Our planet is home to a form of renewable thermal energy that we’ve barely scratched the surface of. There’s so much to learn. For instance — how does geothermal energy work?
Geothermal energy works by harnessing the Earth’s heat to create electricity and heat sources. Power stations generate electricity by using the steam from geothermal reservoirs to run turbines.
We all know that the Earth consists of different layers, with a molten core at the center. The core radiates outwards, warming the Earth between it and us. In fact, the temperature rises by 1° Fahrenheit per every 70 feet towards the center (25° per Kilometer).[1]
These temperatures heat bodies of water underground to produce steam. Geothermal energy captures this steam and uses it to turn turbines that power generators.
Intrigued? Keep reading to find out more!
Table of Contents
How Does Geothermal Energy Work?
Like other fossil-fuel power plants, geothermal power plants use steam to turn turbines. In return, the turbines power generators which create electricity.
For the sake of this article, we’ll be focusing on commercial power generation. However, it’s important to note that you can use geothermal energy to warm your home. By using a heat pump, your home can harness the heat from the ground. Heat pumps are a design strategy of a passive house.
Now, back to how geothermal energy works and how it generates commercial power.
Let’s take a quick look at a geothermal power plant before diving into the details.
First of all, after an underwater reservoir is located, geologists perform some tests. They take samples of the rocks to determine the amount of solubles in the water. These samples also help identify the heat of the reservoir.
After this, drilling commences. Once the drill reaches the reservoir, the pressure forces the water up to a heat pump or turbine. A lot of the water turns into steam as it reaches the surface, turning the turbine and generating electricity.
We can break the method into three parts:
- Locating and rock sampling
- Drilling
- Electrical power generation
Locating And Rock Sampling
It’s not particularly hard to find geothermal vents or water reservoirs. Sometimes it’s as simple as looking for geysers; other times, it’s more complex. Drilling into the earth’s crust and testing temperatures is the most effective way of locating geothermal reservoirs. [2]
Once geologists find a reservoir, the next stage is to test the surrounding rock. First, geologists look at the rocks’ composition and what chemicals or compounds it consists of.
Water is a solvent, and thus the compounds from the rocks often dissolve into the water. The number of solutes in the water will help determine the water’s temperature. It also advises the geologists on the flow rate and how it would affect the machinery.
Some compounds include quartz, tridymite, and chalcedony.
Source: Climatebiz
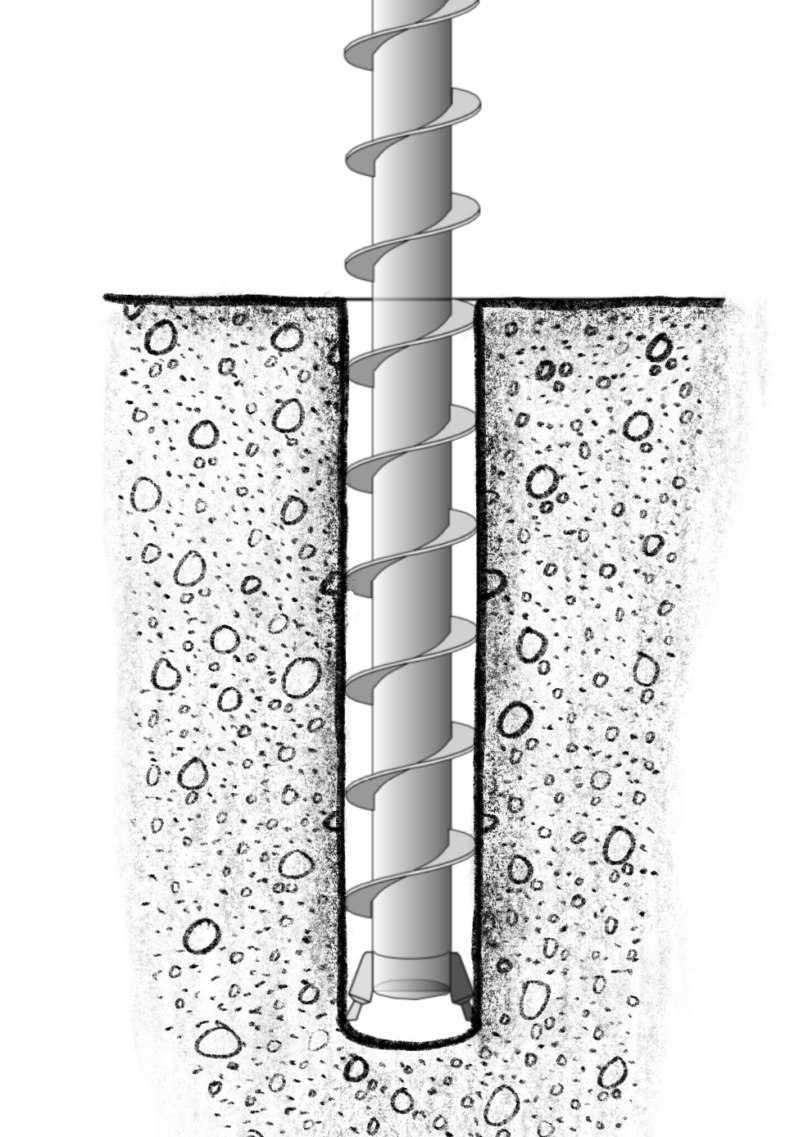
Drilling
The next stage includes drilling into the reservoir to access the water. But, first, engineers build the well, and once they pierce the reservoir, the water shoots up towards the surface.
Geothermal reservoirs can reach up to 360°F (182°C).[3] The water is under an immense amount of pressure while underground. This causes the water to rush through the well and evaporate into steam.
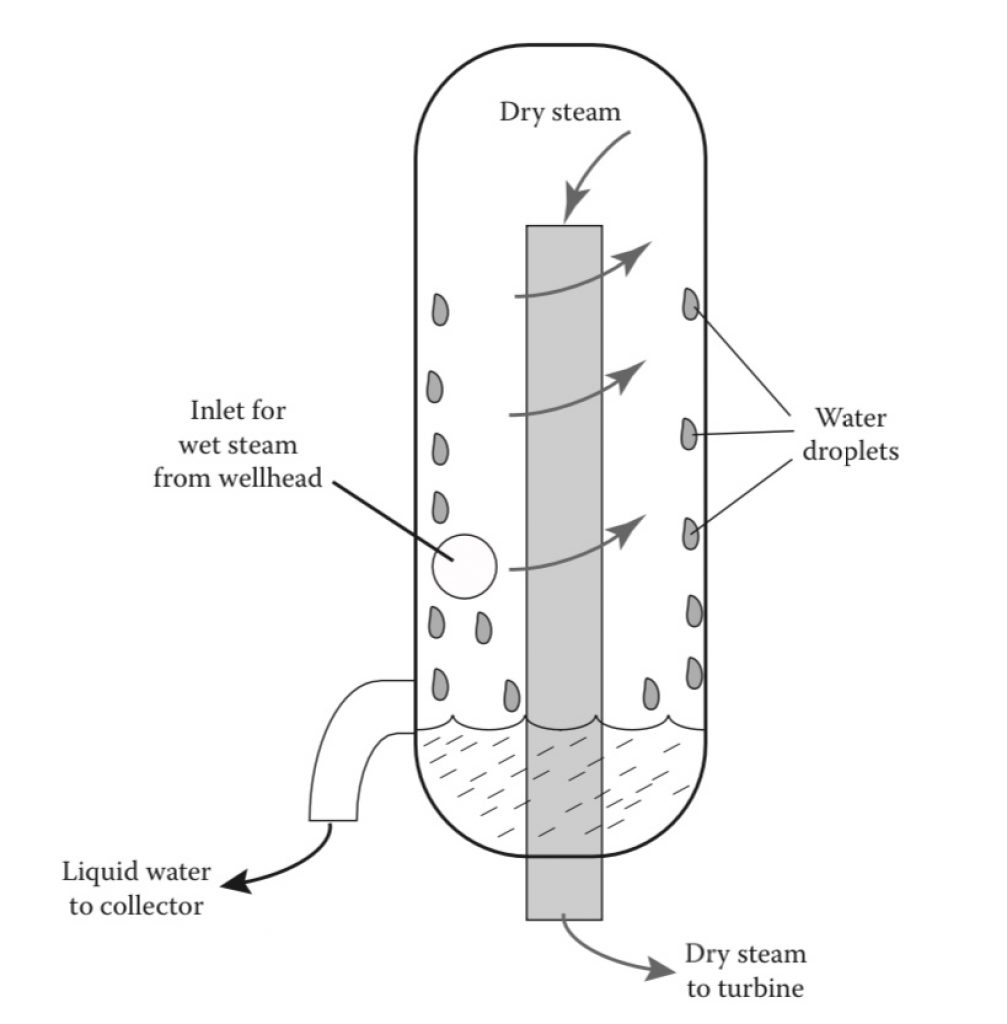
The fluid released from the reservoir consists of high-pressure steam, water, and toxic or explosive gasses.
Because of this, it’s crucial to include blowout prevention equipment (BOPE). In addition, the use of special equipment separates the water and the steam.
The system then directs the steam to the turbines.
Source: Geothermal Energy: Renewable Energy and the Environment
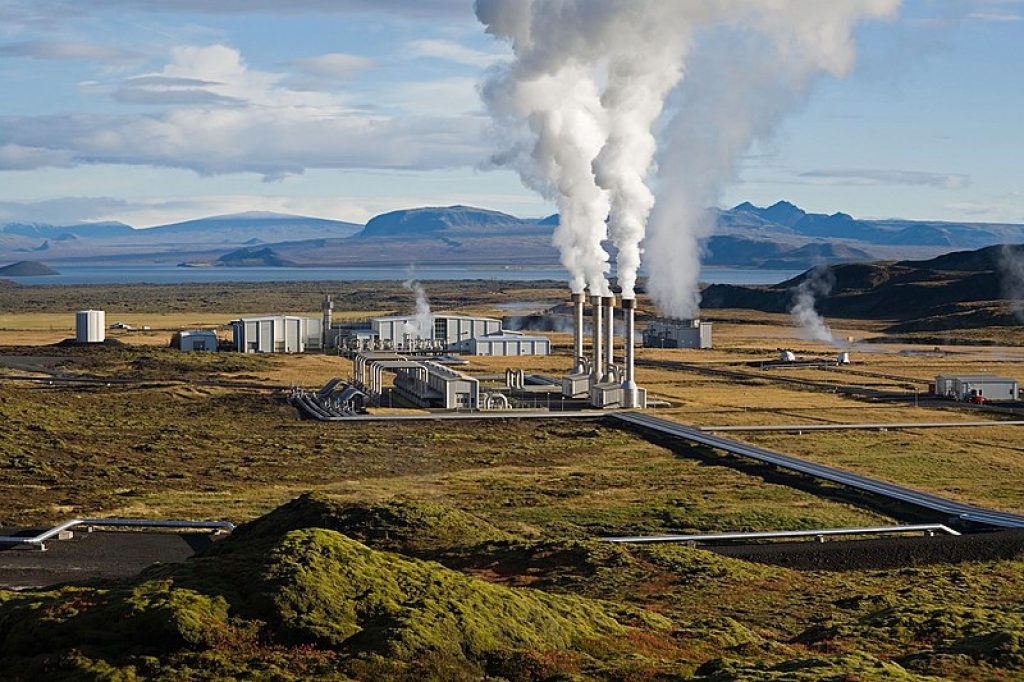
Electrical Power Generation
The steam then passes through the turbines. The turbines spin and turn the kinetic energy into electricity.
Unlike other fossil fuels, no fuel is needed to create the heat to convert the water into steam. And when compared to other alternative energy sources, there is no intermittent production. The baseload for geothermal energy constantly exceeds 90%! [4]

Source: Gretar Ívarsson
How Do We Use Geothermal Energy?
Source: MechDoctor
Since 2002, over 75 countries have been recorded using geothermal energy. Five of these countries use geothermal energy for 10-22% of their electrical needs. [5]
We’re able to use geothermal energy to power generators, heat, cool buildings, and even cook food.
Certain counties like Iceland have taken full advantage of their geothermal hotspots. In 2006, Iceland was producing 322 MWe of electricity. That’s 26% of Iceland’s electrical needs. In addition, 87% of the countries hot water came from geothermal sources.[6]
At the moment, geothermal energy only accounts for 0.3% of the electricity in the world. That’s 49.3 billion kWh/year.[7]
What Are The Advantages of Geothermal Energy?

Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that we can use domestically and commercially. Some of its advantages include reliable energy production, low carbon emission, and sustainability.
“For every kilowatt of electrical energy displaced by geothermal energy, the greenhouse gasses that would have been produced from fossil fuels are reduced by a minimum of 90%. In many cases, they are eliminated completely.“ – Geothermal Energy: Renewable Energy and the Environment.
Three advantages of geothermal energy include:
- Renewable
- Reliable
- No Fuel Required
Renewable
Once the water is pumped through, the power plant reinjects it into the ground. There, the Earth reheats it, and thus we can use the water again.
Some water is lost from the system, like when it escapes as steam. However, seeping water from the ground gradually refills the geothermal reservoirs.
Another important factor to keep in mind is resource reclaim.
The water that runs through the system contains compounds and elements such as silica, zinc, and manganese. These are extracted from the water before it is pumped back down into the Earth.
Reliable
It’s a known fact that solar panels can only generate energy during the day. Most alternative energy sources can only produce power intermittently.
Another example is how wind turbines only work when there is wind or how tidal power depends on ocean swells.
Geothermal energy differs from the rest as it generates energy constantly. This is arguably the most significant advantage of geothermal energy.
The baseload that geothermal energy generates is 90% and up. This means that the geothermal power plant is operating at 90% efficiency, at all times. [8]
No Fuel Required
We all know that conventional power plants require some sort of fuel to create energy.
For example, coal is the fuel source that creates steam in coal power plants. Nuclear power plants split atoms to generate heat.
Geothermal energy power plants don’t require any fuel sources to produce steam. Instead, the Earth acts as the heat source, turning the water into steam.
This means there are barely any waste products produced during the power generation process.
What Are The Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy?
There are always two sides to things in life — geothermal energy is no different.
So while geothermal energy may sound like the ‘power source of the future, it still has disadvantages.
Three disadvantages of geothermal energy include:
- Emissions
- Ground Disturbances
- Mineral Build Up
Emissions
That’s right. Geothermal energy is not 100% emission-free.
Unfortunately, it’s not just H2O that comes out of a geothermal well. CO2 and other harmful gasses escape. These gases, H2S and Mercury, can be detrimental to people in high enough concentrations.
As for the CO2 emission, it’s less than 1% of the CO2 that fossil fuels emit.[9]
Regardless, the CO2 is released into the atmosphere along with the immense heat from the steam.
Ground Disturbances
Unfortunately, ground disturbances can occur when geothermal power plants drill into the water reservoirs. This is the most notable disadvantage to geothermal energy.
Firstly, the drilling can cause seismic activity.
When we consider that most geothermal hotspots are found along fault lines, drilling into the ground seems dangerous.
The drilling won’t cause tectonic plates to shift, but it could cause earth tremors and other seismic events.
Secondly, removing the water from underground can cause ground subsidence.
Think of the geothermal reservoirs as balloons. The water is under a lot of pressure and thus pushes against the rocks around it.
When the drill pierces into the reservoir, the water rushes out. This causes the balloon to default, and suddenly there’s a drop in pressure.
The rocks that are used to this pressure might begin to crumble or collapse.
The movement of the rocks will cause the ground at surface level to sink. This is known as ground subsidence.
Mineral Build Up
We’ve already spoken about the different chemicals and compounds that can be found in the water. But what happens to them when the water turns into gas?
Well, when the water evaporates into steam, the solids are left behind. These solids then build up inside the equipment. This is known as mineral build-up
This mineral build-up will affect the efficiency of the equipment. In worst-case scenarios, the equipment can even break down.
Related Reading: 9 Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy
How Much Power Does Geothermal Energy Produce?
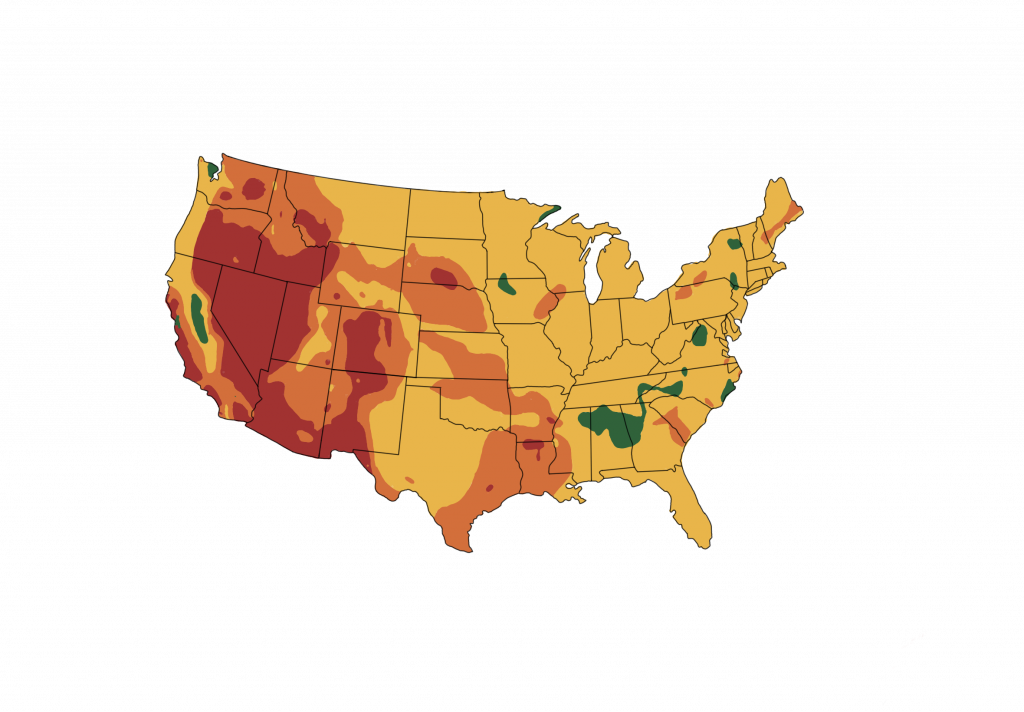
Source: Climatebiz
We’ve just looked at how geothermal energy works and what the pros and cons are. But how much power can geothermal energy generate?
The amount of power will depend on the location of the geothermal power plant. Specific geological sites with higher temperatures will generate more power than others.
These sights are known as geothermal hotspots.
An example of a geothermal hotspot is Hawaii. Hawaii is capable of producing 200MWe of power on a continuous basis.
To put this into context, 1MW can power 190 houses![10] Thus, Hawaii can power 38,000 homes a year.
In Iceland, another thermal hotspot, geothermal energy accounts for 26% of their power and 87% of their hot water![11]
According to this study, the electrical power generated by geothermal energy in 2000 equated to 49.3 billion kWh/year.
Can Geothermal Energy Run Out?

Source: Tara Energy
Unless the Earth freezes over, geothermal energy won’t run out.
Since the heat used to generate steam comes directly from the core of the Earth, geothermal energy won’t run out.
Geothermal energy is 100% renewable and will exist as long as the Earth does!
Final Thoughts
Geothermal energy and how it works is fascinating and sounds like the stuff of the future!
Yet, here it is, in the now!
Some countries depend on it as part of their everyday routine, like Iceland, whilst others are still learning about its potential.
It’s essential to weigh up the pros and the cons. Geothermal energy is renewable and constant yet can have a heavy impact on the environment.
We hope that geothermal technology will only advance and curb the disadvantages of this renewable energy source!

