How do electric cars generate power? How do their motors work, transforming stored energy into a rotary motion? And can the motor create more power through EV tuning?
To answer these questions, we’ve taken a closer look at what EV motors are and how they work. The core elements of an EV motor take advantage of magnets. It’s not magic — instead, the motor is based on simple science (well, kind of).
Over time, humankind has found various uses for magnets, from creating compasses to levitating trains. Now, we’re at the forefront of creating (and constantly innovating) electric cars using electromagnets.
Below, we’ve highlighted the different components of an electric car’s motor and how each one works.
Finally, we’ll explore finer details like purchasing electric motors and their longevity.
Table of Contents
Electric Car Motor Components
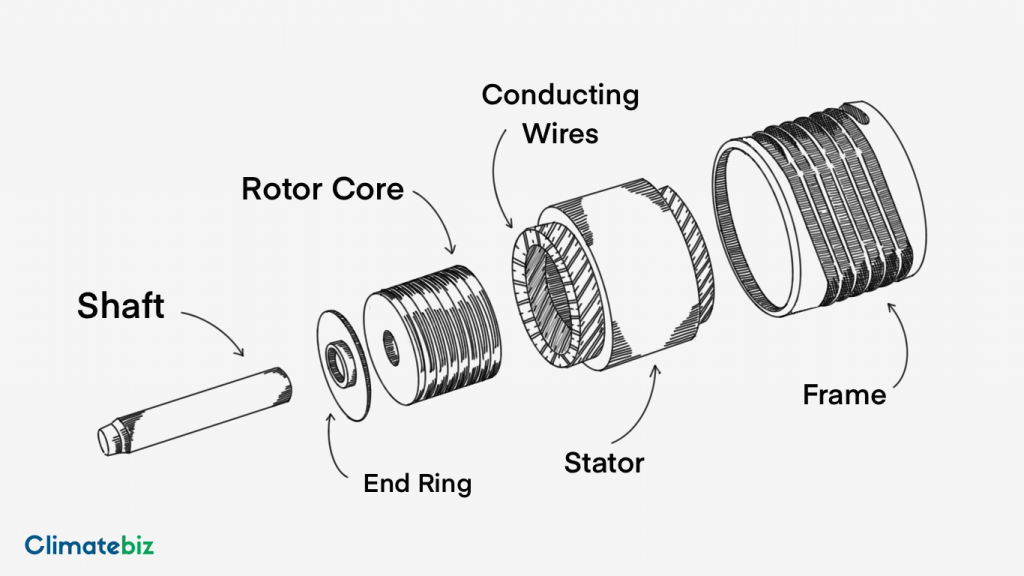
Like all machines and systems, an EV motor consists of different components. For example, the motor can be broken into two main pieces made of smaller parts.
Your average EV motor is a 3-phase, 4-pole induction motor. It uses 4 magnetic poles and converts 3-phase electrical power into mechanical power. For example, a 4-pole motor with a 60 Hz power supply will rotate at 1,800 rpm.
The two main components are the stator and the rotor. Together, they convert the current from the battery into rotary power using electromagnets.
Stator
The stator is a fixed element of the EV motor that generates a magnetic field. It consists of a stator core, conducting wires, and a frame. Remember the electromagnet we mentioned earlier? Well, this is it.
Stator Core
The stator core consists of thin steel rings that are laminated together yet isolated. This forms the frame on which the conducting wires are wound.
Conducting Wire
The conducting wire raps around the stator core — collectively, they form an electromagnet. These wires carry the current from the battery to the stator. A magnetic field is generated when the current moves through the conducting wires.
When the stator core and conducting wires are connected, they’re called field windings.
Frame
The frame is the outer casing that holds the field windings, protecting them and the rotor. This component is also the physical component fixed to the car’s infrastructure.
Rotor
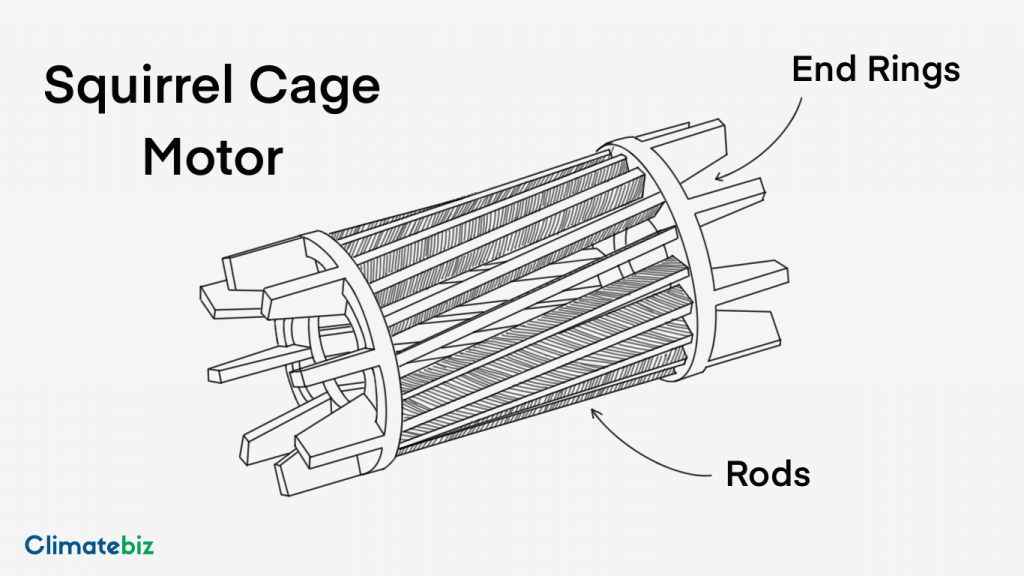
The rotor reacts to the stator’s magnetic field and begins to spin. This component is what generates the mechanical power that’s used to turn the wheels.
The rotor consists of a rotor core, conducting rods, and end rings. Then, the rotor is inserted into the stator and enclosed.
Rotor Core
The rotor core is the component of an EV motor that has the shaft running through it. When the rotor spins, so does the rod, turning the car’s gears.
The rotor core consists of thin round layers of alloy steel laminated together. On the outside of this cylinder are grooves that run diagonally around the core.
When the ruts run diagonally, we call it a squirrel cage rotor. Most 3-phase 4-core motors have squirrel cage rotors.
Conducting Rods
Conducting rods are inserted along with ruts, running diagonally through the core. They’re generally made from aluminum or copper. These rods form a secondary circuit that will interact with the stator’s magnetic field.
End Rings
Rings cap off the rotor core and connect the conducting rods, which causes them to short-circuit. Because the rods short-circuit, they form multiple loops. Each loop is affected by the magnetic fields of the stator and its push-pull effect.
Together, all these components cause the stator to have a torque effect on the rotor, causing it to spin.
How Does An Electric Car Motor Work?
Now that you know how each component fits together, how do they work as a hole? How does EV tuning allow for a more substantial power output by increasing magnetic strength and current?
How Do The Components Work Together?
The conducting rods of the motor run diagonally to distribute the magnetic field. The f
While we’re no mechanics, we can understand the science behind an electric motor. This section will explain how all the components come together in harmony to power your EV.
Generating A Magnetic Field
Current flowing through a wire generates a magnetic field. This field flows perpendicular to the wire, from north to south.
An EV motor takes advantage of this — using magnets to turn the rotor. When two wires are placed close to each other, the electromagnetic field will induce a current in the second wire. As a result, the second wire (the conducting rod of the rotor) gains its own electromagnetic field.
In the case of an electric car, the stator draws power from the car’s batteries, creating its electromagnetic field. This field extends to the rotor conducting rods, which generate their own magnetic field.
When the wires are coiled, the magnetic field is increased. That’s why the conducting wires of a stator or wound around its core — this is the same reason why the conducting rods short-circuit.
The stator pushes and pulls the rotor by creating alternating current and magnetic fields. The rotor’s south pole is pushed away from the south pole of the stator and attracted to its north pole.
Turning Magnetic Fields Into Mechanical Power
The conducting rods of the rotor run diagonally to distribute the magnetic field. The field extends over multiple bars, preventing the rotor from getting stuck between alternating phases.
Here’s where the 3-phases of currents come in. Because its phase induces its own field, it keeps the rotor continuously turning. So phase 1 would push the rotor’s pole away, while phase 2 would attract it.
On average, this causes the rotor to turn at 1,800 rotations per minute. That’s nowhere near enough time to turn your car’s wheels at speed. So, the vehicle uses gears to increase the rotation speed, allowing the car’s wheels to turn faster.
What Is EV Tuning?
You can tweak the performance of each component of an electric vehicle. By improving the performance of the battery, motor, and inverter, we can gain more power from the system. This is what we call EV tuning.
While we can go into tuning each of these components, we’ll focus on the electric motor. After all, we’re investigating how the motor works.
Tuning An EV Electric Motor
One step you can take is to close the gap between the stator and the rotor. The closer these two components are, the more efficient they’ll be. As a result, your rotor will spin faster, generating more mechanical power. However, this does have some adverse effects, which we will touch on later.
Adjusting the hardware of your EV can also generate more power, such as choosing higher conducting wires. Better conducting wires will supply more current to the stator. The more current available, the faster the rotor will turn.
EV Tuning Restrictions
There are a few factors that limit power generation in an electric motor. For example, these motors already generate a lot of heat – that’s why their frames are designed for cooling.
This is a limitation as generating more power will increase the heat generated. Because of this, there won’t be sufficient cooling without an air gap between the rotor and the stator. The last thing you’d want is your motor to burst into flames.
Another thing to keep in mind is that all wires have internal resistance. Most times, you can swap these out, but in the end, it’s a limitation that will always be there.
Can You Buy An Electric Motor For A Car?

Source: Core77.com
There are multiple electric motors on the market — the hard part would be choosing the right one.
A simple google search will bring up multiple articles on how to make your car electric. It’s possible to retrofit your current car and install an electric motor, switching you from petrol to electricity.
Of course, this includes stripping your current system and installing batteries, control systems, and an electric motor. It’s no easy feat, but it’s possible.
Multiple electric motors are available. In fact, electric motors are used for more than just EVs. For example, pumps, elevators, and rainwater systems use induction motors.
You’d have to choose the right 3-phase 4-pole system for your power requirements. Luckily, it’s possible to tune your motor, as we’ve just mentioned. EV tuning will give your car more power and create an efficient system.
Ford Eluminator
Ford has made its Eluminator E-Crate Motor available to the public. This EV motor will be able to power most vehicles, even pick-ups. It has a peak power of 210 kW and a maximum speed of 13,800 rpm. You can find out more on Ford’s website.
How Long Do Electric Car Motors Last?
There are two ways of measuring how long an electric motor lasts:
- By measuring the motor’s lifespan in miles.
- By counting in years.
With our current technology and EV tuning, the average electric motor lasts 200,000 miles. That’s almost long enough to drive around the world 10 times or from LA to NYA 71 times. However, this isn’t much different from a combustion engine. The biggest benefit? An electric motor requires almost no maintenance.
We’ve drawn up a quick table to compare the lifespan of popular EV models in 2022:
| EV Model | Motor Lifespan in Miles |
|---|---|
| 2022 Tesla Model 3 | 500,000 |
| 2022 Chevrolet Bolt | 400,000 |
| 2022 Kia Niro | 200,000 |
According to the U.S. Department Of Transportation, the average American drives 14,263 miles per year. So we can then calculate how many years an electric motor would last.
| EV Model | Motor Lifespan in Miles |
|---|---|
| 2022 Tesla Model 3 | 35 |
| 2022 Chevrolet Bolt | 28 |
| 2022 Kia Niro | 14 |
In conclusion, you can expect a lower-end EV motor to last 200,000 miles/14 years. However, despite this average, most EV manufacturers guarantee 20 years.
How Much Do Electric Car Motors Cost?
For a 3-phase 4 pole induction motor, you can expect to pay anywhere between $385 and $959. These prices all depend on the kilowattage produced.
For example, a 1.5kW electric motor will cost $385, while a 5.5kW motor will cost $959.
Averages
Let’s talk averages. In general, your car will probably need a 2.2kW induction motor. These go for $489 on average, depending on where you buy them and their suppliers.
Now, let’s look at Tesla’s engine prices. An electric motor from Tesla can cost between $15,000 and $20,000. Again, this is specifically for the Model S and X.
On the other hand, the Eluminator E-Crate Motor we mentioned goes for $3,900. That’s a considerable price gap.
EV Tuning And Retrofitting
It sounds tempting to go for the average induction motor, right? Well, while the motor is much cheaper, the conversion of your vehicle won’t be.
Conversion and tuning your electric car will cost an additional $6000 for the parts. You can also expect to pay between $1000 to $2000 for miscellaneous costs while installing your components.
At the end of the day, this option is still cheaper than buying a brand new EV. Just keep in mind that you should do extensive research into which induction motor is best for your car.
If you’re still unsure, contact an EV mechanic for a consultation.
Final Thoughts
Electric motors are pretty complicated but brilliant machines. While the technology has been around for years, it’s incredible to see the current leaps in development.
We’re excited to see what the future holds for electric cars because, in our opinion, the best is yet to come~
Should you have any further insights or opinions on this matter, please feel free to join our community!

