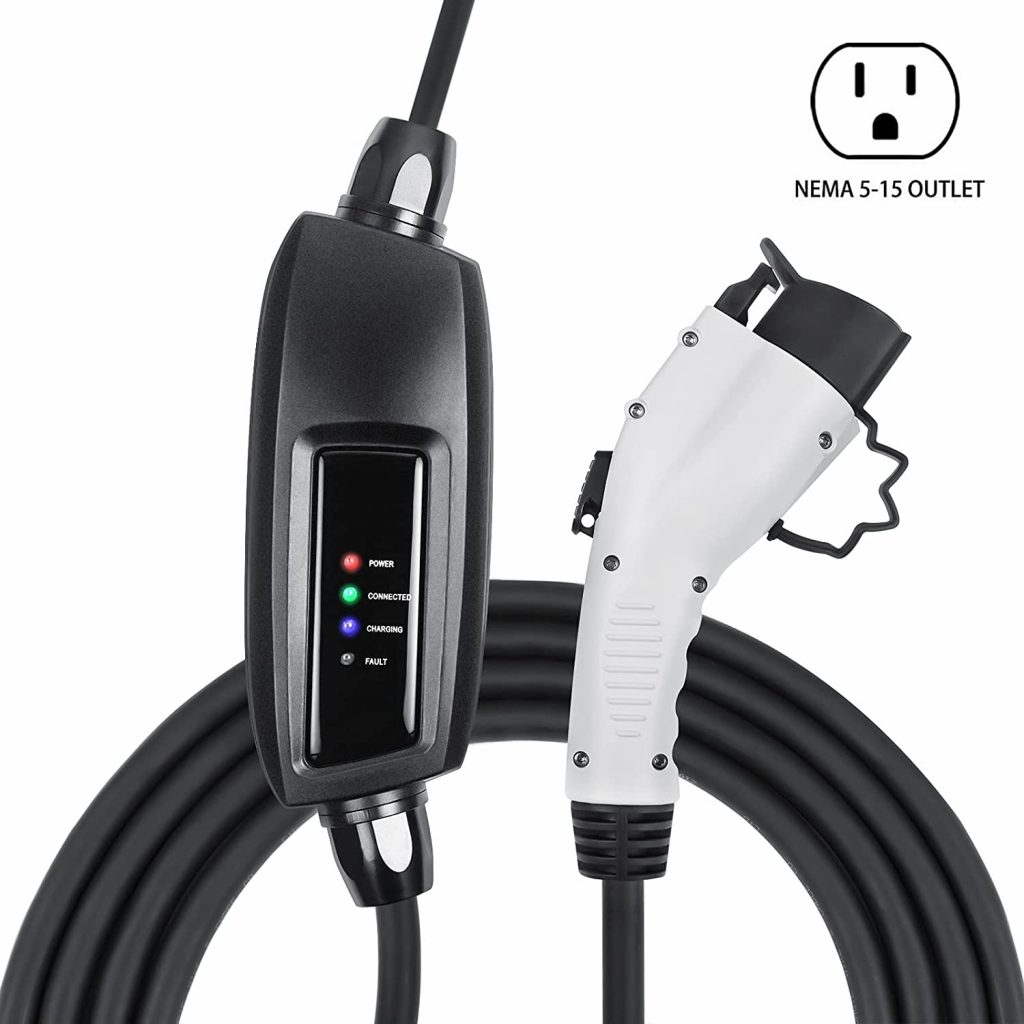
Much attention has been given to the wide range of phenomenal EVs on the market, from speed demon SUVs like the Model X Plaid to luxurious sedans like the Lucid Air dream. But what about that one crucial piece of equipment responsible for keeping these beauties charged, the EV charging cable?
From phones to TVs, cable choice is at the forefront of consumers’ minds. Why? Well, for the simple reason that we want to use our electronic gadgets as much as possible.
EVs are no exception. Your choice of EV charging cable will largely determine whether you spend as much time driving your dream car or sitting on your couch waiting for it to charge.
As such, you must know which EV cable is best suited to your vehicle and/or what to look for in the event that you need to replace your current cable (for whatever reason).
Table of Contents
Different Types of EV Charging Cables
As previously mentioned, there is more than one type of EV charging cable out there.
We’ll break the differences down by discussing the various charging modes and charger plugs (connectors).
Let’s begin by looking at the different charging modes:
Charging mode refers to the safety communication protocol between a charging station and an EV — these standards are universal and adhere to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 61851 Standard.
Mode 1 Charging
This involves home charging from a standard AC power outlet with a simple extension cord and standard plug.
There is no communication between the charging point and the vehicle, meaning no special safety features are present, including shock protection.
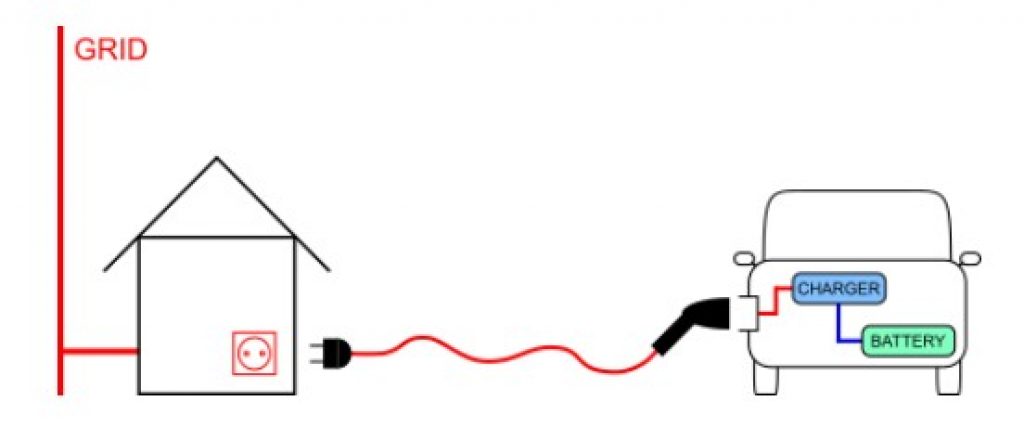
As such, this form of charging is useful for light electric vehicles like scooters and e-bikes, but it’s not considered safe for electric cars.
The lack of safety measures for this mode of charging has caused several countries, such as the U.S., Norway, France, Germany, etc., to restrict or prohibit its use.
| Mode 1 Charging | Values |
|---|---|
| Current | Maximum should not exceed 16 A |
| Voltage | Maximum should not exceed 250 V (single-phase) or 480 V (three-phase) |
Mode 2 Charging
Mode 2 charging is compatible with both household and industrial sockets. It’s commonly used for private charging, while public use is subject to restrictions in several countries.
An EV will typically come with a cable suitable for mode 2 charging. This cable will plug into your vehicle and a standard domestic socket on the other end.
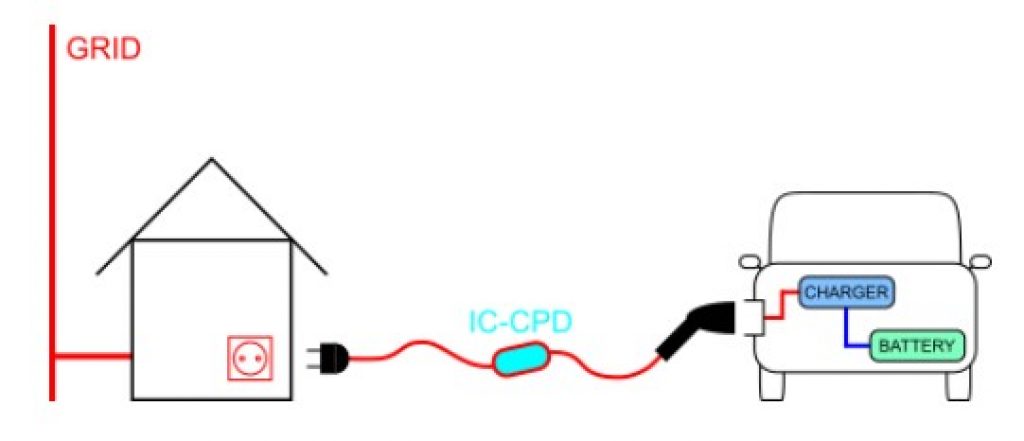
Mode 2 uses a special type of cable that comes with an EVSE In-Cable Control and Protection Device (IC-CPD) that controls the communication between the EV and standard wall plug while providing protective functions.
Safety functions of this mode include:
- Over-current protection;
- Over-temperature protection;
- Detect and monitor the protective earth connection;
- Perform function switching and analyze charging power demand.
| Mode 2 Charging | Values |
|---|---|
| Current | Maximum should not exceed 32 A |
| Voltage | Maximum should not exceed 250 V (single-phase) or 480 V (three-phase) |
Mode 3 Charging
Mode 3 charging uses EVSE that connects your EV to a dedicated charging station like those found in homes, public or commercial parking lots, and workplaces.
In this case, the charging station applies AC to the vehicle’s onboard circuitry to charge the battery.
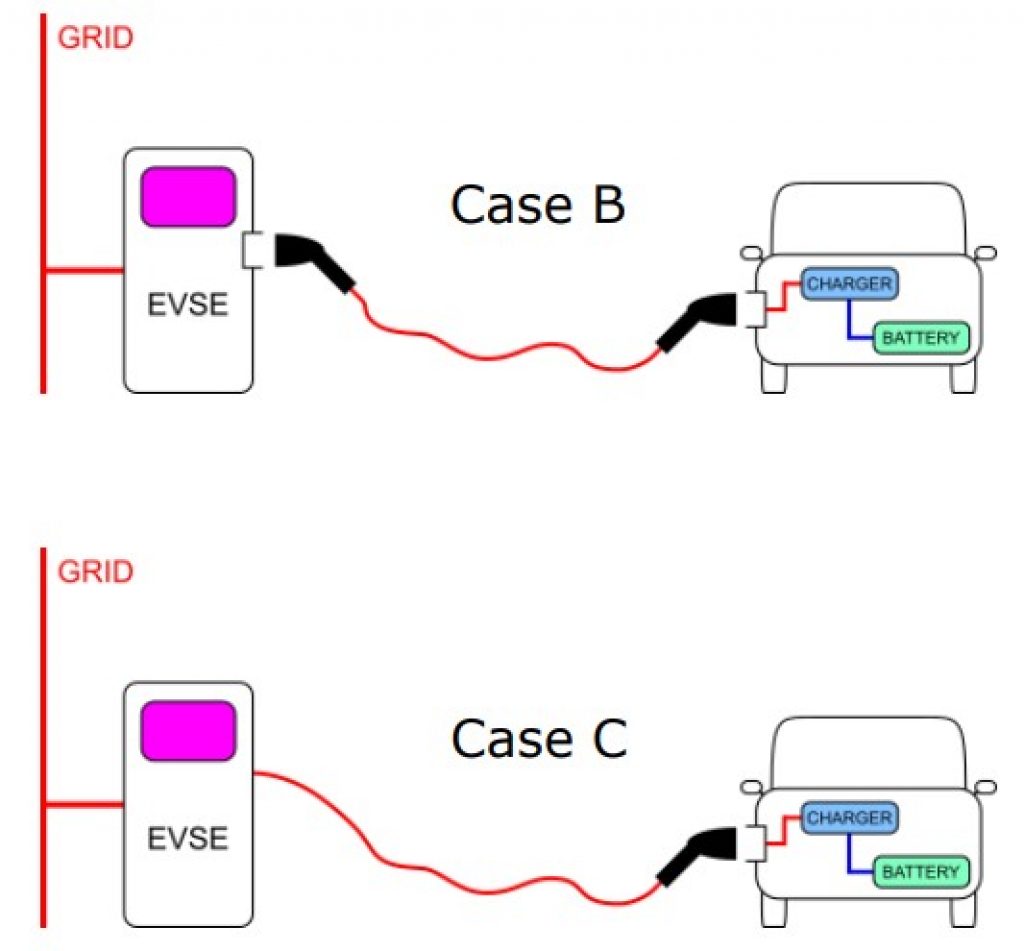
Safety functions of this mode include:
- Verifying the connection between the EVSE and the EV;
- Verifying the protective earth connection;
- Adjusting the charging current to the cable assembly’s maximum current capability.
| Mode 3 Charging | Values |
|---|---|
| Current | Maximum should not exceed 250 A |
| Voltage | Maximum should not exceed 250 V (single-phase) or 480 V (three-phase) |
Mode 4 Charging
The first three modes we discussed all use AC output — converted via an onboard AC/DC converter — to power your vehicle.
Mode 4, on the other hand, incorporates the use of DC output which is converted via an off-board charger before it’s transferred to your EV. In other words, your EV is connected to the main power grid that feeds its DC output through an external charger.
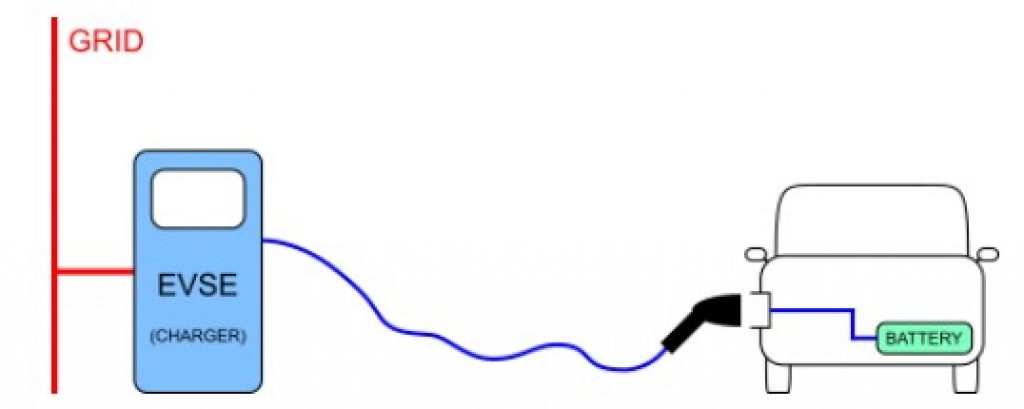

This mode is often referred to as fast or ultra-fast charging — you’re able to reduce the charging time of your EV drastically.
But, because there is so much more power being fed directly to your car’s battery, you must ensure that the control and protection functions and the EV charging cable are permanently connected to the charging station.
| Mode 4 Charging | Values |
|---|---|
| Current | Maximum should not exceed 400 A |
| Voltage | Maximum should not exceed 600 V |
EV Charging Cable Connectors
When researching EV charging cables, you’ll come across the terms single-phase and three-phase. So, before we move on to charging cable connectors, let’s look at what these terms mean:
Single-Phase And Three-Phase
The world’s power grid is divided into three phases — you can view these phases as a three-lane motorway filled with power.
Single-phase AC comprises three conductors: Live (L), Neutral (N), and Earth (E), and provides a maximum charge rate of 7.4 kW.
If you were to use a single-phase EV charger, you’d only use one of the three power lines. As such, it’ll take more time to charge up your vehicle.
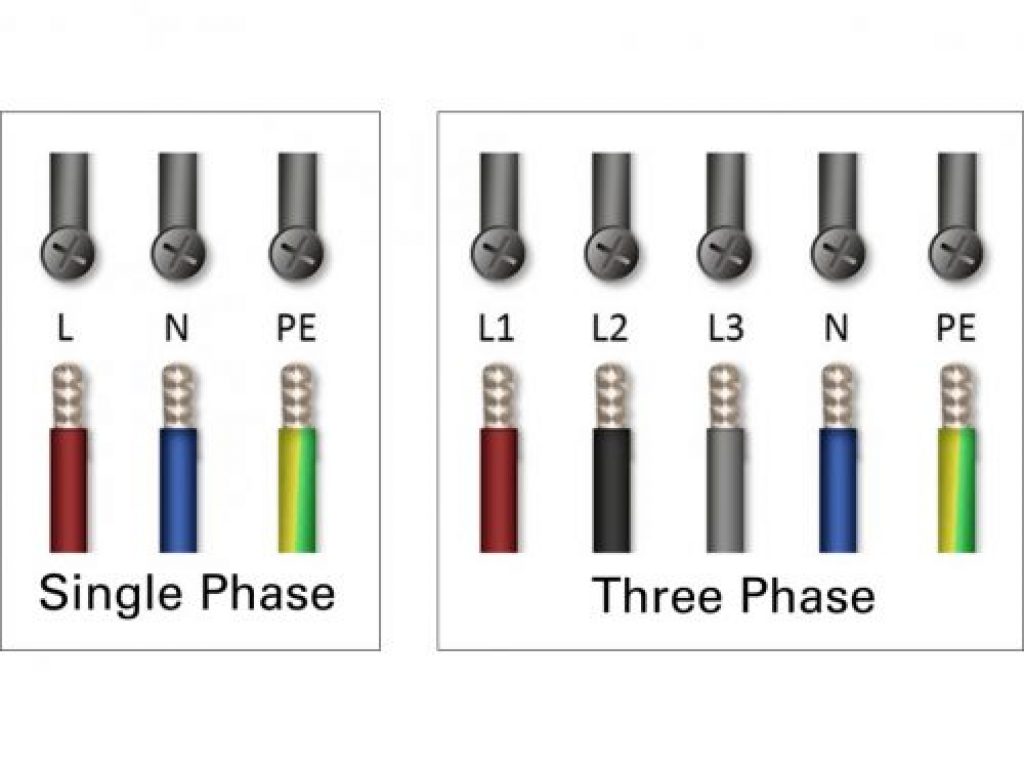

Three-phase AC comprises five conductors: 3 Live (L1, L2, L3), one Neutral (N), and Earth (E), and provide a maximum charge rate of 22 kW.
If you were using a three-phase EV charger, you’d be using all three power lanes to charge your vehicle, and the result would be a much quicker charging time.
Charging Connectors
EV charging connectors are compatible with either Alternating Current (AC) or Direct Current (DC).
This article will focus on connectors relevant to the U.S EV market. Let’s break them down:
Type 1
Also known as the SAE J1772 or J-plug. Every EV manufacturer in North America (except Tesla) uses this connector for Level 1 (120 volts) and Level 2 (240 volts) EV charging.

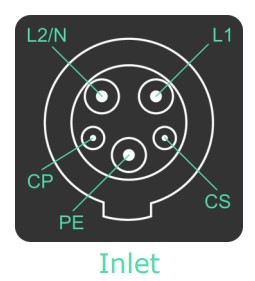
| Type 1 Connector Charging Levels | Output |
|---|---|
| AC Level 1 | Up to 1.9 kW (120V, 16A) |
| AC Level 2 | Up to 19 kW (240V, 80A) |
CCS1
Combined Charging System 1 (CCS1) connectors are Type 1 ( SAE J1772) connectors, but with DC pins added.
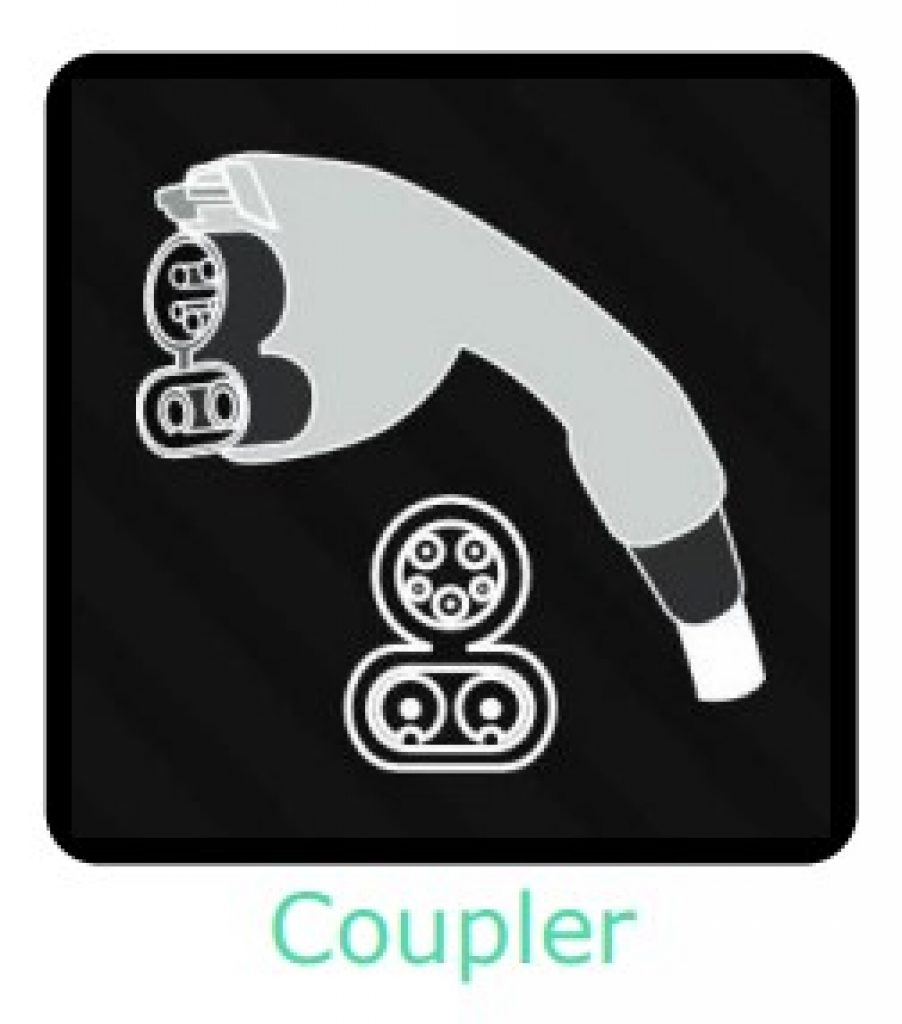
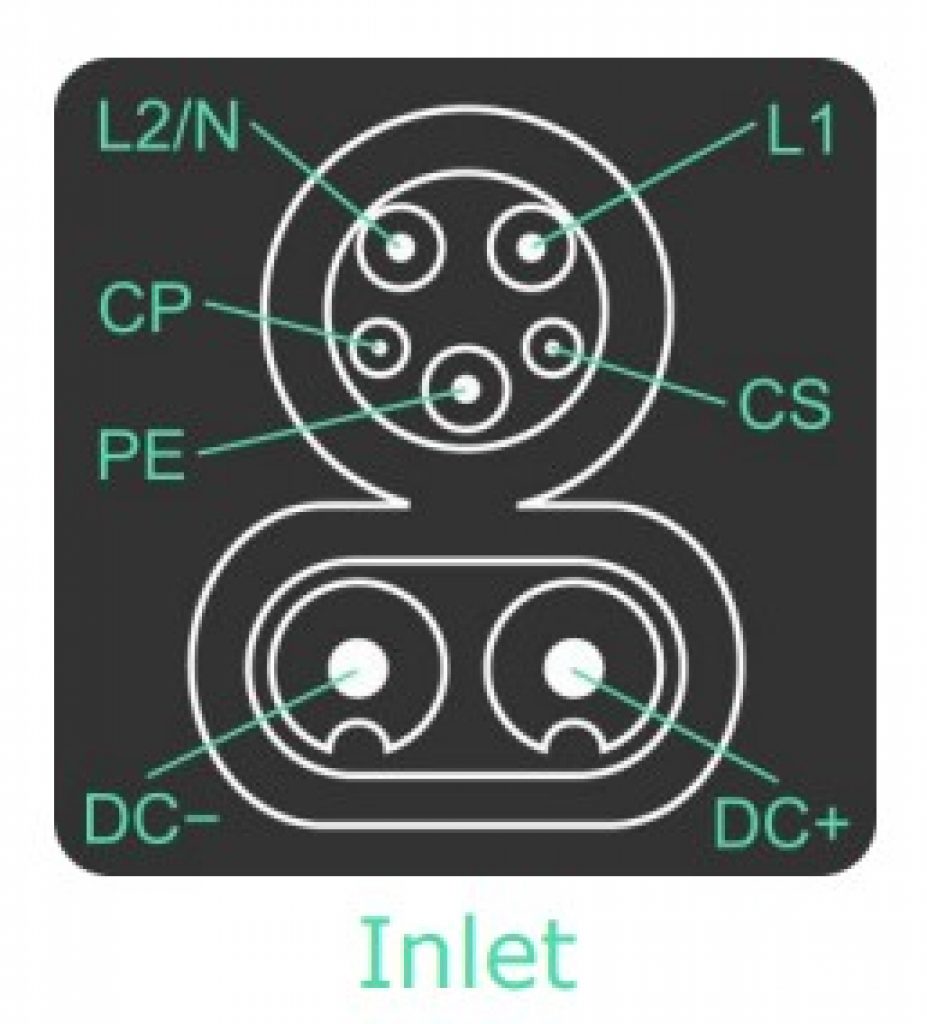
| CSS1 Connector Charging Levels | Output |
|---|---|
| DC Level 1 | Up to 48 kW (600V, 80A) |
| DC Level 2 | Up to 120 kW (600V, 200A) |
CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO plugs do not share part of the connector with the J1772 inlet. As such, cars require an additional ChadeMO inlet.
It must be noted that the U.S will begin to phase out the use of these cables in 2022.
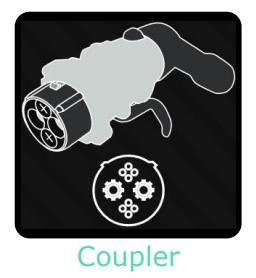
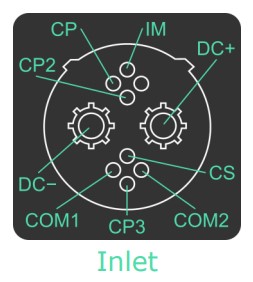
| CHAdeMO Connector Charging Levels | Output |
|---|---|
| DC Power | Up to 120 kW (600V, 200A) |
Tesla
Tesla uses a single connector for Level 1 and 2 DC fast charging — it’s a proprietary connector that accepts all voltage. As such, there’s no need for you to have a separate connector for DC fast charging.
Tesla has an exclusive supercharger network that the company installs and maintains itself. The network is protected by an authentication process that only allows access to Tesla vehicles, so non-Tesla EVs are not able to use these charging stations.

| Tesla Connector Charging Levels | Output |
|---|---|
| AC Power | Up to 19 kW (240V, 80A) |
| DC Power | Up to 125 kW (500V, 250A) |
How To Choose The Best EV Charging Cable
Ideally, you want to choose an EV charging cable compatible with your home’s electrical installation and your vehicle’s onboard charger.
For reference, most EVs fall within a 240-volt, 32-ampere charging capacity.
However, should you be unsure, consult your EVs manual and or check with your car’s manufacturer — better to be safe than sorry!
How Long Do EV Charging Cables Last?
Unfortunately, we haven’t come across enough legitimate data to provide you with a concrete answer to this question.
We have, however, noticed that cables appear to come with anything from 1 to 5-year warranty periods.
Are EV Charging Cables Universal?
No, EV charging cables are not universal.
Looking at the below image, you’ll notice that the U.S (Type 1) and Europe (Type 2) use different connector standards.

However, there are instances, like with the Nissan LEAF, where you can use a foreign cable (CHAdeMO) and an adaptor. But, this will likely change in the future.
5 Best EV Charging Cables You Can Buy
1. Pulsar Plus Level 2 Electric Vehicle Smart Charger
Safe And Reliable: UL listed (2020) for electrical safety. Comes with a NEMA Type 4 rating for water-tightness and dust resistance.
Power Sharing: connect two or more chargers to a single circuit to charge multiple EVs simultaneously.
Power Boost: pair this charger with Pulsars smart meter to enable optimum charging power even in households with limited capacity.
Tech Specs:
| Connector Type | Type 1 (SAE J1772) |
| Charging Levels | 2 |
| Cable Length | 25ft |
| Voltage | 240 Volts |
| Current | 40/48 amps |
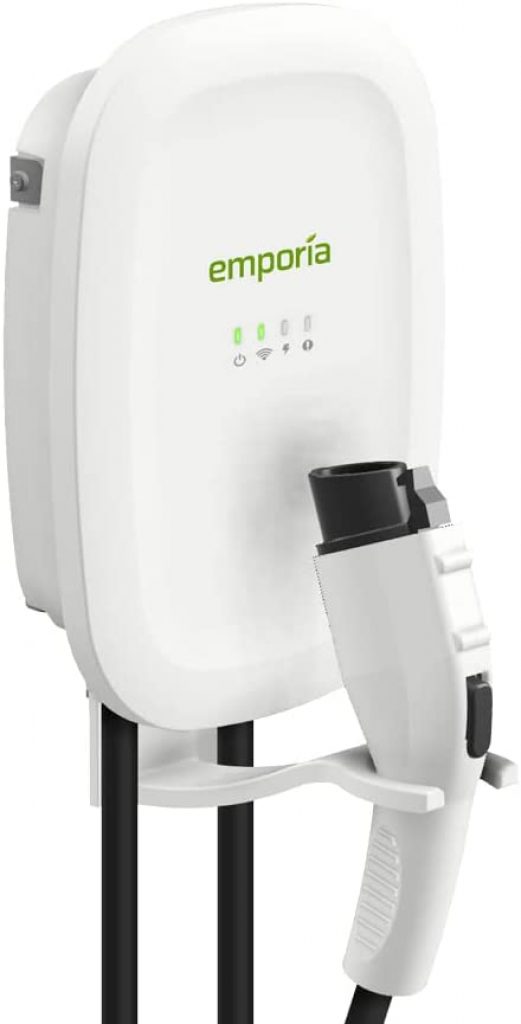
2. EMPORIA ENERGY Smart Level 2 EV Charger
Protection Against The Elements: rugged watertight NEMA Type 4 enclosure
Compatability. The charger comes with an SAE J1772 connector and a 24 ft cable with integrated cable management.
Real-Time Data: monitor energy use and charging sessions with iPhone / Android / Web browsers. Schedule charging and effortlessly manage parameters to handle utility rate charges.
Warranty: 3 years
Tech Specs:
| Connector Type | Type 1 (SAE J1772) |
| Charging Levels | 2 |
| Cable Length | 24ft |
| Voltage | 240 Volts |
| Current | 48 amps |
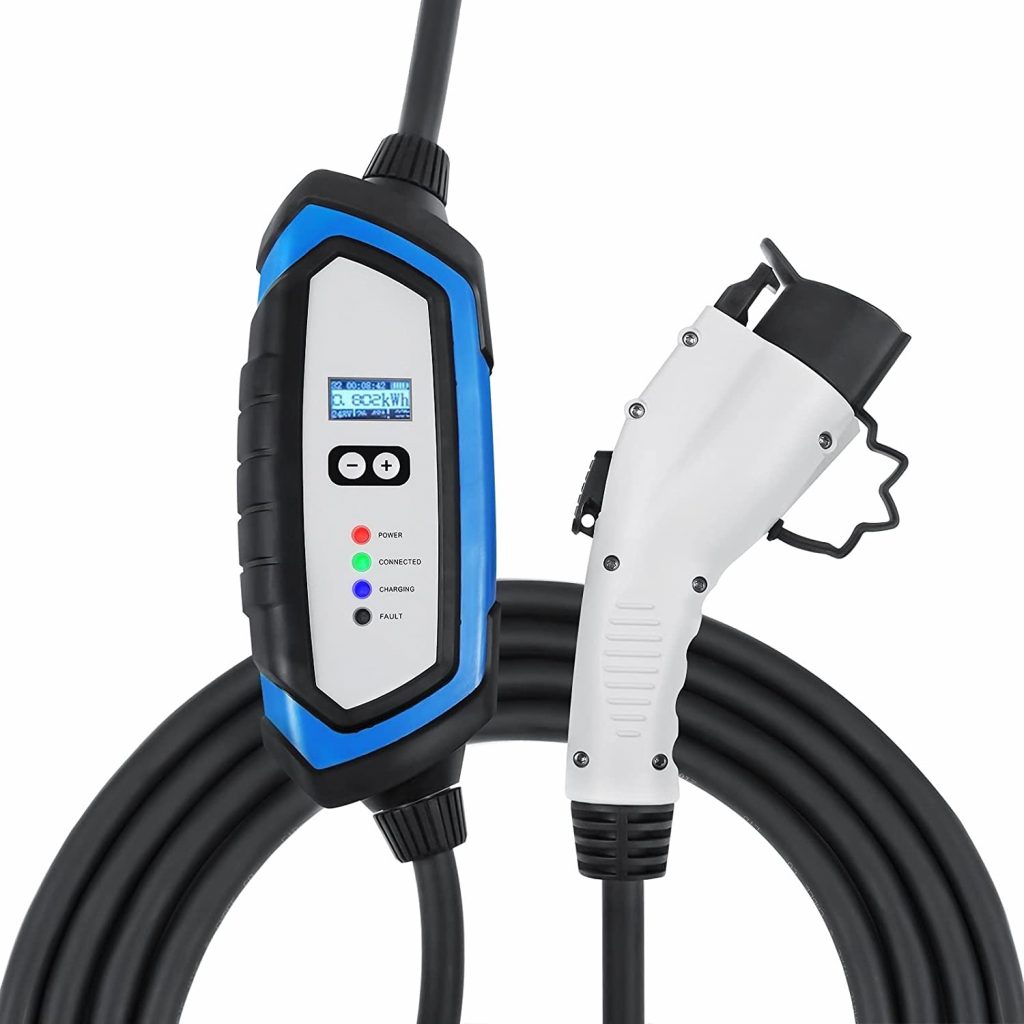
3. Lectron NEMA 14-50 Level 2 EV Charger
Indicator Lights: The LED indicator lights on the charging cable show you where your car is across three different charging levels. It alerts you if a fault is discovered, allowing you to manage the problem right away.
Rugged: the Lectron Level 2 EV charger is made of lasting high-grade, rugged materials.
Warranty: 1-year
Tech Specs:
| Connector Type | Type 1 (SAE J1772) |
| Charging Levels | 2 |
| Cable Length | 18ft |
| Voltage | 240 Volts |
| Current | 32 amps |
4. BougeRV Level 1-2 EV Charger
Levels 1 & 2: Bougerv’s EV charger comes with a NEMA 5-15 adapter that allows Level 1 and 2 charging.
Multi-Level Protection: this cable is protected against lightning, leakage, over-voltage, under-voltage, overheating, and over-current.
Durable: IP55 protection rating makes it suitable for indoor and outdoor use.
Warranty: 12 months
Tech Specs:
| Connector Type | Type 1 (SAE J1772) |
| Charging Levels | 1& 2 |
| Cable Length | 25ft |
| Voltage | 110-240 Volts |
| Current | 16 amps |
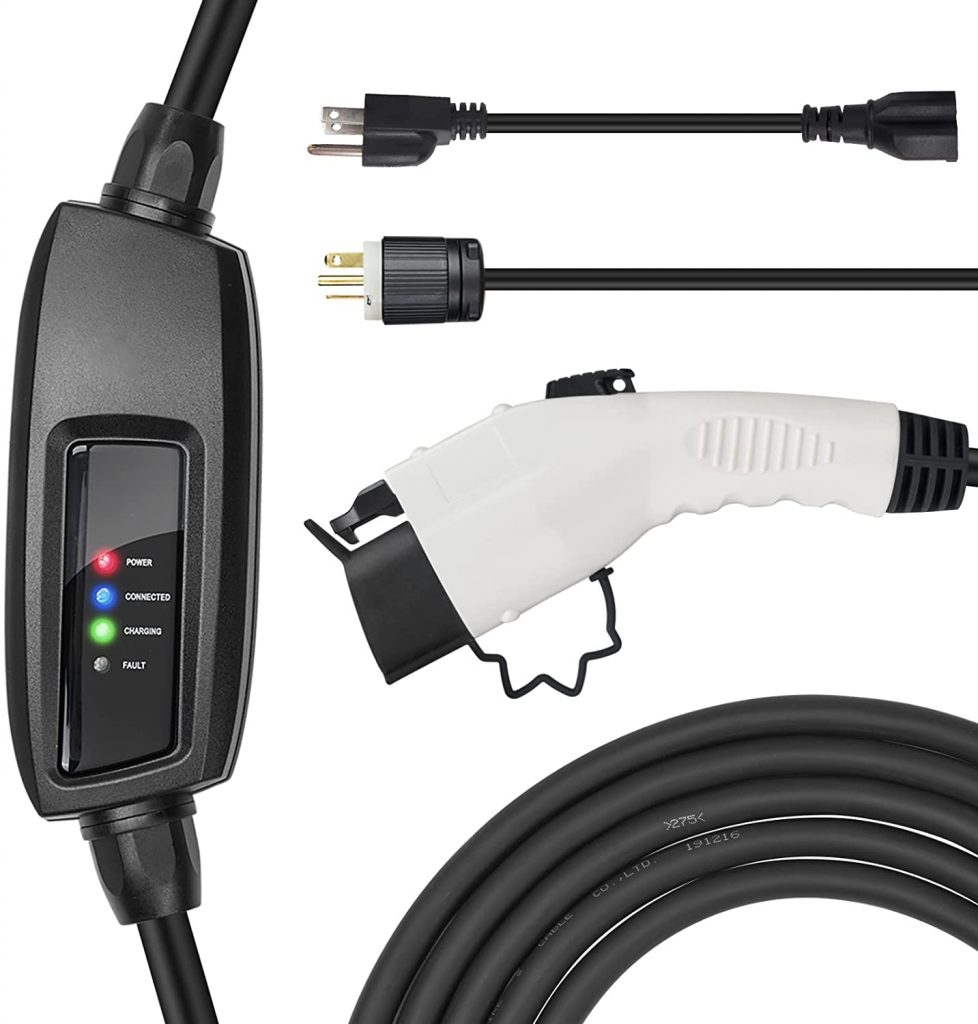
5. Lectron NEMA 5-15 Level 1 EV Charger
Level 1: this Level 1 charger comes with a NEMA 5-15 Plug that connects to a standard outlet in your household.
LED Indicator: the LED indicator lights on the cable show you where your car is across three different charging levels. What’s more, they alert you of existing faults.
Robust: the cable comes equipped with overvoltage, overheating, and overcurrent protection.
Tech Specs:
| Connector Type | Type 1 (SAE J1772) |
| Charging Levels | 1 |
| Cable Length | 21ft |
| Voltage | 110 Volts |
| Current | 16 amps |
Final Thoughts
EV charging cables’ information can appear somewhat overwhelming, especially with all the charging levels, modes, and connector types.
But we’re confident that this article will go a long way in clearing up any knowledge gaps you may have.
Just remember — we’re here to help. So, should you have any further questions, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us in the comments section below. Better yet, join our community!






