply a collection of conducting bars short-circuited by end rings. A 3-phase AC power output is given to the stator.
The three-phase AC in the coils produces a magnetic field. Tesla motors produce a four-pole magnetic field.
This rotating magnetic field induces a current on the rotor bars to make them turn. In an induction motor, the rotor usually lags behind the rotor speed (RMF speed)
An induction motor has neither brushes nor a permanent magnet yet remains very powerful.
The fantastic thing about induction motors is that the rotation speed depends on the frequency of the AC power supply.
This means the speed at which the wheel turns can be altered by simply varying the frequency of the power supply.
This fact makes speed control on a Tesla easy and reliable. In fact, a Tesla motor can range from 0 to 18,000 RPM.
Inverter
The battery pack is what supplies the induction motor with power.
However, it produces DC power, this means that before the supply can get to the motor, it has to be converted from DC to AC power.
This is where the inverter comes into play.
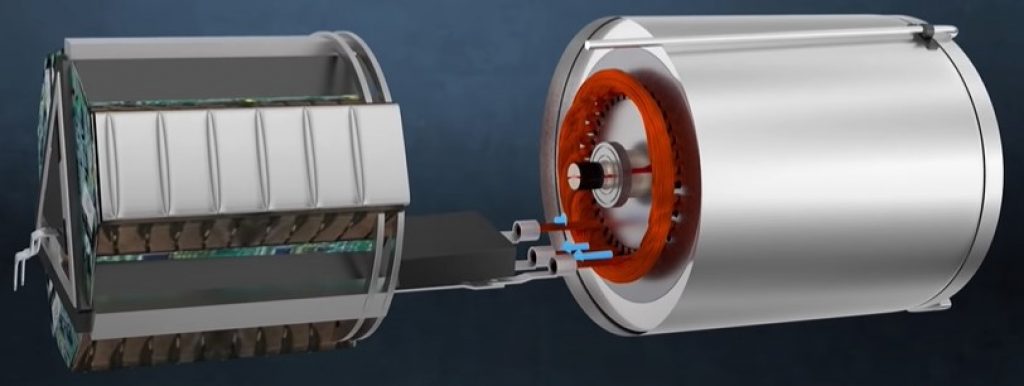
Not only does the invert convert DC to AC, it also controls the AC power frequency, thus controlling the motor speed.
The inverter can even shift the amplitude of the AC motor, which in turn controls the motor output power. Essentially, the inverter acts as the brain of the electric car.
Battery Pack
This may come as a surprise to most, but the battery packs consist of vast collections of common lithium-ion battery cells, similar to those used in your everyday life.
All these cells are interconnected in a combination of series and parallel to produce the required power to run the electric car.
Glycol coolant is passed through metallic inner tubes that intertwine through the small gaps between the cells. This is one principle that sets Tesla apart from other electric car manufacturers.
By using many small cells instead of a few big cells, essential cooling is guaranteed. This reduces thermal hot spots, which produce even temperature distribution among the many cells – leading to higher battery pack life.
All these cells are arranged in detachable modules, leading to about 16 of these modules, which include around 7000 cells.

Do Tesla Cars Break Down Often?
Just how reliable are Tesla cars?
Scientific research has demonstrated that the Tesla Model S can remain operational even after covering a distance of over 400,000 miles (equivalent to 643,737 km) and exhibits infrequent breakdowns. The reason behind this outstanding durability lies in the electric vehicle’s reliance on fewer mechanical components. With fewer moving parts, the probability of malfunctioning is significantly reduced.
When it comes to fuel-powered cars, one of the main causes of a breakdown is a faulty battery.
Now, what about a Tesla car that relies on thousands of battery cells in order to work?
Well, Tesla as a company has not been collecting data long enough to answer this question accurately for all of their vehicles (especially the newer Model 3 and Model Y).
However, we do have quite a few years of data for their slightly older models, like the Model S and Model X.
Below we have created two tables breaking down each model’s battery capabilities:
| Model S & X | Data |
|---|---|
| Average Degradation Rate Per 100,000 Miles | 4% |
| Miles Before 20% Degradation | 500,000 |
| Years Before 20% Degradation | 15+ |
| Charging Cycles | 1,000 |
| Model 3 & Y | Data |
|---|---|
| Average Degradation Rate Per 100,000 Miles | 4% |
| Miles Before 20% Degradation | 400,000 |
| Years Before 20% Degradation | 10-15 |
| Charging Cycles | 1500 |
The above data are broad estimates. Obviously, the battery retention capacities will vary from driver to driver depending on individual driving habits, driving temperature, and fast charging frequency.
What Breaks The Most On Tesla Cars?
Based on industry data and user reports, the most common things to break on a Tesla are:
- Suspension components
- Brake pads
This is likely attributed to the inherent weight of electric vehicles, which tends to be greater than their internal combustion engine counterparts and places more significant stress on the vehicle’s suspension and braking systems.
With that being said, Tesla continues to refine and improve the design of its vehicles, resulting in longer-lasting components and fewer required repairs.
Is A Tesla Car Expensive To Maintain?
Below we have collected and put together data from Tesloop, which has kept a record of its Tesla Model S maintenance expenses over a period of 450,000 miles.
In the table, we will focus on the following:
- RSM – Regular scheduled maintenance
- GVR – General vehicle repairs
Below is a summary of the tables:
Tesla Model S Maintenance Cost Breakdown
Below you will find the complete breakdown of costs, organized into a table:
| Regular Scheduled Maintanence (RSM) | Mileage | Payment Type | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tire Replacement | 51,000 | Customer Pay | $194 |
| Wheel Alignment | 74,469 | Customer Pay | $200 |
| Tire Replacement | 75,135 | Customer Pay | $513 |
| Tire Replacement | 95,242 | Customer Pay | $388 |
| Tire Inspection | 101,303 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 111,609 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Replacement | 126,419 | Customer Pay | $389 |
| Rear Bumper Repairs | N/A | Customer Pay | $1,000 |
| Tire Inspection | 130,404 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 147,329 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Replacement | 159,648 | Customer Pay | $389 |
| Wheel Alignment | 160,000 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 168,014 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 174,787 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 181,418 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 191,123 | Goodwill | $0 |
| 12v Battery Replacement | 194,237 | Customer Pay | $171 |
| Tire Inspection | 210,235 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 218,689 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Replace - Front/Rear Brake Pads/Rotors | 225,351 | Customer Pay | $1,759 |
| Tire Replacement | 231,546 | Customer Pay | $334 |
| Wheel Alignment | 231,570 | Customer Pay | $0 |
| Replaced Headlights | 251,252 | Customer Pay | $2,800 |
| Tire Inspection | 255,345 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 265,408 | Goodwill | $0 |
| General Maintenance | 274,610 | Customer Pay | $2,176 |
| Tire Inspection | 276,984 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Wheel Alignment | 278,732 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Replacement | 278,735 | Customer Pay | $666 |
| Dash Panel Replacements | 290,263 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Vehicle Inspection | 290,461 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 296,168 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 305,181 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Key Fob Features Turned On | 325,271 | Goodwill | $0 |
| 12V Power Outlet Replacement | 325,271 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Vehicle Inspection | 351,816 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Inspection | 351,816 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Replacement | 362,821 | Customer Pay | $362 |
| Tire Inspection | 375,145 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Brake Check | 377,785 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Rear Suspension Check | 377,785 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Repair | 380,058 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Replacement | N/A | Customer Pay | $100 |
| Tire Replacement | 386,025 | Customer Pay | $781 |
| Wheel Alignment | 392,403 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Tire Replacement | 430,400 | Customer Pay | $560 |
| Total RSM | $12,782 |
| General Vehicle Repairs (GVR) | Mileage | Payment Type | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steering Column Control Module | 17,441 | Warranty | $0 |
| nav/supercharging/AP diagnosis | 17,441 | Warranty | $0 |
| Front Drive Unit | 36,404 | Warranty | $0 |
| Forward Facing Camera - Drive Cycle Calibration | 36,404 | Warranty | $0 |
| Calibrate Sunroof | 36,404 | Warranty | $0 |
| Driver Door Handle Assembly Fix | 36,404 | Warranty | $0 |
| High Voltage Battery Replacement | 194,237 | Warranty | $0 |
| Cabin HVAC Fan general Diagnosis | 215,668 | Warranty | $0 |
| Replace Rear Right Door Handle | 230,690 | Customer Pay | $962 |
| Driver Door Handle Assembly Fix | 235,907 | Customer Pay | $962 |
| New Key Fob | 274,019 | Customer Pay | $123 |
| Front Left Door Handle | 278,732 | Customer Pay | $221 |
| Replace Thermal Controller (Air Conditioning) | 279,127 | Goodwill | $0 |
| Replace AC TXV Valve Evaporator | 278,732 | Customer Pay | $436 |
| Air Conditioning | 290,263 | Customer Pay | $1,351 |
| Windshield/Window Repair | N/A | Customer Pay | $139 |
| Key Fob Replacement | 306,072 | Customer Pay | $141 |
| Door Handles | 310,230 | Customer Pay | $749 |
| RR Rocket Panel Re-Attached | 310,230 | Goodwill | $0 |
| High Voltage Battery Replacement | 324,044 | Warranty | $0 |
| Additonal Key Fob Replacement | 325,271 | Customer Pay | $124 |
| Windshield/Window Repair | N/A | Customer Pay | $153 |
| Replaced drivers seat base assembly | 377,785 | Customer Pay | $1,364 |
| Removed bumper and secured parking sensors | 377,785 | Goodwill | $0 |
| AC Actuator | 396,877 | Customer Pay | $318 |
| Rear Stabilizer Bar | 406,304 | Customer Pay | $161 |
| Fore link assy, RH | 406,304 | Customer Pay | $185 |
| FR SUSP AFT link assy | 406,304 | Customer Pay | $240 |
| MS RR lower control arm assy-rwk | 406,304 | Customer Pay | $319 |
| FR UPR CTRL Arm, RH, Dual motor | 406,304 | Customer Pay | $260 |
| FR link assy, LH | 406,304 | Customer Pay | $185 |
| Rear toe link, x-axis | 406,304 | Customer Pay | $72 |
| RR SUSP upper link assy, X-axis | 406,304 | Customer Pay | $210 |
| Labor & Miscellaneous | 406,304 | Customer Pay | $3,500 |
| ASY Liftgate Latch PWR REL | 430,398 | Customer Pay | $39 |
| Actuator Cinching | 430,398 | Customer Pay | $64 |
| Cable, Cinch Liftgate | 430,398 | Customer Pay | $64 |
| Labor & Miscellaneous | 430,398 | Customer Pay | $280 |
| Left Headlight & Damaged Undercarriage Replaced | 446,997 | Customer Pay | $2,202.08 |
| Total GVR | $14,823 | ||
| Total RSM | $12,782 | ||
| Total Cost | $27,604 | ||
| Cost/Mile | $0.07 | ||
| MSRP Fuel Costs, 2.5 miles/kw, @ $0.26/kw for 450,000 Miles | $46,800.00 | ||
| Disclaimer: This vehicle is grandfathered in with free supercharging for life. | |||
| Fully Loaded Costs | $74,404 | ||
| FLC/Mile | $0.19 |
Where Can You Buy Tesla Cars?
Teslas are currently sold in the following countries:
| North America |
|---|
| United States |
| Canada |
| Mexico |
| Puerto Rico |
| Europe |
|---|
| Belgium |
| Hungary |
| Czechia |
| Netherlands |
| Denmark |
| Norway |
| Austria |
| Germany |
| Poland |
| Estonia |
| Portugal |
| Greece |
| Romania |
| Spain |
| Slovakia |
| France |
| Croatia |
| Ireland |
| Slovenia |
| Switzerland |
| Iceland |
| Sweden |
| Italy |
| Finland |
| Luxemburg |
| United Kingdom |
| Middle East |
|---|
| United Arab Emirates |
| Israel |
| Asia/Pacific |
|---|
| Singapore |
| South Korea |
| China |
| Japan |
| Hong Kong |
| Taiwan |
| Australia |
| Macau |
| New Zealand |
FAQs
How long does it take to charge a Tesla vehicle?
The time it takes to charge a Tesla vehicle depends on the model of the vehicle, the battery’s state of charge, and the type of charger being used.
Using a Tesla Supercharger, most Tesla vehicles can achieve an 80% charge in approximately 30 minutes. However, using a standard home charger, it may take several hours to achieve a full charge.
Can Tesla cars be charged using any electric vehicle (EV) charging station?
Tesla cars come with a proprietary charging port, but they can be charged at most public EV charging stations using an adapter.
Tesla provides adapters for various types of charging connectors, allowing owners to use non-Tesla charging stations when needed.
Are Tesla vehicles equipped with regenerative braking systems, and how do they work?
Yes, Tesla vehicles are equipped with regenerative braking systems. Regenerative braking allows the vehicle to convert kinetic energy back into stored energy in the vehicle’s battery whenever the driver applies the brakes or lifts off the accelerator.
This process helps in improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle and extends the driving range by replenishing the battery.
How does the Autopilot feature in Tesla cars function?
Tesla’s Autopilot is an advanced driver-assistance system utilizing various sensors, cameras, and machine-learning algorithms to enable the car to semi-automatically steer, accelerate, and brake.
It can navigate through traffic, change lanes, and park itself under certain conditions, but it requires active supervision from the driver, who must keep their hands on the steering wheel and be ready to take control at any time.
Can the battery in a Tesla car be replaced, and what is the approximate cost?
Yes, the battery in a Tesla car can be replaced. However, the cost of replacing a Tesla battery can be quite high, potentially ranging from $5,000 to $20,000 or more, depending on the model and the battery type.
However, it’s important to note that Tesla batteries are designed to last for a very long time, and many owners may never need to replace them.
What is the warranty period provided by Tesla for their vehicles, especially concerning the battery and the powertrain?
Tesla offers different warranty periods for different vehicle components. The battery and drive unit warranty for the Tesla Model S and Model X is 8 years, with no limit on the number of miles driven.
For the Model 3 and Model Y Standard Range Plus and Standard Range versions, the warranty is also 8 years but is limited to 100,000 miles, and for Long Range and Performance versions, it’s 8 years or 120,000 miles, whichever comes first.
Other components typically have a limited warranty of 4 years or 50,000 miles. Customers are advised to check the latest warranty terms while purchasing.
Final Thoughts
The market share of electric cars, including Tesla’s, has soared from a mere 0.7% to 2.4% of all cars sold in the US in 2020, a remarkable increase over the past five years.
According to recent studies, this figure is expected to grow to 11% by 2025, with projections indicating that over a third of all vehicles sold in the US will be electric by 2030.
For those interested in purchasing a Tesla, please visit the official Tesla website to place your order.

