How do solar panels work — what is the step-by-step process?
The science of solar energy can be perplexing to some.
How exactly do solar photovoltaic (PV) panels magically transform ordinary sunlight into usable electricity? Well, when you dig a little deeper and dissect the panel (quite literally), you’ll find that it all starts to make a bit more sense.
This article aims to uncover how solar panels work and what benefits using solar energy can have on our planet.
Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
Brief History Of Solar Panels
The solar panel’s humble beginnings can be traced back over 100 years.
Years ago, solar energy’s primary job was to help with the production of steam (hello industrial revolution) to power machinery.
It wasn’t until Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect that sunlight would start being converted into solar electricity.
Becquerel’s discovery led Charles Fritts to invent the world’s first genuine solar cell in 1893.
In 1941 an American inventor known as Russel Ohl patented the first silicon solar cell. Ohl’s invention led to the very first solar panel being invented in 1954.
Solar panels unsurprisingly found their first job far away from earth, way up in space in satellites.
Perhaps you remember your first encounter with solar panels; it was likely to be the one embedded in your new calculator!

What Is A Solar Panel?
A solar panel comprises 6 different elements:
- Silicon solar cells
- Metal frame (typically aluminum)
- Glass sheet for protection and casing
- Standard 12V wire
- Bus wire
- Plexiglas
Silicon solar cells are the main component of a solar panel and are responsible for converting sunlight into solar electricity.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
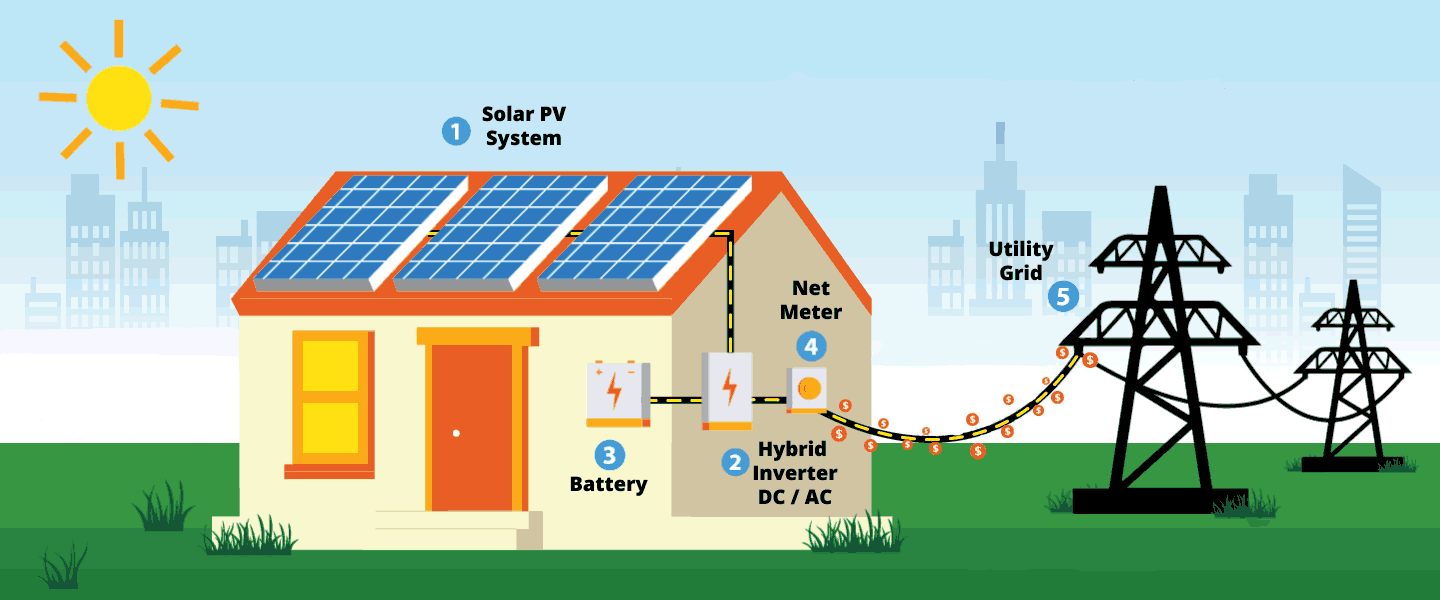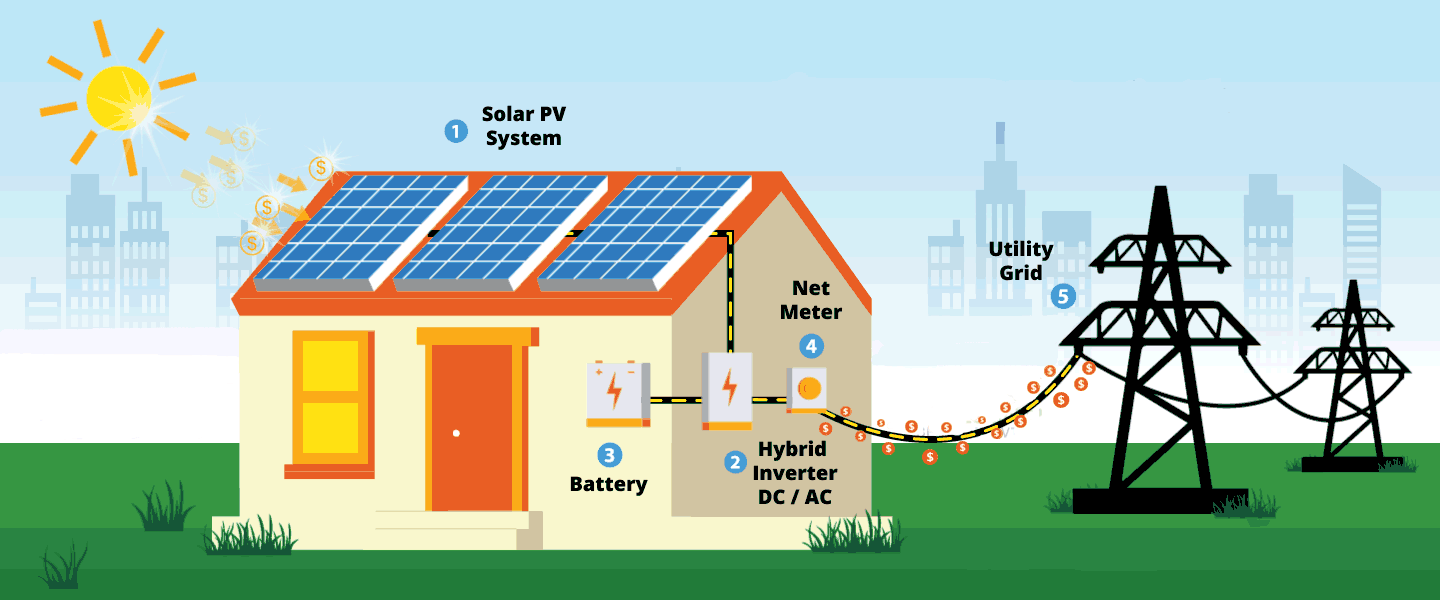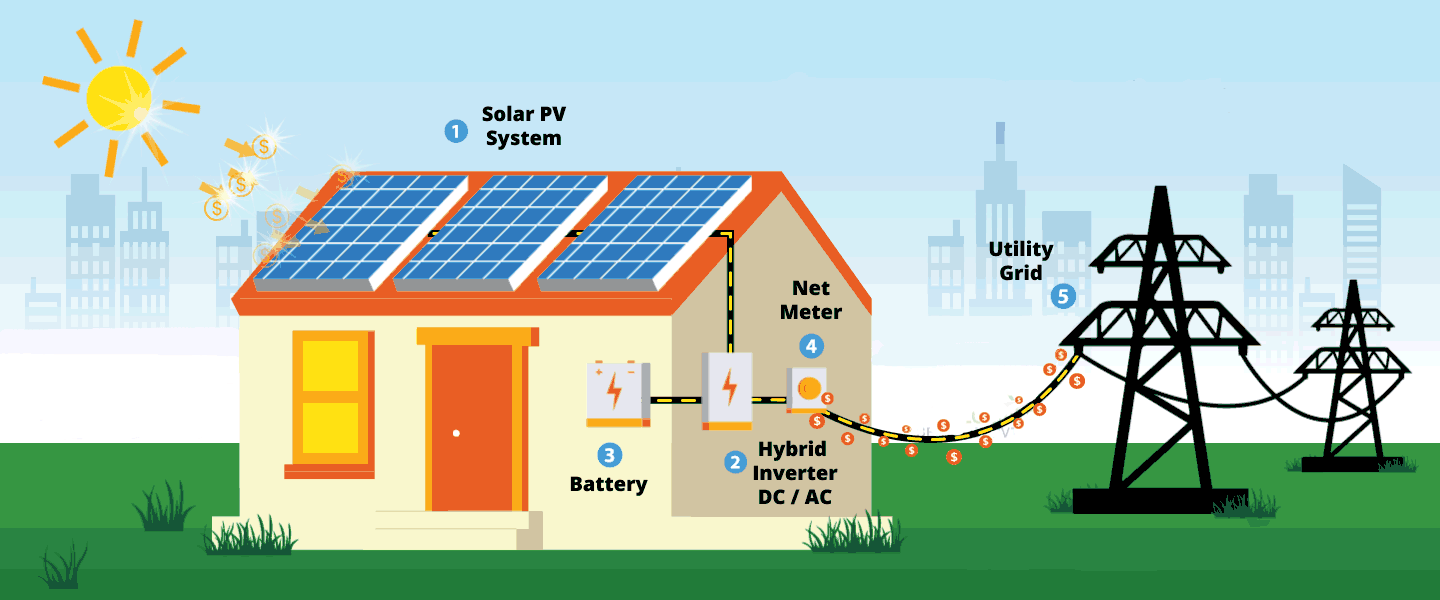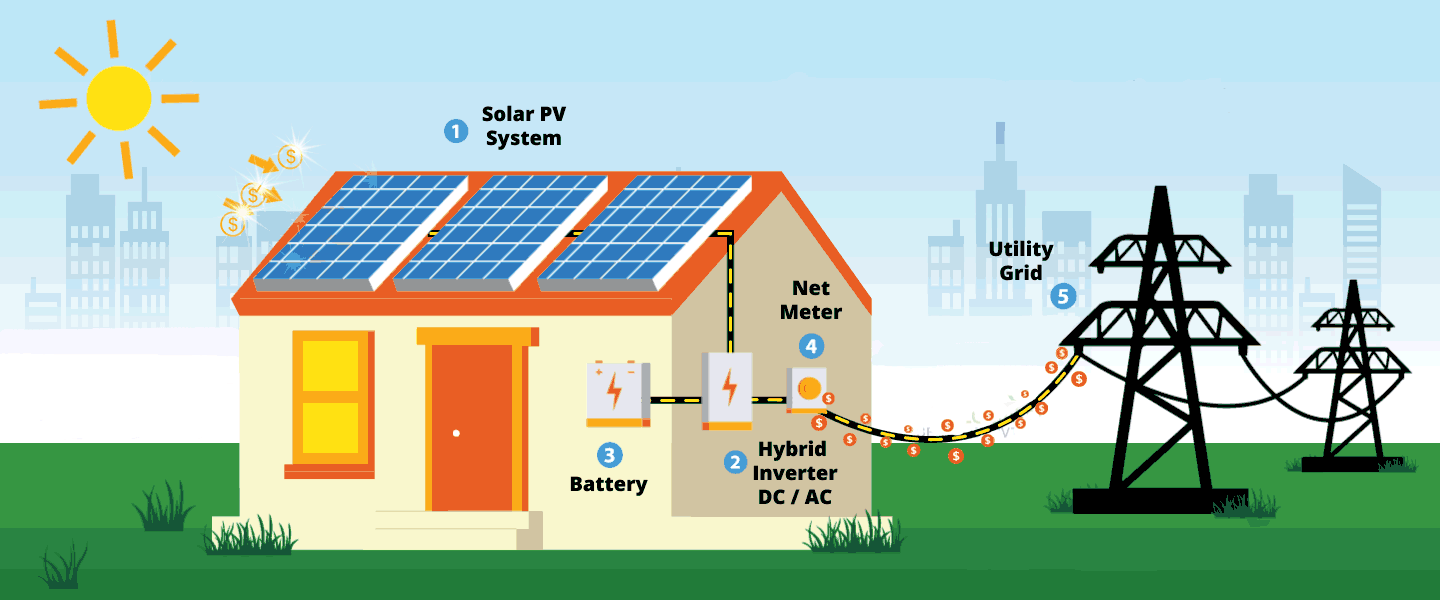
As previously mentioned, a solar panel’s primary and most crucial element is silicon solar cells.
Silicon has the atomic number 14 on the periodic table. It is non-metal with conductive properties that allow the element to convert sunlight into electricity.
When light interacts with a silicon cell, it forces the electrons inside of it to move; this movement initiates a flow of electricity. This process is known as the “photovoltaic effect.”
However, that silicon cells alone can’t really provide your campervan or home with electricity.
For the solar cell’s electrons to escape and supply helpful power, it needs to be paired with special wiring and a metal casing.
It’s also worth mentioning that solar panels come in different cell structures, which we’ll discuss later in the article.
How Solar Panels Work
Time to look at how solar panels work, step-by-step:
Step 1. The sun’s rays make contact with the solar panel, creating an electric field.
Step 2olar electricity generated flows from the silicon cells to the edge of the panel and into the conductive wire.
Step 3. The conductive wire delivers the electricity to an inverter. Inside the inverter, the electricity is converted from DC to AC which is used to power buildings, vans, and motorboats.
Step 4. Once the electricity converts to AC, another wire transports the electricity to a breaker box which distributes the electricity throughout the building as required.
Types Of Solar Panels
There are 3 types of solar panels: polycrystalline, monocrystalline, and amorphous silicon.
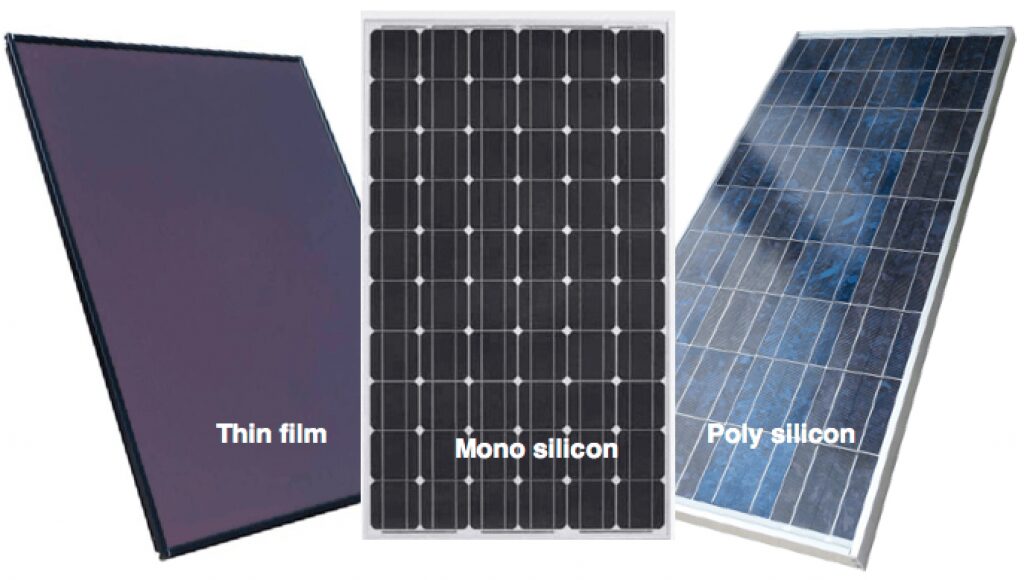
Monocrystalline
Monocrystalline solar panels are made up of one large silicon block.
These silicon cells are more efficient than polycrystalline or amorphous silicon. The production process for monocrystalline solar panels is much more labor-intensive; these panels are usually more expensive than their counterparts.
You can easily recognize monocrystalline cells thanks to their distinct black aesthetic.
Polycrystalline
Polycrystalline solar cells are also silicon cells. However, instead of being formed into a large block, they are rather the end product of melting multiple silicon cells together. Once melted, the silicon molecules are fused into the panel itself.
Polycrystalline solar panels are less efficient than mono cells and are less expensive.
You can identify poly solar panels by their conventional bluish hue.
Amorphous Silicon
Amorphous Silicon cells are used to create the newer flexible solar panels.
These cells are non-crystalline. Instead, they’re attached to glass, plastic, or metal materials. They are usually very thin and, because of this, are lean and pliable.
Although these solar panels can be pretty practical, they are inefficient compared to monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Solar Energy?
| Advantages of Solar Energy | Disadvantages of Solar Energy |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Source | Installation Cost |
| Lowers Electricity Bills | Weather Dependent |
| Many Applications | Energy Storage is Expensive |
| Affordable Maintenance Costs | It takes up a lot of space |
| Tech Development | Associated with Landfill Pollution |
Renewable Energy Source
Like many other energy sources, solar energy is a trustworthy, clean, renewable energy source that we can harness anywhere on earth, on a near daily basis
Solar energy will be available for as long as we have the sun. Which, according to scientists, should be for at least another 7 to 8 billion years!
Lowers Electricity Bills
Solar panels will allow you to use less of the grid’s energy supply, reducing your monthly utility bills. How much is the reduction? Well, this depends on your solar system
Many Applications
You can use solar energy for electricity (photovoltaic), applications. However, you can use it for heat (solar thermal) too.
Solar thermal can distill water in regions with limited clean water supplies.
In the future, solar will most likely be introduced in mass to building materials — think solar bricks!
Affordable Maintenance Costs
If you install solar panels from a reliable company such as SunPower, you’ll likely see them last between 25 to 30 years.
Maintenance includes a simple cleaning twice a year to ensure you maximize your panel’s solar absorption rate.
As there are no moving parts, there is generally no wear and tear, and the only thing that needs replacing is the inverter — you can do this every 5 to 10 years. This means after your initial investment into solar energy; you can expect significantly few ongoing costs to maintain the equipment.
Tech Development
In the future, we will undoubtedly see advances in quantum physics and nanotechnology.
This would significantly enhance the effectiveness of solar panels and double, or perhaps even triple, the electrical input of the solar systems!
What Is The Most Efficient Solar Panel?
In May 2022, the most efficient solar panel is the SunPower Maxeon M-Series, with 22.8%.
A solar panel’s efficiency is the ratio of energy it produces over the power it receives from the sun. Therefore, a SunPower Maxeon panel with an efficiency of 22.8%, can produce up to 21.18W per sqft.
To better understand what this figure means, let’s look back 10 years ago. In 2010, solar panels’ average efficiency was 14.7% (vs. 19.2% in 2020) or 13.65W per sqft — a performance increase of 30% in 10 years!
Can We Reach 100% Solar Panel Efficiency?
Unfortunately, silicon solar panels will never reach 100% efficiency.
This is due to a theoretical limit of 33.7% for a silicon solar cell (Shockley–Queisser limit) and 86.8% for any material and structure.
However, we can continuously improve efficiency by combining different materials. The most efficient laboratory solar cells reach 39.5% under regular sunlight and 47.1% under concentrated sunlight.
Related Reading: 5 Best SunPower Solar Panels You Can Buy
Do Solar Panels Work On Rainy Days And During Night?
Solar panels do work in the rain and during cloudy days. However, their production is low, 70% to 80% lower than on an average sunny day.
For example, if your 1kW solar system is producing 4kWh per day regularly, this could go down to 0.8kWh in the worst weather.
As for the night, solar panels do not produce electricity at all because moonlight carries very low energy, so low that panels cannot convert it into usable energy.
Solar energy from the moonlight is 400,000 times lower than sunlight.
Related Reading: Do Solar Panels Work At Night?
What Is The Newest Technology In Solar Panels?
Current solar panels are not perfect. While some now have a long lifespan (up to 40 years) and low cost of production, they are limited by:
- their maximum efficiency
- energy-intensive production
- poor performance under low light conditions
Promising Developments
Two promising technologies are being developed to tackle these problems.
First, organic solar cells hold the promise of printable solar on any substrate. Their efficiency is currently reaching 18.2% in the laboratory. Additionally, their active material is called solar ink, cheap to produce, easy to set up with one of the best performances indoors with diffuse light.
The second “game changer” PV technology is the perovskite cells. Perovskite is a new kind of material that is also cheap to make. In the laboratory, it is currently deposited on top of regular silicon solar cells to boost their efficiency.
With perovskite solar cells, there are high hopes of breaching the limit of 33% efficiency for silicon solar panels within a few years. Current efficiency is 29.8% in a lab.
Final Thoughts
We hope this article sheds more light on the question, “how do solar panels work?”.
Please let us know how your experience with solar energy has been so far in the comments section below.

