Vehicle-to-grid charging and discharging (V2G) is a technology that connects electric vehicles (EVs) to the power grid.
But why is this important? What purpose does it serve you as an owner/prospective owner of an EV?
To put it simply, an EVs ability to charge from the grid helps meet demand and provides stability.
Overall, V2G is a promising technology that has the potential to transform the way we use and generate electricity. In the future, vehicle-to-grid technology could help us move towards a cleaner, renewable, and more efficient energy system.
In this article, we look at how this technology functions, the companies that offer it, its benefits, and more.
Table of Contents
What Is Vehicle To Grid Charging?
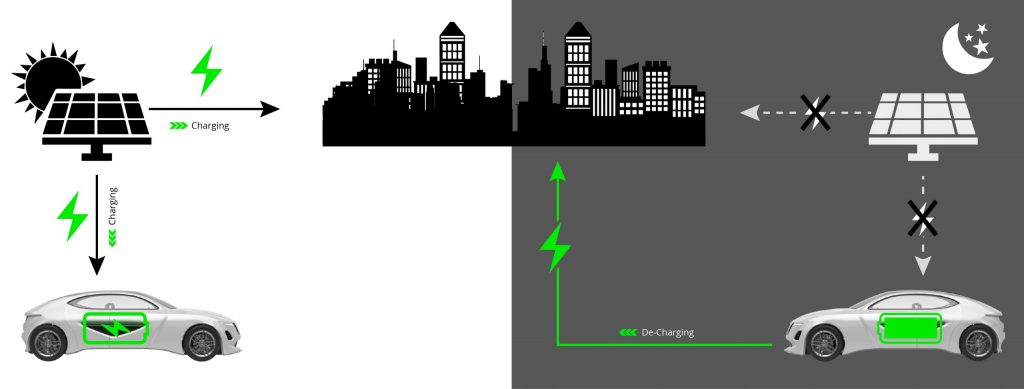
Vehicle-to-grid charging is a technology that allows EV owners to sell electricity back to the grid. This technology uses chargers that connect EVs and their batteries to the grid via a bi-directional power flow, providing the vehicle with a clean, renewable energy source.
Vehicle-to-grid charging and discharging can occur at home or public charging stations. This technology charges an EV when electricity rates are low and sells electricity back to the grid when rates are high.
These chargers can also provide backup power to the grid during peak demand or power outages.
Currently, this charging technology is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about energy storage and consumption.
Source: https://elektrobit.com
Where Can You Find V2G Chargers?
V2G chargers are typically large, industrial-scale devices installed at utility-scale facilities such as power plants or substations. However, there is a growing trend towards installing smaller, residential-scale V2G chargers.
Residential-scale chargers are typically installed at the customer’s home and used to charge their vehicle and provide power to the grid.
How Does V2G Work?
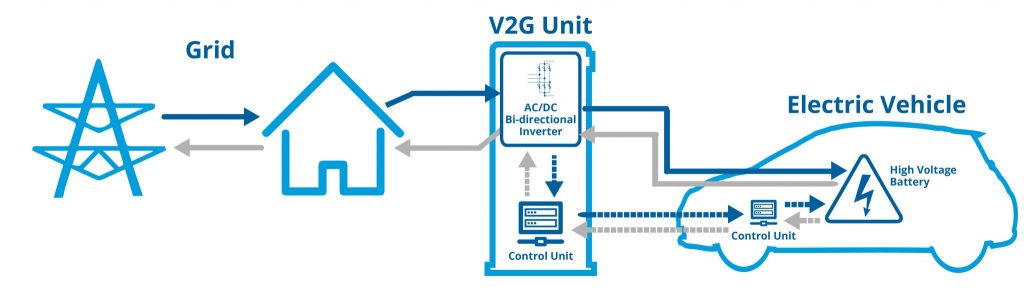
A V2G charger uses an EV battery’s stored energy to provide power to the grid when there is a high demand; it connects to the EV via a special cable.
V2G chargers typically connect to the grid through a utility-scale inverter using AC and DC. The inverter then converts the EV battery’s power from DC to AC and sends it to the grid — the EV battery charges when the charger is linked to the vehicle.
These chargers can also provide backup power to the grid in the event of a power outage. When the charger is connected to the grid, it can charge an EVs battery and then provide that electricity to the grid during a power outage; this helps keep the lights on and critical services running during an outage.
Operating A V2G charger
- Connect the charger to the vehicle’s onboard charger control unit.
- The control unit controls the charging and discharging of the vehicle’s battery.
- The charger communicates with the control unit to set the charge/discharge parameters.
- The charger continues to charge and discharge the vehicle’s battery according to the set parameters.
Source: https://toka.energy
Which Companies Offer V2G Services?
Several companies offer V2G services:
- Powertec Electric Inc (Winnipeg, Canada): Powertec Electric Inc offers V2G charging stations for residential and commercial customers.
- Enel X (San Carlos, California): Enel X offers V2G-enabled charging stations for home and business use. The company also has a cloud-based management platform that helps customers manage their energy usage.
- Green Charge Networks (Santa Clara, California): Green Charge Networks specializes in V2G-enabled battery storage systems for businesses. The company also offers a V2G-enabled charger for home use.
What Are The Benefits Of V2G?
- V2G provides a more stable and reliable electricity grid;
- The charging technology helps utilities to meet peak demand without the need for expensive and polluting power plants;
- A vehicle-to-grid charger helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by displacing fossil-fuel-generated electricity;
- The technology provides a source of revenue for electric vehicle owners through V2G services;
- Vehicle-to-grid chargers improve the efficiency of the electricity grid by using stored energy in electric vehicles;
- The charging technology provides a backup power source for critical infrastructure during power outages.
Are There Any Challenges With V2G Charging And Discharging?
The potential challenges of vehicle-to-grid technology include:
- The round-trip efficiency of charging and discharging may be lower than traditional grid-tied charging, due to energy losses in the battery.
- Vehicle-to-grid systems may require specialized and/or expensive V2G-enabled electrical equipment.
- The charging and discharging process may put additional stress on the battery, potentially reducing its lifespan.
- V2G services may not be available during power outages or other grid disruptions.
The Future Of V2G Technology
Despite V2G’s inherent challenges, the future of this technology looks very bright; it has the potential to completely transform the energy sector by making it more efficient and sustainable.
Future Benefits
V2G will help:
- Reduce carbon emissions;
- Improve grid stability;
- Provide a more reliable and affordable source of energy for consumers.
- Provide ancillary services to the grid, such as frequency regulation and volt/var control.
The potential benefits are significant, and the technology is already deployed on a commercial scale. Furthermore, it could play a pivotal role in helping to integrate intermittent renewable energy sources into the grid.
The technology is still in its early stages of development but has already shown great promise. In the future, V2G may become an essential part of the global energy system.
Case Studies Of V2G Implementations Around The World
In the early days of V2G, projects were limited to small-scale demonstrations and trials. As the technology has become more refined, several large-scale V2G projects have emerged worldwide.
Here are a few examples:
United States
The Department of Energy’s Vehicle Technologies Office supports research at several national laboratories; this includes the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and Sandia National Laboratories.
NREL is currently working on a project in Colorado. This project uses Nissan LEAF electric vehicles (EVs) to provide grid services such as frequency regulation and load following.
The project aims to demonstrate that the technology can provide economic and environmental benefits for both EV owners and the electric grid.
Europe
In Europe, the technology is tested and implemented on a large scale as part of the EU’s Smart Grid Demonstration Project led by the utility company Vattenfall. It involves more than 1000 V2G-enabled EVs and is taking place in Hamburg (Germany), Amsterdam (Netherlands), and Copenhagen (Denmark).
So far, the project has been a success, with V2G-enabled EVs providing considerable economic and environmental benefits, including power balancing, peak shaving, and voltage control.
Japan
The Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) is working on a V2G project using Honda Fit EVs to provide ancillary services to the electric grid.
The project aims to reduce demand charges; this accounts for a significant portion of TEPCO’s costs.
In Summary
These are just a few examples of V2G projects that are underway around the world.
However, it’s expected that even more large-scale projects will be announced in the coming years.
Final Thoughts
Vehicle-to-grid is a promising technology with the potential to transform the energy sector.
These chargers help reduce carbon emissions, improve grid stability, and provide a more reliable and affordable energy source for consumers.
In the future, V2G could play a pivotal role in helping to integrate intermittent renewable energy sources into the grid.
The technology is still in its early stages of development but has already shown great promise. In the future, V2G may become an essential part of the global energy system.
Do you have any experience with vehicle-to-grid technology? If so, we’d love to hear about it in the comments below. Alternatively, let us know your thoughts by joining our community!

