Ever-present and evergreen, the eastern red cedar tree is known for its hardiness, beauty, strength, and size.
These luscious, dense conifers are fast growing and can be found from Canada to Florida, even crossing Texas.
But interestingly enough, the cedar tree isn’t a real cedar; it’s actually a Juniper species.
Despite that, these gorgeous trees have proven to be excellent sources of medicine and valuable tools in cultural practices.
This article teaches you what there is to know about this tree species, where they occur, their growth, and what precautions to take when planting them around your home.
Table of Contents
What Is An Eastern Red Cedar Tree?
The eastern red cedar (scientific name Juniperus varginiana) is commonly known as the Red juniper.

Source: Atlanta Journal-Constitution
This tree is a type of conifer species and is of small to medium size; it can develop up to a staggering 50 feet.
How does it look? You can’t miss the bark, typically light reddish-brown, thin, fibrous, and shreddy.
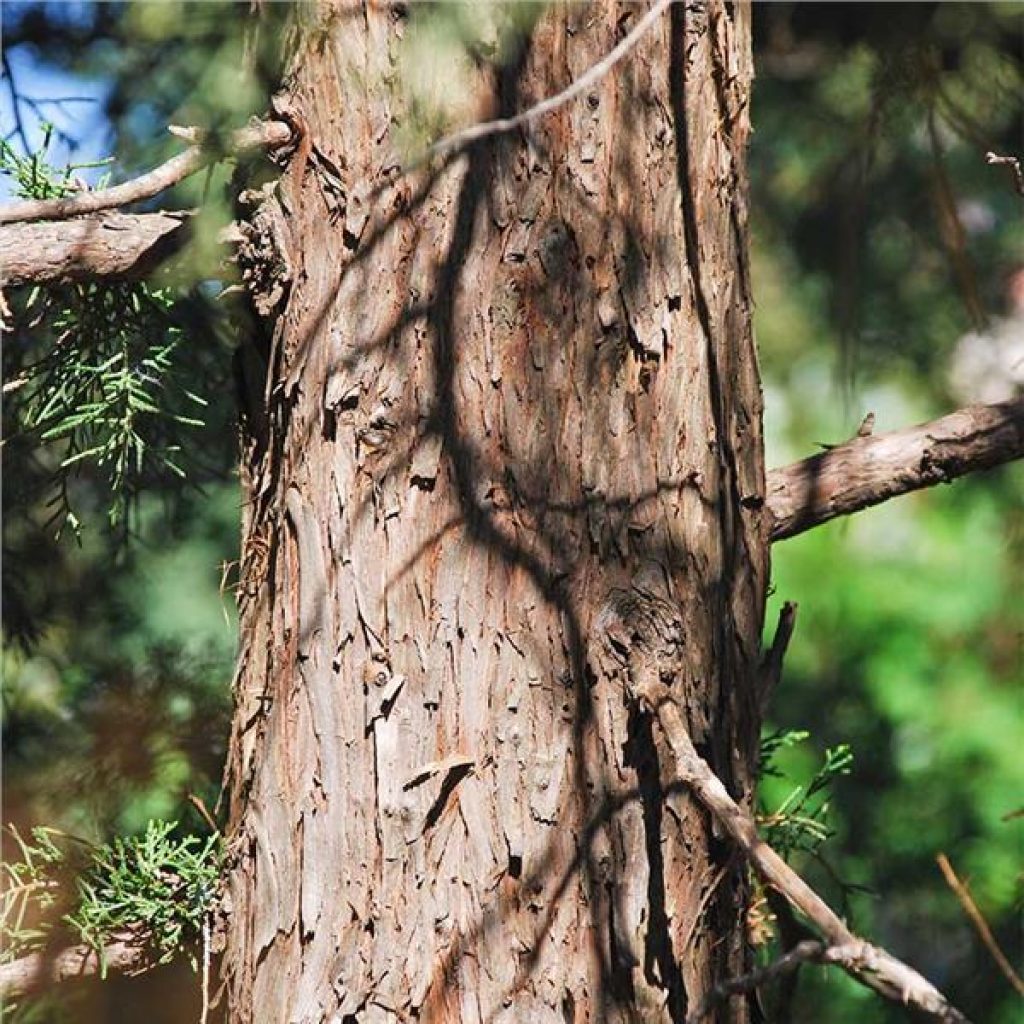

The heartwood of the tree is dark with a slightly purplish red. It turns to a dull red or reddish-brown, and the sapwood is whitish in color.
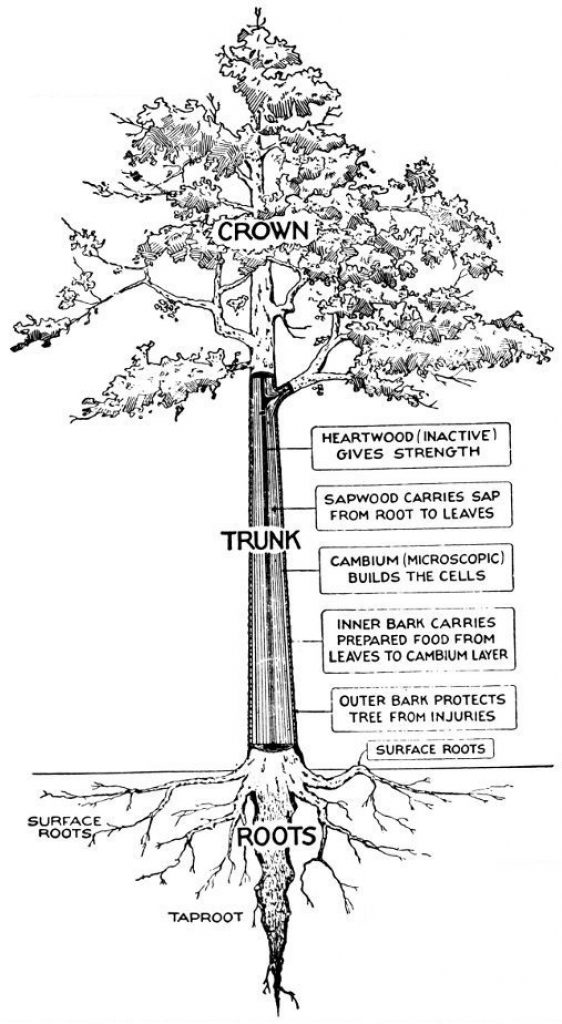
Source: Project Gutenberg
The wood is non-porous (so it’s pretty tough), has an even texture, is moderately heavy, and is quite resistant to decay.
Beautiful greenery is a hallmark of this tree, courtesy of its leaves. The leaves are skinny, often described as needle-like, and feel spongey to the touch.
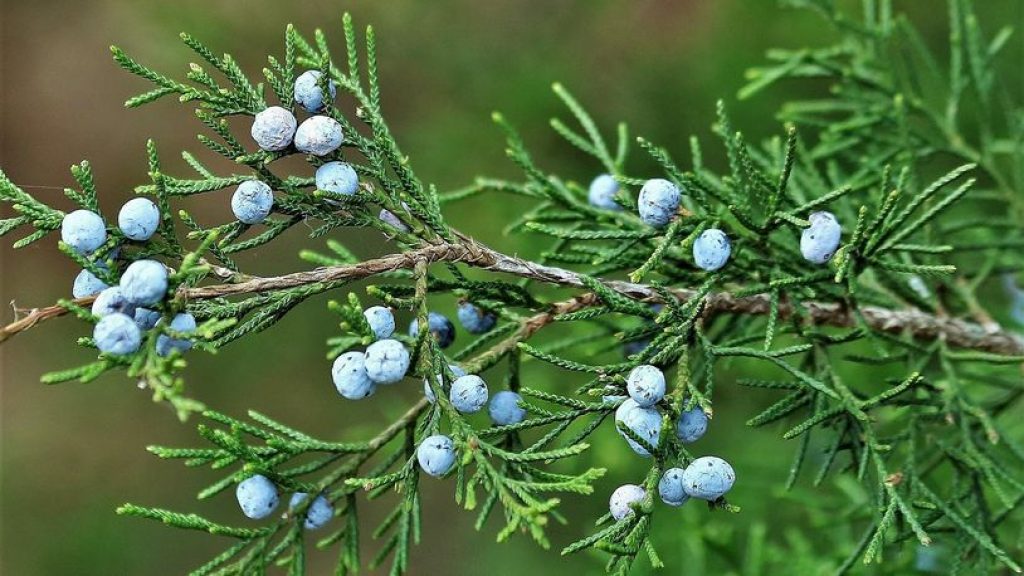
The eastern red cedar is dioecious, meaning that male and female reproductive organs are present on separate plants. The male flowers are smaller and lighter in color, whereas the females carry brighter blue flowers.
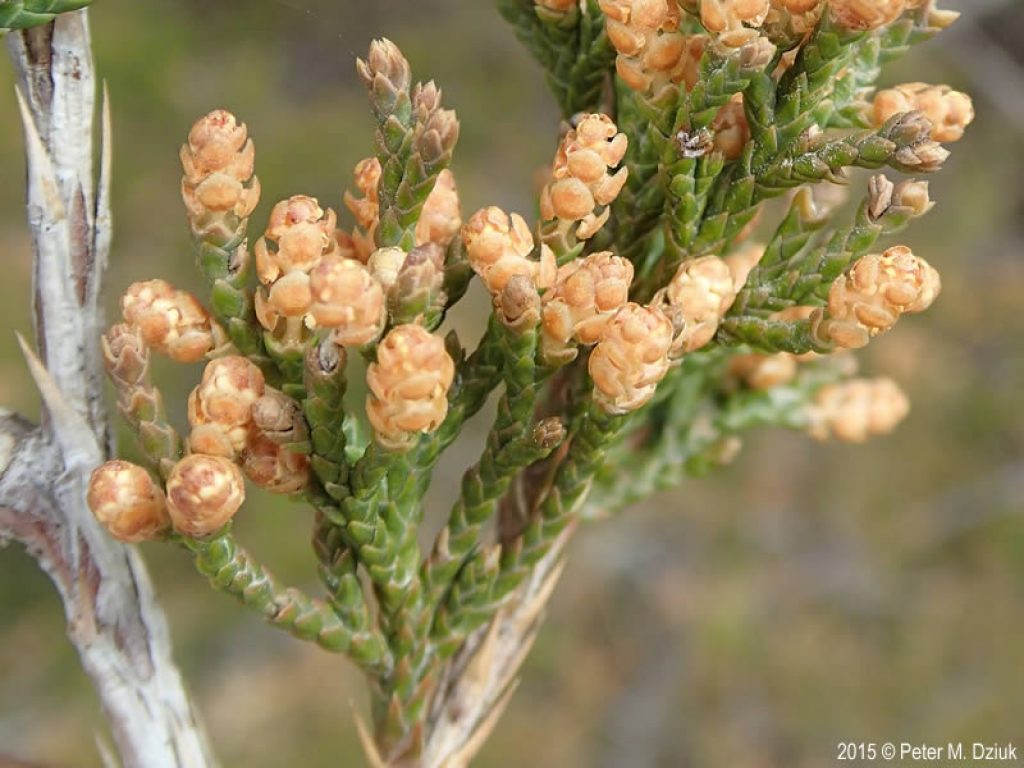

Source: Minnesota Wildflowers
The seeds are present as round berries and are dark blue in color; they generally don’t grow longer than 8cm.
The eastern red cedar tree grows on various land sites all through the eastern side of the USA, including Illinois, Iowa, Oklahoma, and Mississippi.
Where Do Eastern Red Cedar Trees Grow Best?
The eastern red cedar tree has a pretty broad natural distribution, pointing to its ability to develop under various climatic conditions. In other words, the tree is hardy to the harsh cold and the sun’s unforgiving rays!
Moreover, the eastern red cedar grows in a wide range of soils, ranging from wet, marshy land to dry stone outcrops; these lush trees endure soil pH levels from 4.7 right up to 7.8.
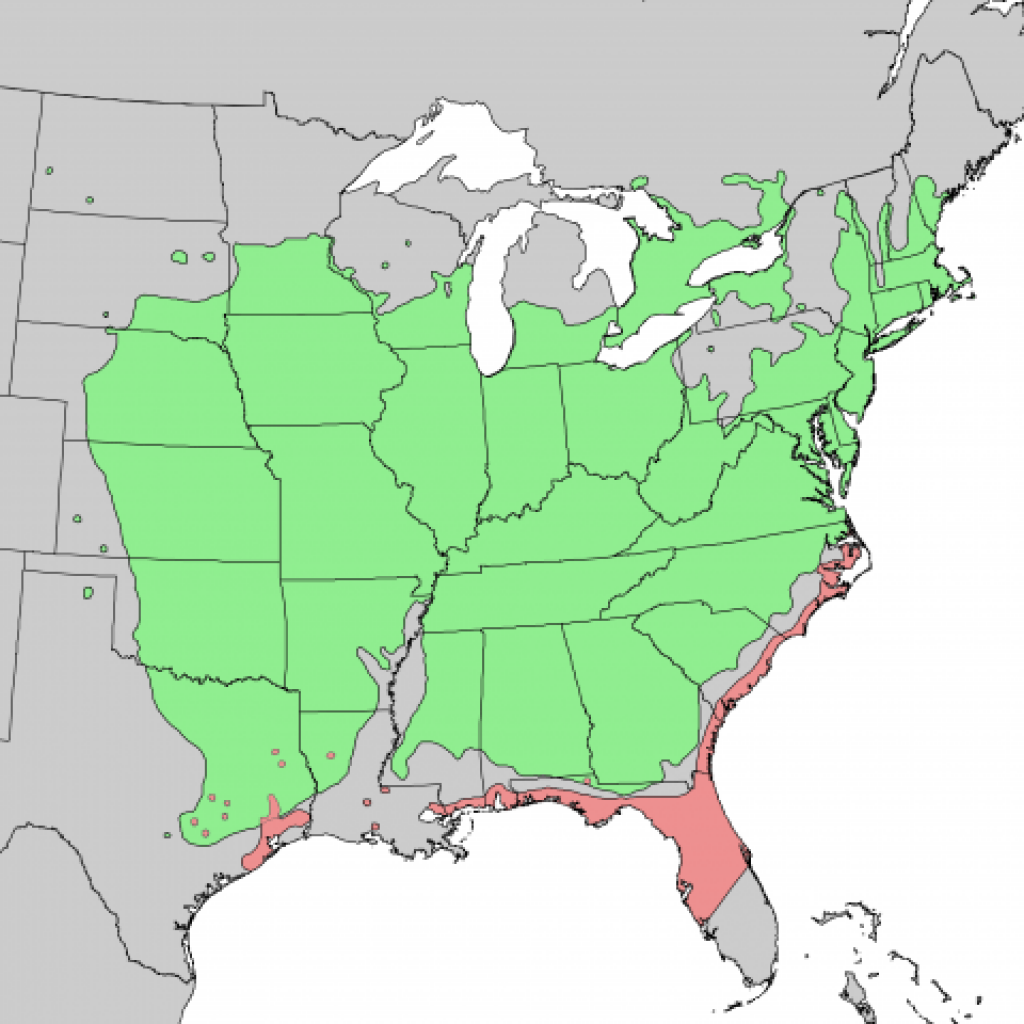
Source: Lake forest college
Location-wise, you can expect to find the eastern cedar tree from Canada to Florida and even Texas.
It is native to the eastern parts of The U.S. and Canada; its distribution spans Nova Scotia to Ontario and through the northern Great Plains. It then ranges from Texas to Florida. You can also expect to see it on the Atlantic coast.
But the best growth occurs throughout the limestone outcrop areas in eastern Iowa, right across to the drier regions in the west!
How Fast Do Eastern Red Cedar Trees Grow?
Male trees grow quicker than pre-productive females before becoming viable for reproduction (also known as cone advancement).
Since males start cone advancement at 4 years and females at 10 years, it initiates the growth of crowns that stretch out over the thick covering of early growth conditions. This dynamic leads to much greater pollen dispersal and increased growing ability.
Because of their later cone advancement, females are often taller at the time of primary reproduction, but that doesn’t mean they grow faster!
How Tall Do Eastern Red Cedar Trees Grow?
Research in Oklahoma found eastern red cedar developed to 6.5 feet (in the east) over 8 years. The trees reached the same height over 10-14 years in western Oklahoma.
A slightly older tree of about 28 to 29 years old ranges from 20.3 feet to 27.2 feet.
What Are The Benefits Of Eastern Red Cedar Trees?
The eastern red cedar is a local species that benefits natural life, depending on its regional population density.
Wildlife
The thick strands of eastern red cedar provide excellent getaway cover for a range of natural life!
In fact, there are about 71 vertebrate species, including opossums, raccoons, foxes, wildcats, donkeys, white-tailed deer, coyotes, cottontail hares, and wild hogs, that use the eastern red cedar tree as a protective territory.
Birds such as cedar waxwings, robins, ring-necked fowls, mockingbirds, blue jays, northern cardinals, crows, and starlings, eat from the tree and are huge role players in dispersing eastern red cedar seeds.
This process takes place in their digestive systems — yes, through poop!
Humans
According to the United States Department of Agriculture, the eastern red cedar is incredibly useful to humans.
Here, you’ll find some of the uses relative to parts of the tree:
| Component | Uses |
|---|---|
| Boiled red cedar tree leaves | Used to treat arthritis and rheumatism |
| Seeping of red cedar tree leaves | Often used to treat a sore throat and persistent coughing |
| Preparations made from the leaves and roots, as well as the berries | Used to treat asthma and to control various types of bleeding |
| Distilled oil made from the red cedar tree | Used in pharmaceuticals in the United States |
| Red cedar tree bark | Used for infrastructures such as making mats and beds |
Other Uses
Eastern red cedars act as phenomenal windbreakers, visibility screens, and mulch.
How so?
Trees acting as windbreaks help lessen wind-induced disintegration, particularly for energy structures.
Planting them for use as visibility screens helps prevent wandering eyes from peering into your property or place of work.
Finally, the eastern red cedar is often cut for mulch, used in landscaping projects, and chipped for its usefulness in power plants.
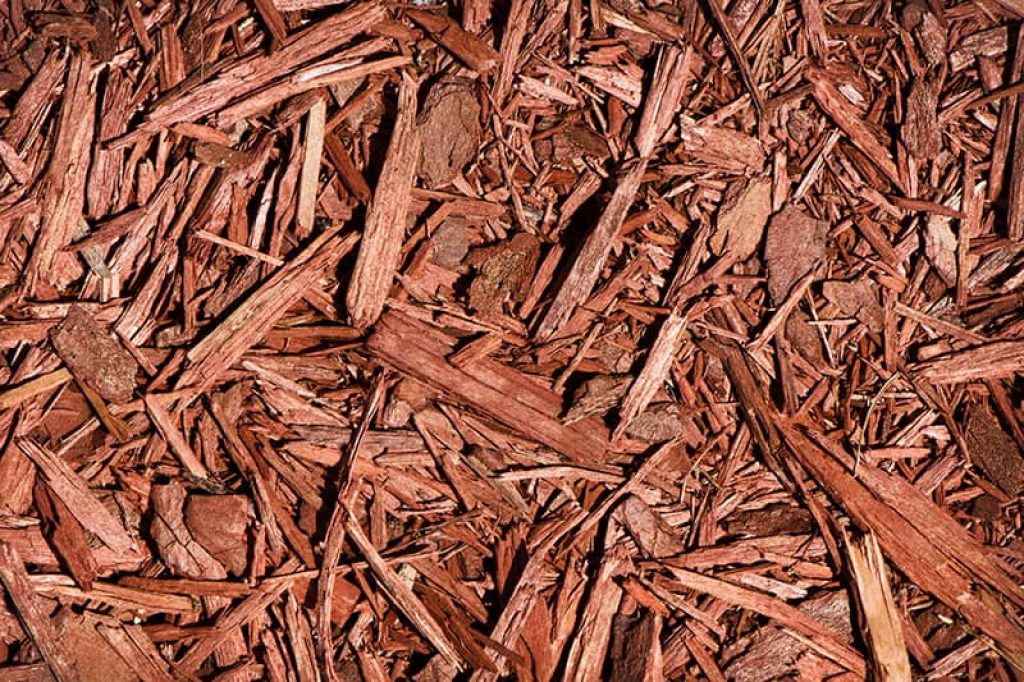

Source: Trees.com
Do The Roots Of An Eastern Red Cedar Tree Grow Deep?
It’s all about searching for assets when it comes to the roots of an eastern red cedar tree!
The tree’s root structure forms to access the best nutrients and water possible.
In saying that, there are expected patterns in tree root growth in specific environments.
In higher sloped areas, tree roots tend to be excessively longer and bigger and slope upwards, whereas down-sloping deeper roots are seen primarily in drier regions.
This phenomenon is commonly referred to as a positive hydro-tropic reaction.
How Long Do Eastern Red Cedar Trees Live For?
The eastern red cedar tree only reaches sexual maturity after about 10 years. When they reach 60 years, they are often harvested for saw timber.
Untouched, these trees often live to about 150 years old, but some trees live to be older (around 300 years old).
According to Towson University, the oldest of these trees is rumored to be a whopping 940 years old and occurs in West Virginia.
Determining Age
You can determine the age of a tree down in a few different ways. These include:
- The girth of the tree (uncut trees): the girth of a tree generally grows just under an inch (2.5 centimeters) per year. This means you can measure the girth and calculate the age.
- Tree rings (cut trees): to do this, you need to look at the cut portion and count the dark rings. You can start in the middle of the cut stump and count from the first dark ring you see. Continue to do this, moving outwards from the middle right until you reach the last dark ring on the edge. The end number of dark rings you have counted shows you the tree’s age in years.
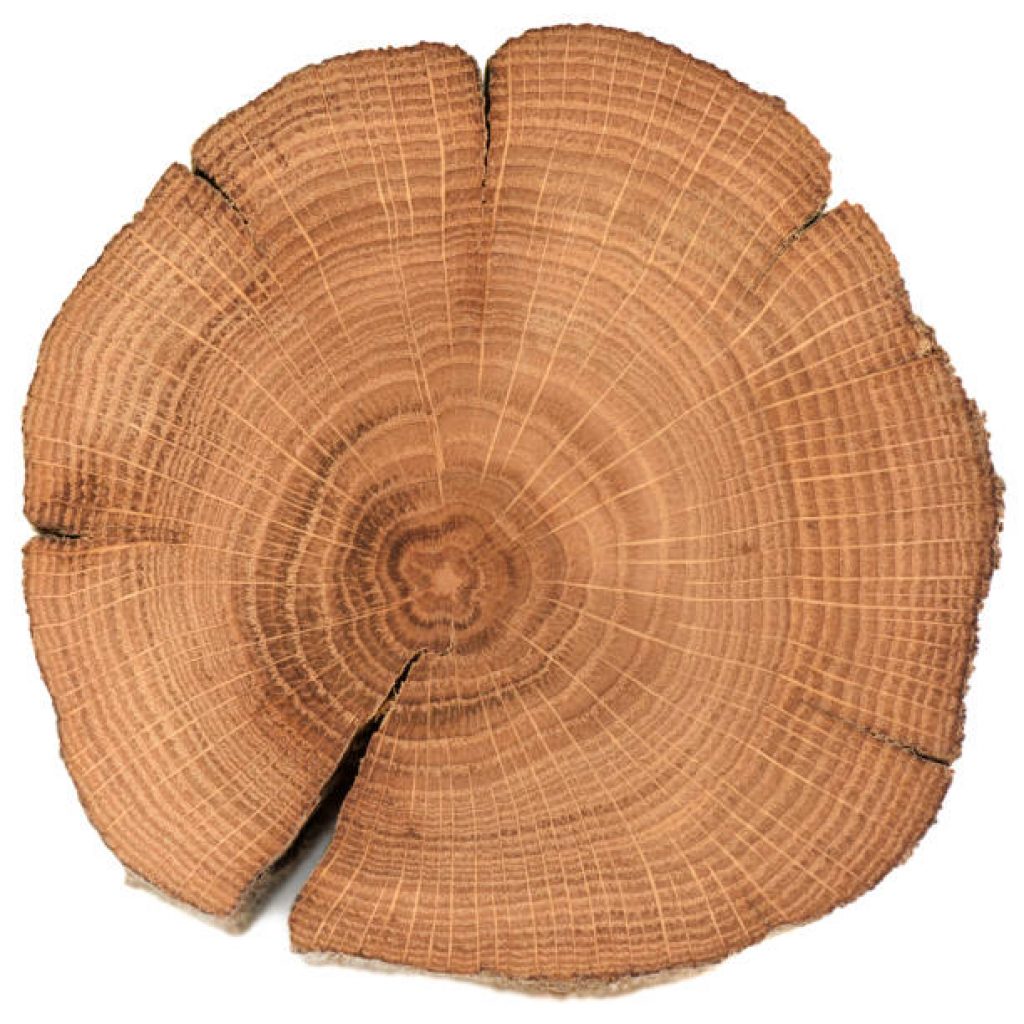

Source: iStock photos
How Close To My House Can I Plant An Eastern Red Cedar Tree?
Whether you live in a brick home or a pre-fab structure, there is no direct guideline on how close you should plant your eastern red cedar tree to your house.
However, the Virginia Native Plant Society recommends that you plant them at least 5-6 feet away from your home or any other structure — they are fast growers!
It also depends on where your home is situated. How so?
The geology of where you live greatly influences how the tree grows.
More specifically, the root structure of the eastern red cedar wood changes depending on the conditions of the soil under your house. If the soil is shallow and rocky, the roots of the eastern red cedar tree will be more spread out.
Generally speaking, it’s not recommended that you plant the tree too close to your house or fence; it will limit its natural growth!
Final Thoughts
The eastern red cedar tree is an old gem, that’s for sure!
These trees have a vast history of medicinal and cultural uses and serve as important role players in wildlife activities.
When growing the tree on your property, you must plant it at least 5-6 feet from the closest structure because of its eagerness to grow!
These dense conifers offer many uses around your home, from wind breaking to preserving nature.
The hardiness of the trees makes for quite an effortless growth indeed!
If you want to share your thoughts or ask us a question, please feel free to reach out to us in the comments section below! Alternatively, visit our forum and share your opinions with us!

