Reading solar panel specifications is a complex task. You’ll find dozens of figures and data across multiple categories. But what does it all mean? And how much of this information will be of use to you?
In this article, we review an LG solar panel‘s data sheets to uncover the various technical specifications, including the 5 most important ones.
After reading through this info, you’ll be able to compare different solar panel models and select the perfect fit for your future solar system.
Table of Contents
How To Read Solar Panel Specifications?
Solar panel specifications, also called solar panel data sheets, combine all the technical information about a solar panel.
This information is handy for electrical engineers building systems, professional installers, and anyone interested in buying solar panels for domestic use.
A typical solar panel data sheet has 2 pages. The following are examples:

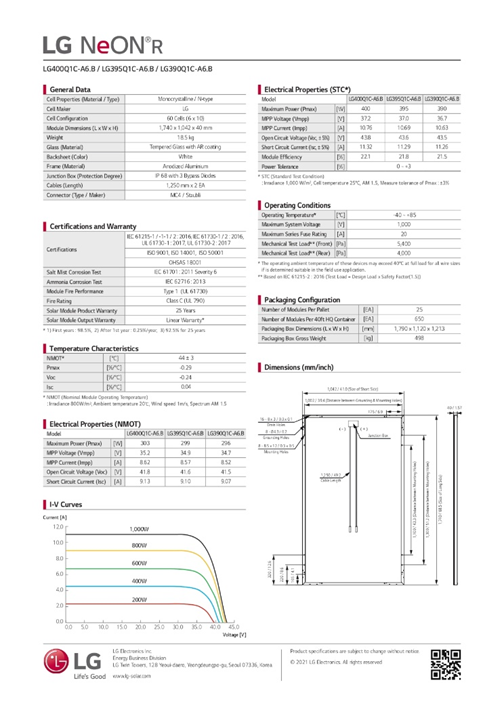
The first page provides you with a general description of the solar panel while highlighting key features.
The second page includes the following technical description with figures:
- Operating conditions
- General data
- Electrical properties
- Temperature characteristics
- Certifications and warranty
- Packaging configuration
Using an LG solar panel — the LG NeONr — we will explain each technical term and highlight the 5-most important ones to guide your choice.
On the first page of the LG solar panel, you’ll find five features:
- The maximum power of the solar panels available in the NeONr series (from 390W to 400W)
- The performance warranty: 92.5% from initial specification after 25 years of use
- The overall product warranty: 25 years
- Highlight the building quality of the solar panel
- Number of solar cells in one solar panel
This is an initial look at a solar panel’s specifications.
From this data, we can conclude that the solar panel is powerful enough (a 400W panel is standard in 2022) and offers a significant performance warranty.
Now let’s dig into the second page and the technical specifications.
Solar Panel General Specification Explained
The general data section provides information on the physical characteristics and dimensions of the solar panel.
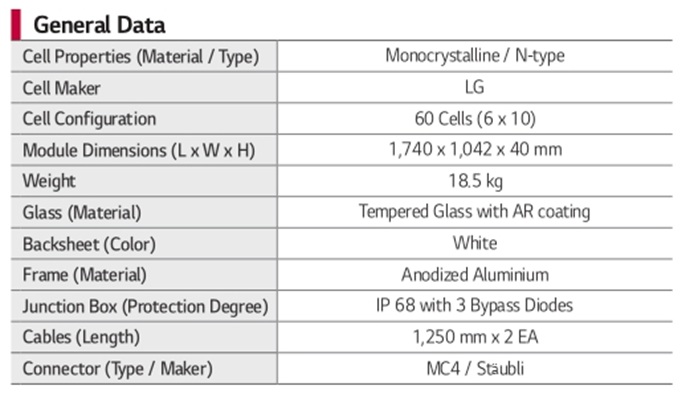
Most Important Specifications
- Cell properties: in this specific case, monocrystalline solar cells;
- Size of the solar panel: module dimensions; and
- Weight of the solar panel.
Solar Panel Electrical Specification Explained
Your solar panel generates electricity under sunlight. Therefore, its electrical properties are the most critical data to consider when evaluating performance.
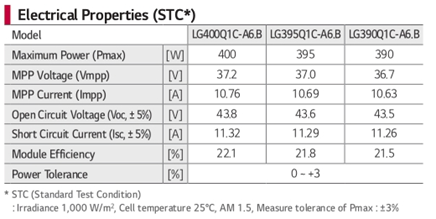
You’ll find electrical properties in the STC (Standard Test Condition) section.
The figures within this section are from tests conducted under perfect conditions. In the real world, such a scenario would include full summer sun (clear sky) at noon and a 77°F (25°C) outside temperature.
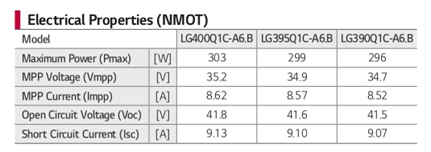
Let’s be honest; these conditions don’t occur very often. For this reason, electrical measurements are also taken at NMOT (Nominal Module Operating Temperature) at a lower solar power.
These measurements give realistic electrical figures reflecting more accurate performance levels.
For example, UNDER STC, the 400W solar panel’s maximum power is rated at 303W.
Electrical Parameter Terms
- Maximum power (Pmax): the highest output power in Watt of the solar panel.
- MPP Voltage (Vmpp): the maximum output voltage when connected to a load.
- MPP Current (Impp): the maximum output current when connected to a load.
- Open Circuit Voltage (Voc): the voltage when no load is connected.
- Short Circuit Current (Isc): the current when no load is connected.
- Module efficiency (%): the percentage of light received by the solar panel converted into electricity.
- Power tolerance (%): all measurements are given with a +/-3% error margin.
Please note: to calculate Max Power (Pmax), multiply Vmpp by Impp. In our example: 37.2*10.76 = 400Watt.
I-V Curves
You’ll find an I-V curve in every solar panel’s datasheet. They reflect the output current and voltage at different levels of sunlight irradiance.
The below example shows 5 curves, each at different solar irradiation power (from 1000W/m2 to 200W/m2).
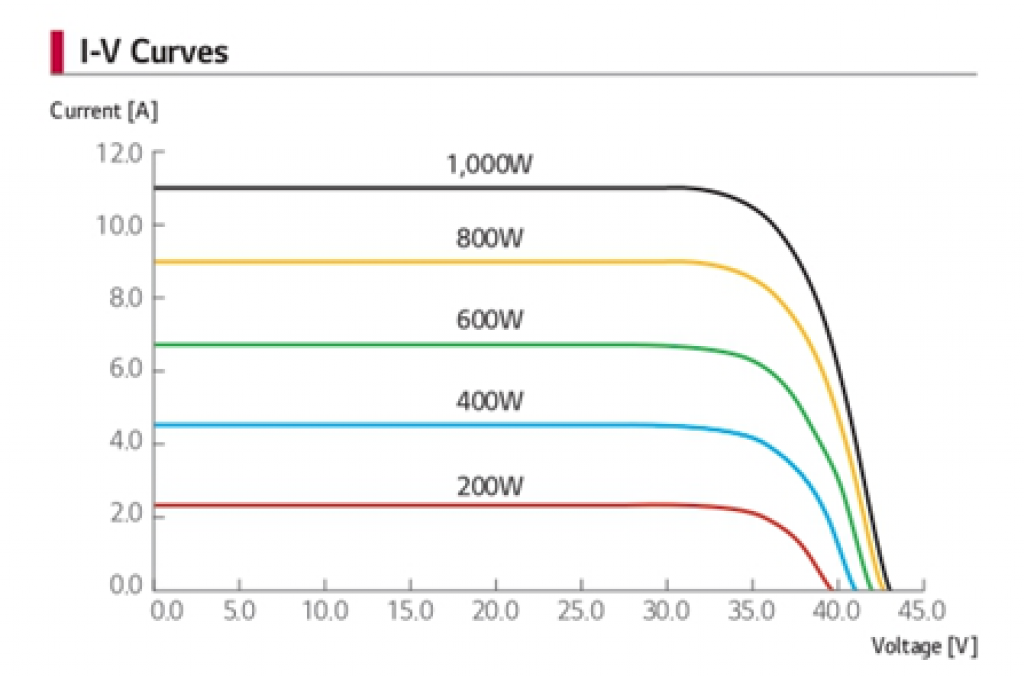
The first one, at 1000W/m2, is for full sun. Then it decreases to 200W, which can be considered relatively cloudy conditions.
What Information Can You Retrieve From These Curves?
Firstly, you’ll learn that solar panels produce electricity even under very low light.
For example, at 200W irradiation, a panel can still produce more than 2.2Amps at 35V, equivalent to 77W power output.
Secondly, a solar panel’s output voltage typically remains constant (35-37V), even under low light conditions. Sunlight power only affects the current output (in Amps).
Additionally, I-V curves help compare how different solar panels of the same power perform under low light conditions.
Related Reading: Solar Panel Output (Average energy output explained)
Solar Panel Operating Conditions Explained
A solar panel is designed to operate outdoors for more than 25 years. Consequently, it has to be robust enough to cope with extreme climate conditions.
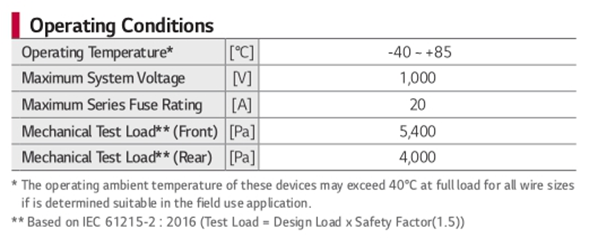
Operating Conditions Terms
- Operating Temperature: the temperature range at which the solar panel can work.
- Maximum System Voltage: the maximum voltage of the system that the solar panel is linked to. The value considers each panel’s voltage if solar panels are connected in serry. In this case, the voltage is 37V. Therefore, a maximum of 1000/37 = 27 solar panels can be connected in serry.
- Maximum Series Fuse Rating: the maximum current that a solar panel can safely handle.
- Mechanical Test Load: the maximum pressure a solar panel (front and back sheet) can handle. Most solar panels can resist hurricane wind speeds and handle up to 6 feet of snow.
Solar Panel Temperature Characteristics Explained
The temperature of a solar panel dramatically affects its performance. As described in our dedicated article, high temperatures (above 25°C) decrease the power output.
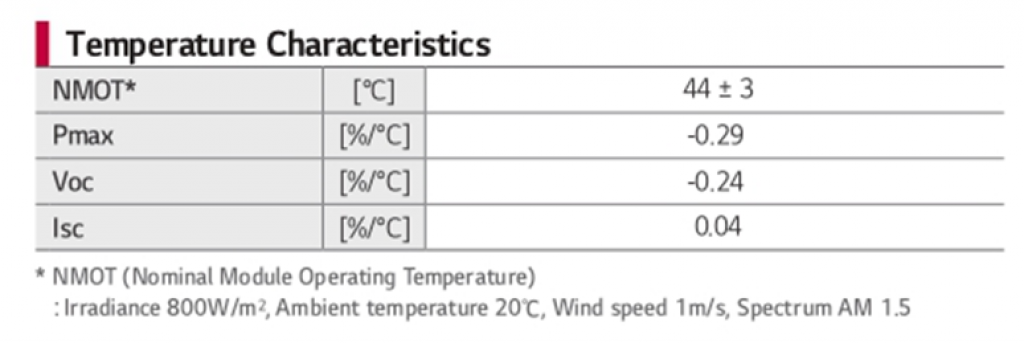
Temperature Characteristics
- NMOT: Nominal Module Operating Temperature, also called NOCT (Nominal Operating Cell Temperature), is the temperature of a solar panel under an irradiance of 800W/m2 and at 20°F (68°C). This is considered the average temperature of your solar panel in a real scenario.
- Pmax: expressed in %/°C is the power output degradation for every increase in °C of the solar panel. For example, if the temperature of your solar panel reaches 44 °C (112°F), this is 19°C (66°F) more than the rated temperature under Standard Test Conditions (STC). Consequently, the Pmax is reduced by: 19*0.29= 5.51%
From 400W, the Pmax is now: 378W.
- Voc: expressed in %/°C is the voltage degradation for every increase in °C.
- Isc: expressed in %/°C is the current increase for every increase in °C.
Please note: a solar panel’s surface can reach 60°C (20°F), which translates into a power output degradation of 10.15% or maximum power of 360W for this 400W LG solar panel.
Solar Panel Certifications And Warranty Explained
Finally, you’ll find the certifications and warranty in a chart like the one seen below.
The two most significant specifications are:
- Solar Module Product Warranty: the total service years of your solar panel (25 years)
- Solar Module Output Warranty: how your solar panel power output behaves over its lifetime
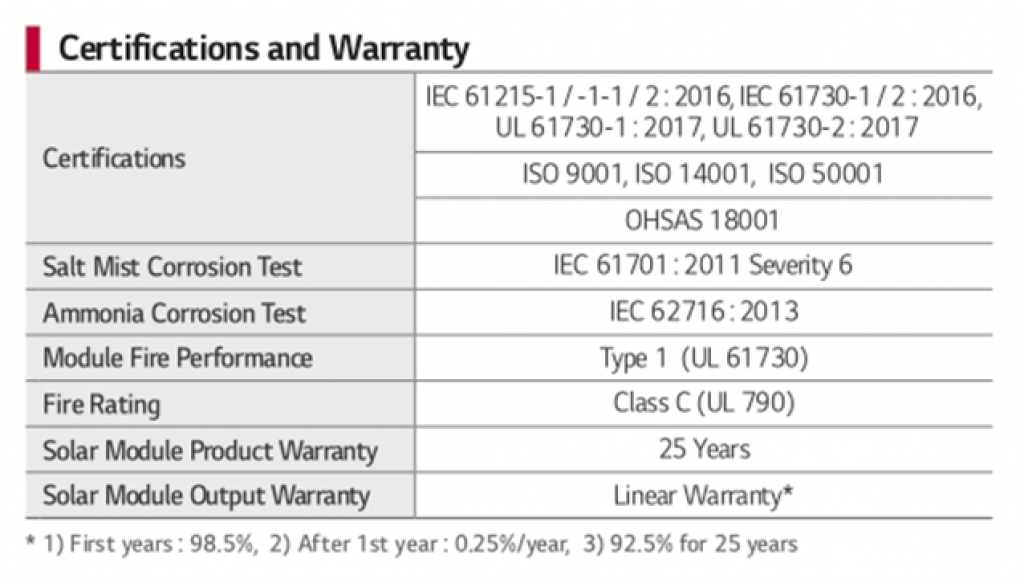
In that specific case, the performances decrease linearly after the first year.
It will drop to 98.5% of initial power output after one year, then decrease by 0.25% every year for 25 years; ending up at 92.5% of initial performances after 25 years of use.
Please note: even after their product warranty expires (25 to 30 years), your solar panels can still produce 92 to 80% of their initial power ratings.
5 Most Significant Specifications For A Solar Panel
We have reviewed all the solar panel specifications, but not all of them are significant.
To help you compare different solar panels, we have listed the 5 most important ones to look out for
- Solar Panel Power: evaluates the maximum power
- Solar Panel Temperature Coefficient: demonstrates the effect of temperature on performance.
- Solar Panel Voltage And Current (Vmpp): helps you see if the values match your solar inverter inputs and design and wire your solar system.
- Solar Panel Size: helps you determine the footprint of your future solar system.
- Solar panel warranty: helps you determine how long your solar system will last for/produce electricity.
Final Thoughts
Solar panel specifications are becoming increasingly complicated. You’ll find countless figures, curves, percentages, and lists of obscure certifications. In this article, we clarified that all of this information is useful to describe your product.
However, only a handful are significant to you, the buyer.
More specifically, we highlighted 5 specifications that should be checked when choosing a solar panel:
- Power output
- Temperature coefficient
- Voltage and Current output
- Size
- Warranty
We guarantee that with these 5 parameters, you’ll be able to compare different panels and choose them wisely.

