Hybrid inverter vs. off-grid inverter — which is best?
Well, the answer involves several factors:
- Your needs
- The cost of each inverter type
- Whether the inverter is compatible with your system
But there are probably many more questions whirring through your mind, so it’s time to power up those brain cells and see which one could work for you!
Table of Contents
What Is A Hybrid Inverter?
A hybrid inverter is an all-in-one solution that generates power in the same manner as a standard solar inverter. However, it has additional fitted battery connections to store energy for later use. Moreover, hybrid inverters can feed back into the power utility grid.
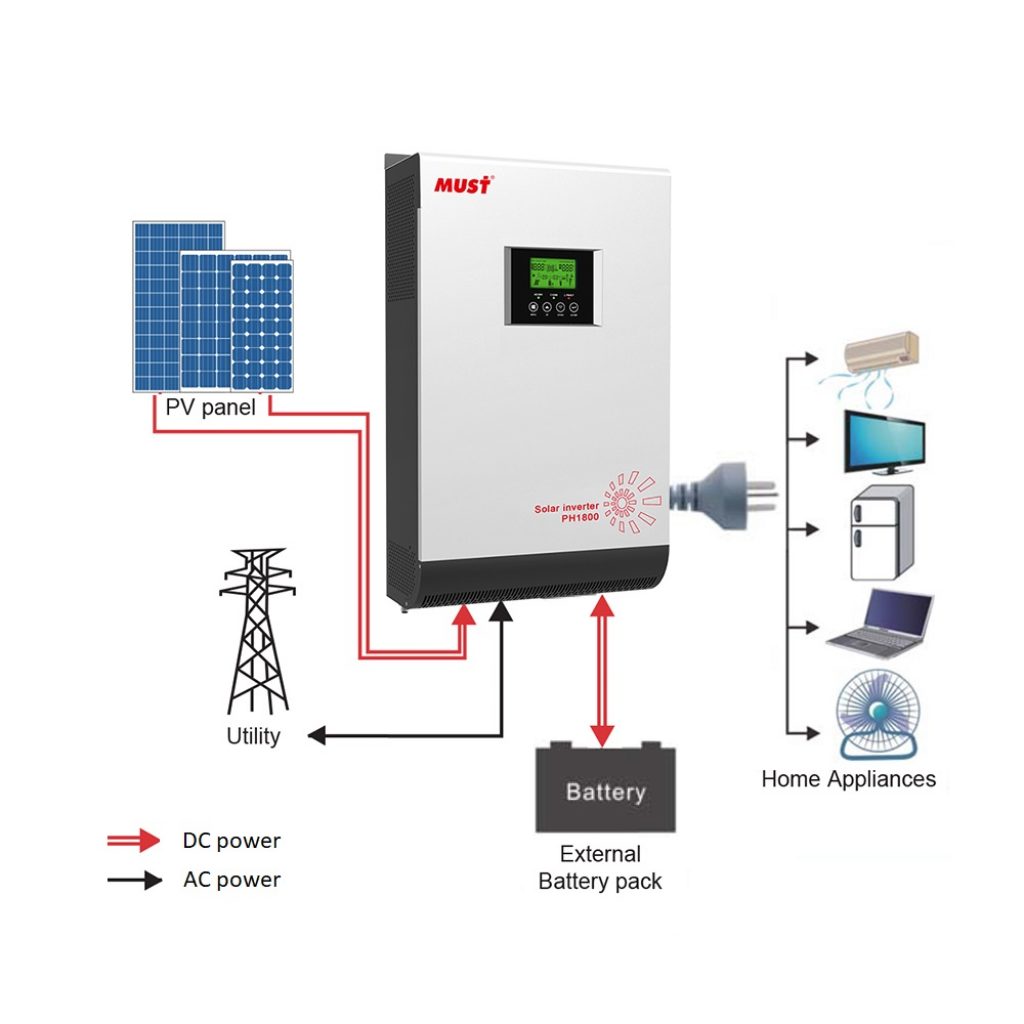
Source: MUST hybrid inverters
What Is An Off-Grid Inverter?
An off-grid inverter will draw power from a charged battery, convert the power from DC to AC, and output it into a household. It is essentially similar to a hybrid inverter, with one major difference: it cannot feedback power into the utility grid.
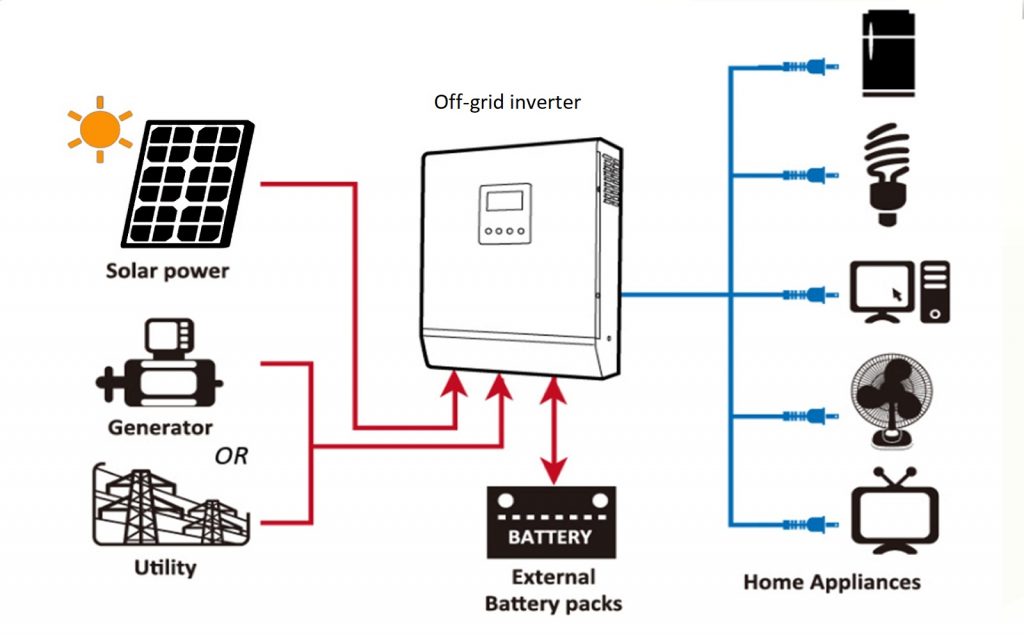
Source: JsdSolar
Hybrid Inverter Vs. Off-Grid Inverter
Several factors determine the inverter best suited to your needs. These include the relationship with the utility grid, inverter sizes, cost, and battery compatibility.
Furthermore, it’s vital to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each inverter. (We will address these later)
| Aspect | Hybrid Inverter | Off-Grid Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship with the utility grid | Connected to grid and solar Draw and feedback into the grid. | Connected to a backup source (generator or grid) Can only draw power from the grid. |
| Inverter size | Must match maximum summer demand. | Must match 1.2 times maximum summer demand. |
| Inverter cost | $1500-$8000 | $1500-$6000 |
| Battery compatibility | The inverter can accomodate all types of solar batteries. Compatible with a broader range of voltages and less restriction of inverter choice. | The inverter is compatible with all types of batteries. Inverter power from 1kW to 2kW works with 12V batteries, 2kW to 4kW with 24V batteries, above 4kW 48V batteries |
Relationship With The Utility Grid
A hybrid inverter connects to the utility grid and a solar system battery pack. It can feed from both systems and send power back into the utility grid when there is a surplus.
In contrast, an off-grid inverter does not feed back power into the utility grid; but can still be connected to an external AC backup source such as a generator or the utility grid.
Inverter Size
Correct inverter sizing is imperative for a successful powering experience.
This is especially true for off-grid inverters as their goal is to minimize the use of a backup power source.
Inverter size depends on seven factors matching maximum demand and inverter capabilities. These include:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum power rate | This is the amount of DC and AC power the product can work with. |
| DC to AC ratio | The measure of nominal power and the household output. |
| Input voltage | DC voltage delivered by the solar panels to the inverter |
| Output voltage | AC Voltage output delivered by the inverter to the house |
| Operating frequency | The frequency matched to the nominal frequency of what needs to be powered or the utility grid to which it connects. |
| Surge power output | The amount of power that an inverter can handle during a surge. In general, two times the rated power |
| Charge rating | The ability of the inverter to enable the battery to complete a full charge cycle. |
However, the temperature is another major factor you must consider with off-grid systems.
In hotter environments, the size of your inverter should be around 1,2x that of the highest demand. This is because higher temperatures negatively affect inverter output.
The following table illustrates a scenario whereby a 6kW inverter at 77°F/25°C only outputs 4.8kW at 104°F/40°C.
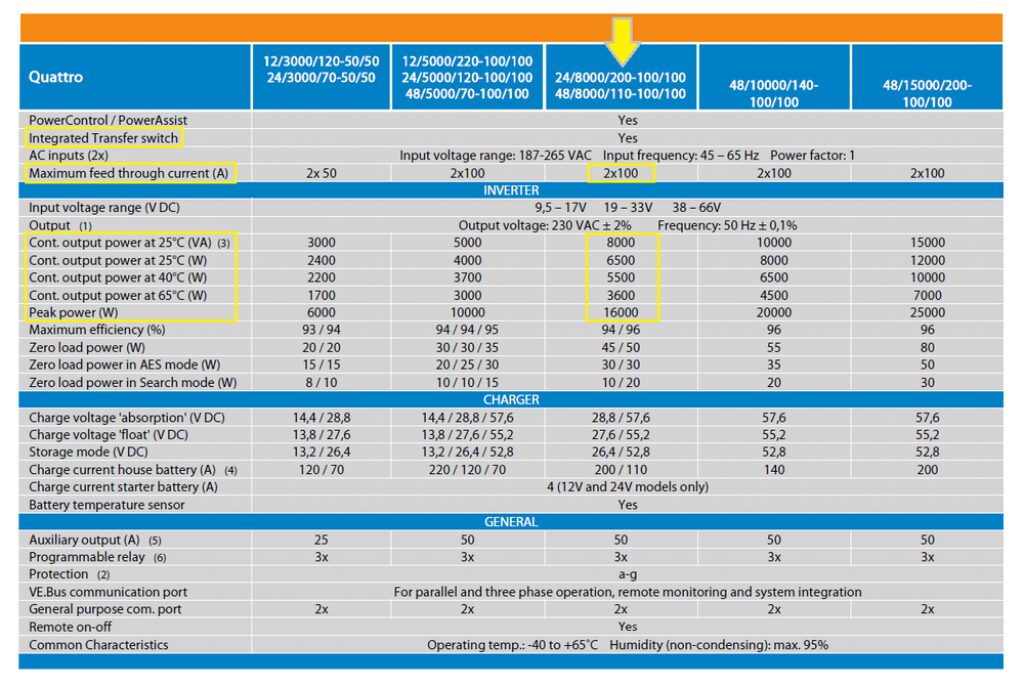
Source: Victron Energy
So you can expect an off-grid inverter to be bigger than that of a hybrid system.
Inverter Cost
- Hybrid Inverters: can set you back anywhere from $1,500 (small capacity inverters) to $8,000 (larger capacity inverters).
- Off-Grid Inverters: an off-grid inverter will cost roughly $1,500 (2.5kW) to $8,000 (15kW).
Battery Compatibility
Communications Compatibility
In the earlier days of solar systems, most inverters were designed to work with lead-acid battery types.

Source: Clean Energy Reviews
Many lithium-ion battery systems have specific management units which require inverters that match these communications. Have no worries, this is now the case for all new inverters both hybrid and off-grid.
Battery Voltage Compatibility
Both hybrid and off-grid inverters work with a specific nominal DC battery voltage.
Inverters often use 48-volt lithium batteries. Occasionally though, small-capacity inverters (from 1kW to 3kW) can only use 12-volt or 24-volt systems.
This a major factor to look at before buying your batteries, the rated voltage should match the inverter voltage.
Hybrid Inverter Vs. Off-Grid Inverter: Advantages And Disadvantages
| Hybrid Inverters | Off-Grid Inverters | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | Can draw power from the grid to meet demand Programmable for different modes Feedback into grid | Cheaper Pre-wired and user friendly Accept power backup |
| Disadvantages | Costly Cannot be upgraded | Cannot feedback into the grid |
Hybrid Inverter: Advantages
The primary benefit of a hybrid inverter is its ability to draw power from the utility grid when solar energy does not match energy demand, making it consistent and reliable.
In the opposite scenario, a hybrid inverter can feed surplus solar energy back into the utility grid, which often comes with the bonus of green energy tax rebates or breaks.
Additionally, hybrid inverters have various programmable modes. They can:
- Act as a standard solar inverter.
- In backup mode, they will automatically use stored solar power when the utility grid cuts out.
Finally, in some instances, hybrid inverters include cloud synced monitoring functions, charge control, and inverter functionalities into one unit at a lower price than off-grid inverters.
Off-Grid Inverter: Advantages
A major plus of off-grid inverters is how much cheaper they are compared to hybrid inverters. Moreover, they can be easily installed within an existent solar system.
They ensure continuous power supply even if the batteries are empty thanks to their backup connection.
Hybrid Inverter: Disadvantages
You will need to completely rework your system when adding a hybrid inverter into a solar system; this will be heavy on your pocket!
Additionally, initial installation costs are exceptionally high compared to off-grid inverters.
Off-Grid Inverter: Disadvantages
The most significant disadvantage of an off-grid inverter in a solar system is its inability to feedback power into the utility grid.
You might find yourself in a situation in which your solar production exceeds your needs and if your batteries are full, you will end up wasting this extra power.

Source: Growatt
Hybrid Inverter Vs. Off-Grid Inverter: Which Is Best For You?
Your System Demands
If you need more power than your off-grid system can supply, you should strongly consider upgrading to a hybrid system that draws from the grid when necessary and can feed into the grid in surplus situations.
Choosing an off-grid inverter should only be when there is no grid connection available. In that case your demand will be met by the off-grid solar system eventually assisted by a backup generator or any other external power source.
Inverter Battery Compatibility
Communication Compatibility
Lithium batteries, the best choice for a solar battery, require specific communication capabilities for their BMS to operate.
Both types of inverters are now compatible with the latest lithium batteries and the older lead acid batteries (AGM and Gel type).
Voltage Compatibility
Hybrid and off-grid inverters both integrate a DC battery charger and a DC to AC inverter. They are designed to work at a specific DC voltage (12V, 24V or 48V) and the solar battery should absolutely match this nominal voltage.
There is a direct relationship between the operational DC voltage of an inverter and its maximum power output as depicted in the chart below:
| Inverter DC voltage – Solar battery voltage | Max. Output power |
| 12V | 1.2kW |
| 24V | 3.5kW |
| 48V | 6kW |
This relationship is mainly due to the max. Amps an inverter can handle.
For example, a power output of 6kW with a 12V inverter requires a current of 500 Amps! (12V x 500Amps= 6kW) which is extremely dangerous and would require oversized wires.
In the meantime, the same power output with a 48V inverter draws only 125Amps, this could be safely handled by the inverter.
Related Reading: The Only Inverter Size Chart You Will Ever Need!
Hybrid Inverter Vs. Off-Grid Inverter: Which Is Cheaper?
Hybrid inverters can either be small or large; this works out cheaper, with the average inverter costing you between $1,500 – $8,000.
The added plus regarding hybrid inverters is the possibility of gaining tax breaks or rebates when they are used to feed surplus energy into the grid.
Off-grid inverters must be 1.2 times the maximum power demand size in off-grid systems. Thus, these inverters will be substantially larger, and you do not have the added advantage of using your surplus energy as a grid feeder for green energy tax rebates.

Source: Inverter.com
System Considerations
Installation costs for hybrid and off-grid inverters don’t vary much, with a 10kW inverter costing roughly $2800 for installation.
In saying that, companies often provide installation and maintenance packages when purchasing an inverter; this could save you in the long run!
The bigger buck biter here is upgrading. To upgrade a system from off-grid to hybrid would require restructuring to allow for a hybrid inverter and bi-directional utility connection — costing hundreds of thousands!
Upgrading an off-grid system and inverter is also quite pricy as you’ll need to ramp up more than one component in your power system (such as the battery voltage).
The choice ultimately remains yours, with varying costs for various extras in a system.
Here is a short video explaining a little more about one of the hybrid inverters out there!
Final Thoughts
All things considered, a hybrid inverter provides more flexibility in size choice and cost. A bonus is that this system can have you feeding surplus energy into the grid and pay back your earlier costs!
Off-grid inverters are heavier on the pocket as you don’t benefit from federal tax rebates. However, this is the ideal inverter if you know your requirements and want to live independently from the grid.
The bottom line: choosing between a hybrid inverter vs. off-grid inverter depends on your needs.
If you want to share your thoughts or ask us a question, please feel free to reach out to us in the comments section below! Alternatively, visit our forum or follow us on Twitter!

