A 1000-watt inverter can power tablets, laptops, and gaming devices, but is it enough for your refrigerator to run efficiently?
A refrigerator is the cornerstone of any modern household. Even the most well-prepared off-grid enthusiasts rely on them to store their beloved food and beverages.
These cooling devices use compressors to evaporate a refrigerant which causes a decrease in temperature. Naturally, the bigger the refrigerator, the higher its power.
When utility electricity is not available (in an RV, a boat, an off-grid cabin, during a power outage), an appropriate size inverter connected to a battery bank can power a refrigerator.
In this article, we look at the entry-level 1000-watt inverter — will it be powerful enough for a refrigerator or a freezer? And if so, what is the maximum size of the fridge it can run?
Table of Contents
Will a 1000-watt inverter run a refrigerator?
A 1000-watt inverter will run a domestic refrigerator up to 25 cubic feet.
Contrary to popular belief, refrigerators are not powerful appliances. This assumption might originate from the older models (more than 20 years old) that could commonly draw up to 850W.
Nowadays, the most efficient refrigerators only need around 250W for a 17cu.ft model.
That said, there are still some limitations to a 1000W inverter running a refrigerator. Let’s find out what the actual power requirements of such an appliance are.
Estimate your refrigerator’s real power requirements
A refrigerator connected to an inverter requires a certain amount of power to function correctly.
To determine your refrigerator’s power, look for its voltage and rated current. Next, multiply the voltage (V) by the current (A) to get the rated power (W).
Here’s an example:
The Frigidaire Gallery Series 22.3cuft has a voltage of 120V and a rated current of 2.5A. Consequently, its power is 300 (120 x 2.5). However, the power requirements for this refrigerator are slightly higher than its rated specifications.
The difference between rated power and required power originates from t e type of electric load. You may already know that there are two primary types of electric loads:
- Resistive loads: Among resistive loads, you’ll find electric water heaters or incandescent lamps. These loads are 100% efficient — an electric kettle rated at 1000W will draw 1000W from your inverter. Additionally, they don’t experience a power surge upon starting.
- Inductive loads: The voltage and current waves in inductive loads are out of phase. This creates an electromotive force that moves in opposition to the supply voltage. Consequently, inductive loads experience a power surge upon starting and require more power than their rated power to function correctly.
Among inductive loads, you’ll find:
- compressors
- water pumps
- refrigerators/freezers
- air conditioning units
- vacuum cleaners
- power tools
- microwave ovens
- electric motors
Contrary to resistive loads, inductive loads are not 100% efficient.
Power factor
Power Factor (PF) was introduced to quantify the efficiency of a load. This is the ratio between the active or real power (kW) and the apparent power or demand (kVA).
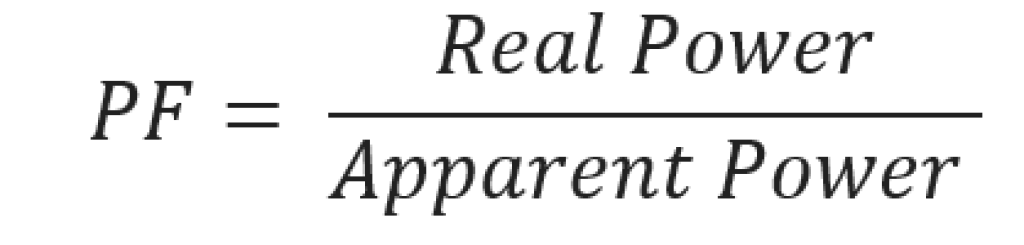
To find the apparent power, multiply the voltage (V) by the current(A) measured by your appliance during operation. The closer your power factor is to 1, the more efficient your device is.
Consequently, an appliance with a low power factor draws more amps than a load of the same helpful power with a higher power factor.
Note to our readers: the apparent power (VA) is the real power the inverter has to supply.
The consequence of low PF on inverter size
Refrigerators and freezers have the lowest power factor (around 0.75). That translates into an increased current requirement.
For example, if a refrigerator has a rated power of 150W with a PF of 0.75, its power requirement is 25% higher, around 190W. Moreover, it’s prone to power surges upon starting — up to 3 times its rated power (450W).
Select the inverter accordingly
We can determine a refrigerator’s maximum power relative to a 1000W inverter. We’ll assume that the inverter allows a 3-time power surge for 1 second.
With a PF of 0.75, the maximum power is:
1000 x 0.75 = 750W
In conclusion, a 1000W inverter can handle a 750W refrigerator.
Real-world example
In the picture below, taken from an off-grid system, you’ll see a device that monitors the electrical parameters of a 3.5kW/3.5kVA inverter. Three freezers are connected to the inverter for a total useful power of 632W.
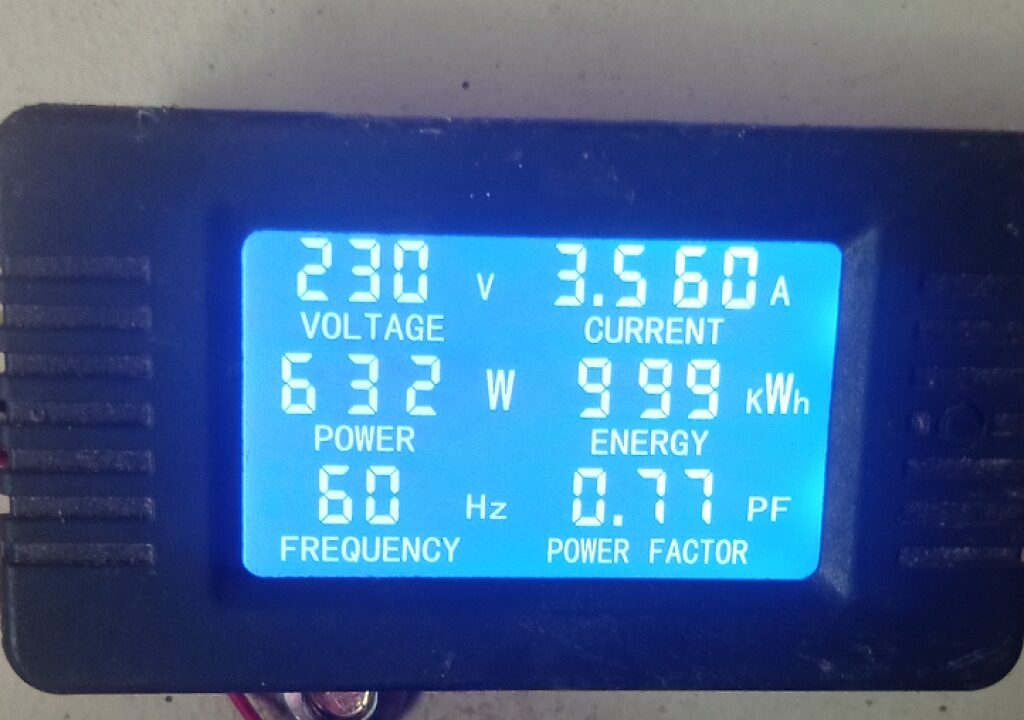
The current is 3.56 A, and the voltage is 230V., while the apparent power is 819VA (3.56 x 230). Consequently, the power factor is:
632/819 = 0.77
819VA is what the inverter should be able to handle. That’s 23% more than the freezers rated useful power.
Below is a list of refrigerators that a 1000W inverter can run:
| Brand | Model | Useful Volume (cu. ft) | Rated Power (W) | Minimum Inverter Size (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fisher & Paykel Series 7 | RF170WLKUX6 | 17.1 | 385 | 500 |
| Frigidaire Gallery Series | GRSC2352AF | 22.3 | 375 | 500 |
| Bertazzoni Professional Series | REF36FDFIXNV | 22.5 | 287 | 500 |
| Summit | FFBF286SS | 16.8 | 276 | 500 |
| Beko | BFBF3018SSIM | 16.2 | 228 | 300 |
| AccuCold | FFAR121SS | 10.1 | 204 | 300 |
| Bertazzoni | REF24BMFXNV | 10.7 | 150 | 200 |
| Sharp | SJB1255GS | 11.5 | 140 | 200 |
| Summit | FFBF181ES2 | 11.7 | 69 | 200 |
Will a 1000-watt inverter run a freezer?
A 1000-Watt inverter is capable of running a freezer up to 20 cu. Ft.
Freezers operate similarly to refrigerators or ice machines — their compressor evaporates a refrigerant that condensates into a cooling circuit and generates cold. This means freezers fall under the inductive load category with a power factor close to 0.75.
Rule of thumb
To determine whether a 1000-w tt inverter can run your freezer, add 25% to its rated power.
For example, the 17cu. Midea freezer has a rated power of 2.2Amps x 115V = 253W. The minimum inverter power needed for this freezer is 253 x 1.25 = 317W. In addition, the inverter must handle a power surge of 3 x 253W = 759W for 1 second.
Below is a selection of freezers that a 1000W inverter can run:
| Brand | Model | Useful Volume(cu.ft) | Rated Power (W) | Minimum Inverter Size (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermador Freedom Collection | T18ID905LP | 7.8 | 350 | 500 |
| Gaggenau | RF411705 | 8.6 | 350 | 500 |
| Liebherr Monolith | MF1851 | 7.8 | 345 | 500 |
| Bertazzoni | REF18FCIPIXL | 8.22 | 327 | 500 |
| Liebherr Premium Plus Series | HF861 | 7.8 | 300 | 500 |
| Midea | WHS625FWESS1 | 17 | 253 | 500 |
| Kelvinator | KCCF210W | 20.9 | 200 | 300 |
| AccuCold | VT65MLPLUS2 | 3.2 | 150 | 200 |
| Summit | SCFF1842 | 2.7 | 126 | 200 |
What other appliances can a 1000-watt inverter run?
Aside from a refrigerator or a freezer, a 1000W inverter can run dozens of appliances. Remember that connecting an inductive load to your inverter will require 25% to 40% more than its rated power to function correctly.
Below is a list of appliances that a 1000W inverter can run:
| Appliance | Power (W) |
|---|---|
| Electric fan | 70 |
| LED TV | 120 |
| 8000 BTU aircon | 720 |
| 6000 BTU aircon | 500 |
| Ice machine | 100 |
| Laptop | 100 |
| Corded drill | 700 |
| Curling Iron | 40 |
| Desktop computer | 400 |
| Water pump (0.5HP) | 370 |
| Food blender | 400 |
| Inkjet printer | 40 |
| LED light | 10 |
| USB charger | 50 |
| Projector | 250 |
A 1000W inverter allows you to run multiple appliances at the same time as long as the total power of these appliances doesn’t exceed 1000W. That said, a 1000W inverter cannot run several standard devices. These include:
- blow dryer
- vacuum cleaner
- coffee maker
- dishwasher
- washing machine
- portable heater
- toaster
- clothing iron
Final thoughts
Thanks to more than 20 years of technical improvements, our refrigerators and freezers’ efficiency has considerably increased.
Nowadays, even the largest refrigerators with freezer compartments (more than 20 cu. ft) require less power than a desktop computer.
As a result, a 1000-Watt inverter is perfect for almost any size refrigerator or freezer — alongside other appliances — as long as the total power required doesn’t exceed 1000 watts.

